Affect vs. Effect-Difference Between With Examples
Some words are often confused due to their similar spellings or pronunciations. “Affect” and “effect” are two such words that frequently cause confusion.
In this article, we will explore the definitions, differences, and grammatical aspects of “affect” and “effect” to shed light on their distinct meanings.
Meanings and Examples
Affect Meaning
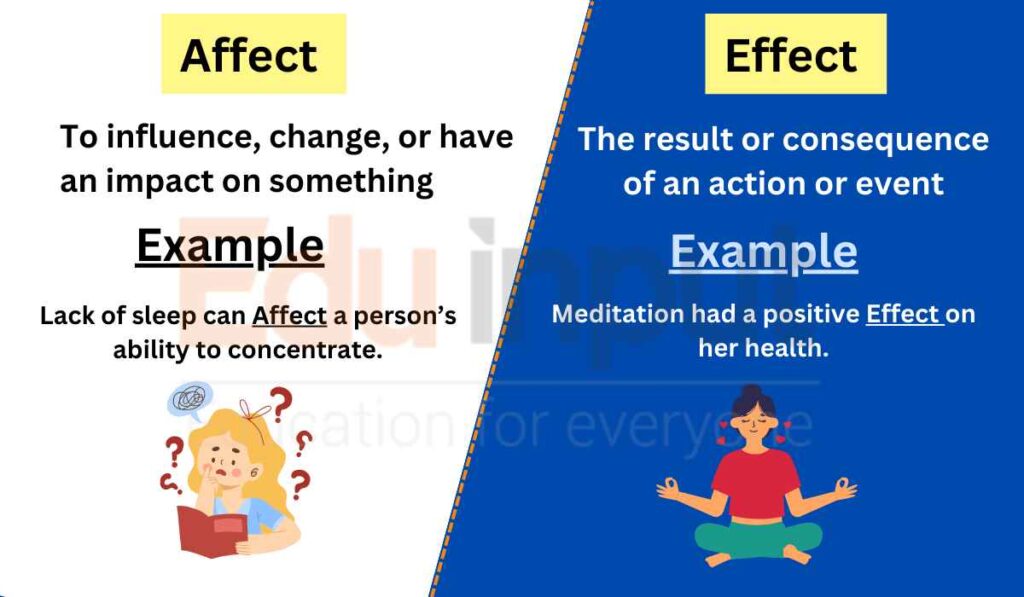
Verb: The meanings of Affect are “to influence, change, or have an impact on something”.
Affect Examples
- The rainy weather affected their plans for a picnic.
- Lack of sleep can affect a person’s ability to concentrate.
- His words affected her deeply, bringing tears to her eyes.
- The economic recession affected the company’s profitability.
- How we perceive ourselves can affect our overall well-being.
Effect Meaning
Noun: The meanings of Effect are “the result or consequence of an action or event”.
Effect Examples
- The effect of the medication was immediate relief from pain.
- The new policy had a positive effect on employee morale.
- The movie had a profound effect on its audience, provoking thought and discussion.
- The hurricane had a devastating effect on the coastal community.
- The effect of his speech was a sense of empowerment and inspiration.
Differences Between Affect and Effect
Here is a table showing Differences Between Affect and Effect:
| Meaning | To influence or have an impact |
|---|---|
| Result or consequence | Resulting, consequence |
| Part of Speech | Verb, Noun |
| Pronunciation | əˈfɛkt, ɪˈfɛkt |
| Usage | Influencing, impacting |
Grammatical Aspects
As Noun
Affect: “Affect” is not commonly used as a noun.
Effect: “Effect” primarily functions as a noun, representing the result or consequence of an action or event.
As Pronoun
Affect: “Affect” is not used as a pronoun.
Effect: “Effect” is not used as a pronoun.
As Verb
Affect: “Affect” functions as a verb, indicating the action of influencing or having an impact on something.
Effect: “Effect” can function as a verb, meaning to bring about or cause something, but this usage is less common.
As Adjective
Affect: “Affect” does not have an adjective form.
Effect: “Effect” can function as an adjective, indicating something that is caused or brought about.
As Adverb
Affect: “Affect” does not have an adverb form.
Effect: “Effect” does not have an adverb form.
Usage in a Paragraph
The teacher’s enthusiastic teaching style affected the students positively, sparking their curiosity and eagerness to learn. As a result, the effect was evident in their improved grades and heightened engagement in class discussions. The teacher’s ability to affect the students’ learning experience had a profound effect on their academic performance and overall educational journey.




Leave a Reply