Arithmetic Operator in C++ | Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication, Division, Modulus
Arithmetic operators are very important in C++. They allow us to add, subtract or multiply numbers together. In programming, they play a vital role in our programs. For example, we might want to calculate the sum of two numbers.
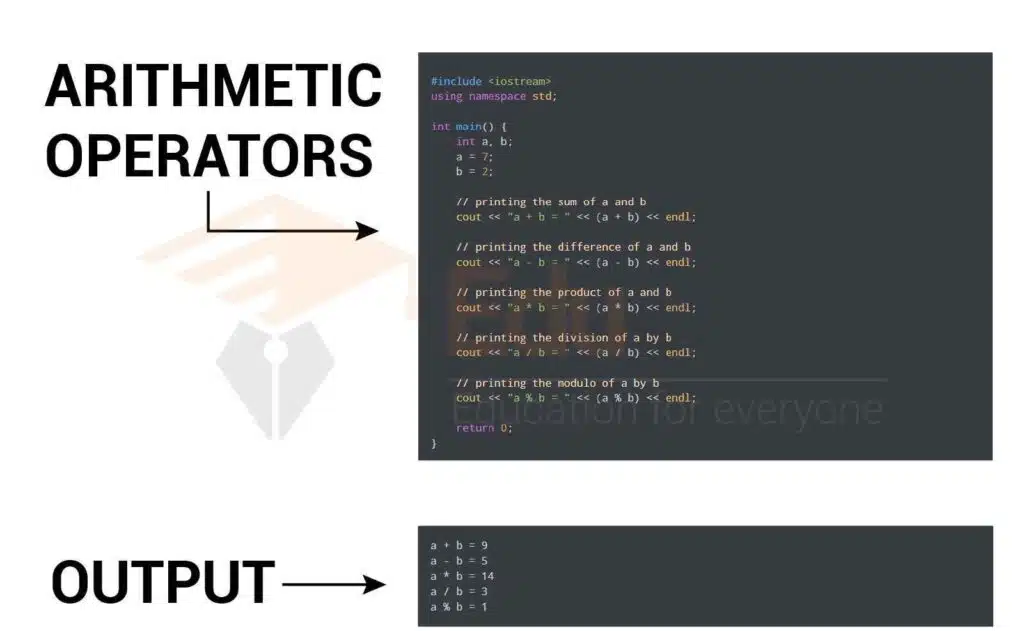
Addition (+): The result of adding two numbers together. Subtraction (-): The result of subtracting one number from another. Multiplication (*): The result of multiplying two numbers together.
| Operation | Symbol | Description |
| Addition | + | 5 + 4 = 9 |
| Subtraction | – | 10 – 3 = 7 |
| Multiplication | * | 3 * 4 = 12 |
| Division | / | 6 / 2 = 3 |
| Modulus | % | 60 % 3 = 0 |
Addition Operator in C++
The addition operator is used to add two values or two variables. The symbol of the addition operator is “+”
For Example
a + b; , 5 + 6 = 11
Int main()
{
Int a, b;
a = 5;
b = 4;
cout << “a + b =” << a + b <<endl;
}
Subtraction Operator in C++
This operator is used to subtract the two numbers or variables. The symbol used to subtract the number is “-”.
For example
a – b; , 10 – 2 = 8
Int main()
{
Int a, b;
a = 10;
b = 4;
cout << “a – b =” << (a – b) <<endl;
}
Multiplication operator in C++
This operator is used to multiply the two numbers and variables. The symbol of multiplication is “*”.
For Example
a * b; 10 * 2 = 20
Int main()
{
Int a, b;
a = 10;
b = 4;
cout << “a * b =” << (a * b) <<endl;
}
Division Operator in C++
This operator is used to divide the two numbers or variables. The first number is divided by the other. The symbol is used for this operator is “ / ”.
For Example
a / b; , 20 / 5 = 4
Int main()
{
Int a, b;
a = 20;
b = 4;
cout << “a / b =” << (a / b) <<endl;
}
Modulus Operator in C++
This operator computes the reminder of two values or variables when divided. The symbol of the modulus operator is “%”.
For Example
a % b; 40 % 2 = 0
Int main()
{
Int a, b;
a = 20;
b = 4;
cout << “a % b =” << (a % b) <<endl;
}






Leave a Reply