Capacitor | Capacitance Of a Parallel Plate Capacitor
A device used to store electric charge is called a capacitor. It stores electrical energy in an electric field.
Download the pdf notes of Capacitor and Capacitance Of a Parallel Plate Capacitor Class 12 Physics
Construction of a capacitor
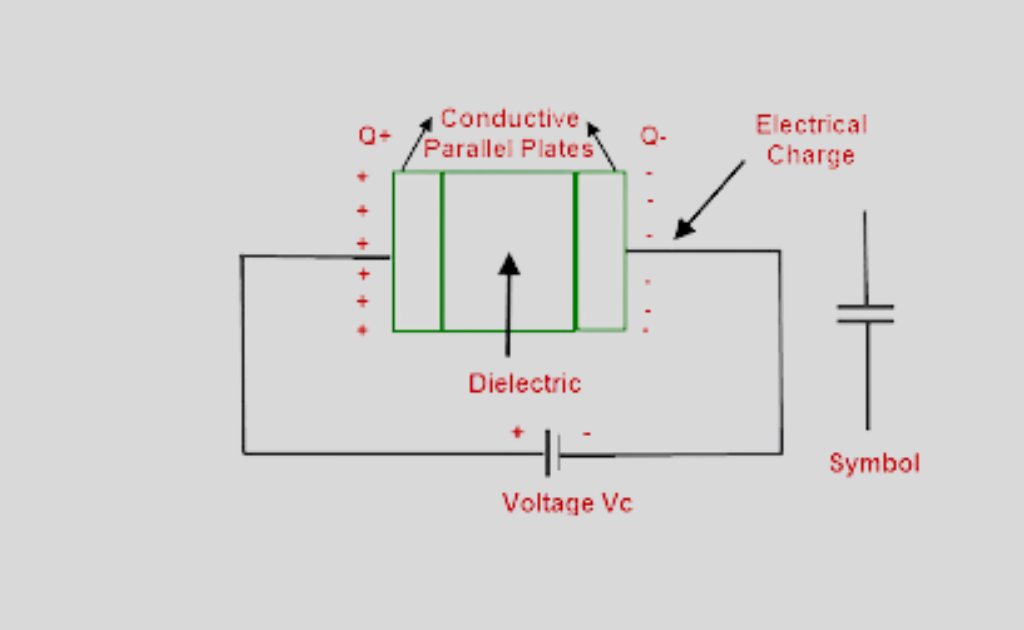
It consists of two conductors usually in the form of parallel plates placed near each other and separated by vacuum, air, or some dielectric. Such a capacitor is called a parallel plate capacitor.
How Does A Capacitor Work?
When the plates of such a capacitor are connected to a battery of voltage v, the plate connected to the positive terminal acquires +Q charge and the other connected to the negative terminal acquires –Q in an equal amount.
These charges appear on the inner surface of the plates due to attraction.
Types of Capacitors
There are two main types of capacitors:
1. Fixed Capacitors
Fixed capacitors have a set, fixed capacitance. Several types of fixed capacitors are commonly used in electronic circuits, each with their properties and characteristics.
Ceramic Capacitors
Ceramic capacitors use a ceramic dielectric material like titanium dioxide or barium titanate. They are inexpensive, small, and have low inductance. Common types are multi-layer ceramic capacitors (MLCCs) and ceramic disc capacitors.
Film Capacitors
Film capacitors use insulating plastic film like polyester or polypropylene as the dielectric. They have more stable capacitance across temperature variations. Film capacitors are used for general-purpose coupling and bypassing applications.
Power Film Capacitors
Power film capacitors use self-healing plastic film dielectric and are designed to handle high voltages and temperatures. They are used for high-power applications like motor starting and power conditioning.
Electrolytic Capacitors
Electrolytic capacitors use an oxide layer dielectric on an aluminum or tantalum anode. They have high capacitance but are polarized. Electrolytic caps are used for filtering and buffering in power supplies.
Supercapacitors
Supercapacitors, also called ultracapacitors or electric double-layer capacitors, store large amounts of energy. They are polarized and can substitute batteries in some applications.
2. Variable Capacitors
Variable capacitors allow the capacitance to be changed mechanically by altering the spacing between the capacitor plates. The two main types of variable capacitors are:
Tuning Capacitors
Tuning capacitors are variable capacitors used in analog tuning circuits. They are made of two air-spaced plates. The capacitance of the capacitor can be changed by adjusting the distance between the plates. This is done using a mechanism, such as a screw or a knob.
Tuning capacitors allow the frequency of radio tuners and receivers to be adjusted. They are often paired with an inductor to make a tunable resonant circuit. A resonant circuit is a circuit that oscillates at a specific frequency. The frequency of the oscillation can be changed by adjusting the capacitance of the tuning capacitor.
Trimming Capacitors
Trimming capacitors are adjustable capacitors used to make precise capacitance adjustments. They are typically smaller than tuning capacitors and are used to fine-tune capacitance in a circuit. Trimming capacitors can be adjusted using a small screw adjustment.
Trimming capacitors are often used during manufacturing or servicing to set capacitance accurately to a specified value. They can also be used to adjust capacitance in a circuit to compensate for variations in components or environmental conditions.
Polarized and Non-Polarized Capacitors
Capacitors can be either polarized, meaning they operate with one voltage polarity, or non-polarized for operation with either polarity.
Electrolytic and supercapacitors are polarized and can only withstand voltage in one direction. Reversed voltage can damage them.
Ceramic, film, and power film capacitors are non-polarized. They can operate with either voltage polarity applied.
Applications of Capacitors
Here are some applications of capacitors:
- Ceramic capacitors are used in:
- Power supplies
- Filters
- Oscillators
- Timers
- Decoupling
- Bypassing
- Film capacitors are used in:
- Power supplies
- Filters
- Oscillators
- Timers
- Coupling
- Decoupling
- Bypassing
- Power film capacitors are used in:
- Motor starting
- Power conditioning
- Pulsed power applications
- High-current inverters and drives
- Electrolytic capacitors are used in:
- Power supplies
- Filters
- Smoothing
- Buffering
- Supercapacitors are used in:
- Electric vehicles
- Renewable energy systems
- Uninterruptible power supplies (UPS)
- Power tools
- Medical devices
Expression for the capacitance of a capacitor
Let Q be the magnitude of the charge on either of the plates. It is found that charge Q stored by the capacitor is directly proportional to the potential difference V.
Q ∝V
Q=CV
Where C is the constant of proportionality known as Capacitance or capacity of a capacitor, its value depends upon the geometry of the capacitor and the medium between the plates.
The ability or capacitance of a capacitor to store charge is called capacitance.
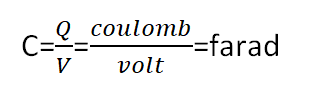
So the S.I unit of capacitance is C/V which is called farad after the famous English scientist faraday.
The capacitance of a capacitor is one farad if a charge of one coulomb, given to one of the plates of a parallel plate capacitor produces a potential difference of one volt between them.
Farad is a big unit for practical purposes its sub-multiple units are used.

The capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor
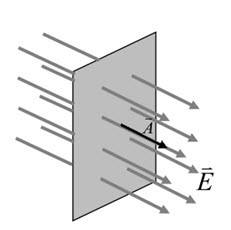
Consider a parallel plate capacitor consisting of two parallel metallic plates each of area A and separated by a distance d. the distance between the plates is small than their size. So the electric field E is uniform and confined in the region between plates.
Let air or vacuum be present as a medium between plates. Then capacitance of the parallel plate’s capacitor is given by
Cvac=Q/V
Q is the charge and V is the potential difference between the plates. Since E is uniform so the potential difference is given by
V=Ed (2)
But electric intensity between two oppositely charged plates is given by
E= σ/ϵr
By putting value in equation 2
V= σd/ ϵr (4)
If Q is the charge on either of the plates of area A, then surface charge density is given as
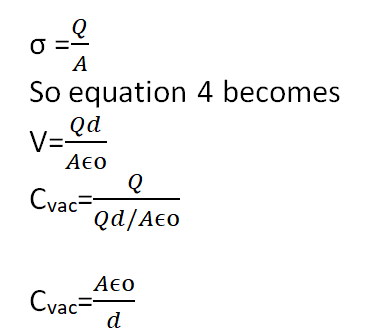
Thus capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor depends upon the nature of the medium, the area of plates, and the separation between plates.
Capacitance is directly proportional to the area of plates and inversely proportional to the separation of the plates.
Related Article: What is Supercapacitor?
Capacitance for Dielectric
If an insulating material called dielectric of relative permittivity ϵr is inserted between the plates. There is some difference between capacitor and dielectric.
Then the capacitance of the capacitor is increased by the factor ϵr called the dielectric constant.
Consider an experimental demonstration in which a charged capacitor is connected to a voltmeter giving the potential difference between plates.
When the dielectric is placed between the plates the reading of the voltmeter decreased so
C=Q/V
Since Q remains constant so when v decrease the value of C increase. Then
Dielectric coefficient
The ratio of the capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor with an insulating substance as the medium between plates of its capacitance with vacuum as a medium between them
Cmed/Cvac= ϵr
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQs)
What does a capacitor do?
A capacitor is a device that stores electrical energy in an electric field. It is a passive electronic component with two terminals.
Capacitance depends upon which factors?
Area A of the plates
The separation d between plates
The medium between the plates
What is farad?
The capacitance of a capacitor is one farad if a charge of one coulomb, given to one of the plates of a parallel plate capacitor produces a potential difference of one volt between them.

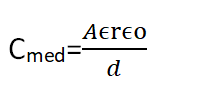



Leave a Reply