Advantages and Disadvantages of Bus Topology
The main advantage of bus topology is its cost-effectiveness, as it requires minimal cabling, which lowers installation expenses. Its straightforward design makes it easy to set up and manage, making it a great choice for small networks. However, a significant disadvantage is its reliance on a single central cable; if this cable fails, the entire network will go down. Additionally, increased network traffic can lead to data collisions, disrupting communication and reducing overall performance.
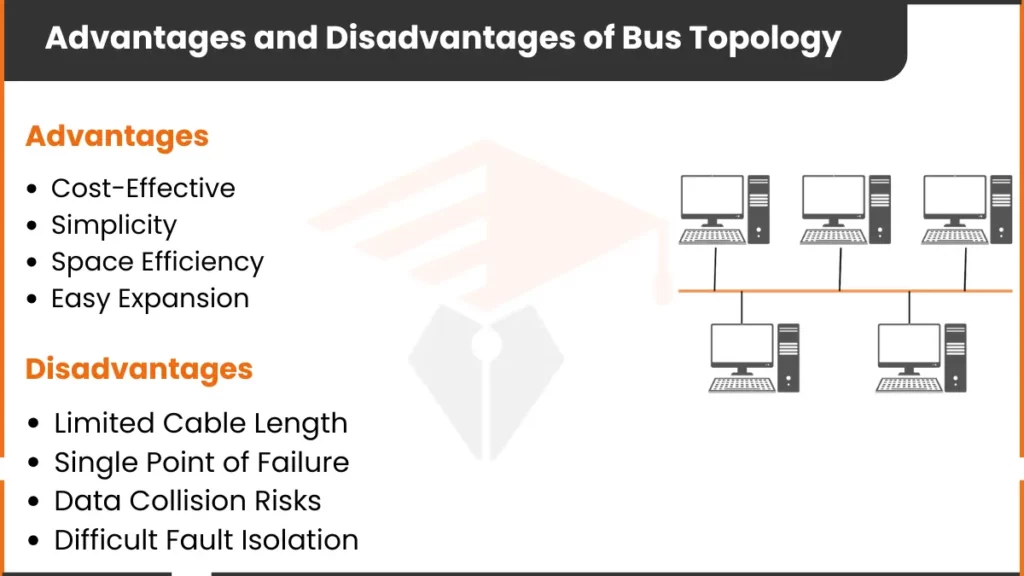
Advantages of Bus Topology
The following are the benefits of bus topology
1. Cost-Effective
Lower Installation Costs: Bus topology requires only one main cable, significantly reducing the amount of cabling needed to be, compared to other network designs like star or mesh. This means lower costs for materials and labor during installation.
Minimal Hardware Requirements: Unlike topologies that require additional networking equipment such as switches or hubs, bus topology operates with basic components, which can lead to further savings.
2. Simplicity
Easy Setup and Configuration: Setting up a bus topology is straightforward because all devices connect to a single central cable. This makes it an attractive option for users with limited technical expertise. The uncomplicated design allows for quick deployment in small network environments.
Straightforward Troubleshooting: When problems arise, they can often be traced back to specific devices or sections of the cable. This localized fault identification simplifies troubleshooting, allowing for faster repairs and less downtime.
3. Space Efficiency
Compact Design: Bus topology requires less physical space than other configurations. For example, star topology needs a central hub, which can take up more room. The bus topology can be particularly advantageous in environments where space is at a premium.
4. Easy Expansion
Simple Device Addition: Adding new devices to a bus topology network is an uncomplicated process. New devices can be directly connected to the bus without significant changes or disruptions to the existing network. This flexibility helps grow organizations that may need to increase their number of connected devices over time.
Disadvantages of Bus Topology
Here are some drawbacks of bus topology:
1. Limited Cable Length
Maximum Length Restrictions: The bus topology has a maximum cable length, which restricts the number of devices that can be effectively connected to the network. Exceeding this limit can lead to poor performance.
Signal Degradation: As the distance from the main cable increases, the signal can weaken, leading to potential communication failures. This makes it crucial to plan network layout carefully.
2. Single Point of Failure
Network Vulnerability: A significant drawback of bus topology is its reliance on a single cable. If the main bus cable fails, the entire network is rendered inoperable. This can lead to considerable downtime and loss of productivity, particularly in business environments.
3. Data Collision Risks
Increased Traffic Issues: With multiple devices sharing the same cable, the likelihood of data collisions rises, especially as more devices are connected. Collisions occur when two devices attempt to send data at the same time, resulting in both transmissions being disrupted and requiring retransmission. This can significantly reduce the overall efficiency of the network and slow down data transfer rates.
4. Difficult Fault Isolation
Challenges in Problem Identification: Identifying and isolating faults can be complicated in bus topology. A failure in one section of the cable can affect all connected devices, making it difficult to determine where the problem lies. This can lead to longer repair times and increased frustration for users.
What is the most famous topology?
Star topology is a famous topology
Why do we need bus topology?
Bus topology is useful for small, simple networks. Here’s why:
Low Cost, Easy Setup, Good for Small Networks, Uses Less Cable, Temporary Networks
How reliable is a bus topology?
A bus topology is not very reliable for large or critical networks.
Why bus topology is less secure?
Bus topology is less secure because:
Shared Cable: All devices use the same cable, so data can be seen by any connected device.
Easy to Hack: Anyone can connect a device to the cable and access data.
No Main Control: There’s no central system to manage or protect data.



Leave a Reply