Difference between Collenchyma, Sclerenchyma, and Parenchyma
November 30, 2024
The major difference between collenchyma, sclerenchyma, and parenchyma is the difference of their cell wall thickness. But the other factors such as cell type, cell shape and structure also play an important role in their functioning.
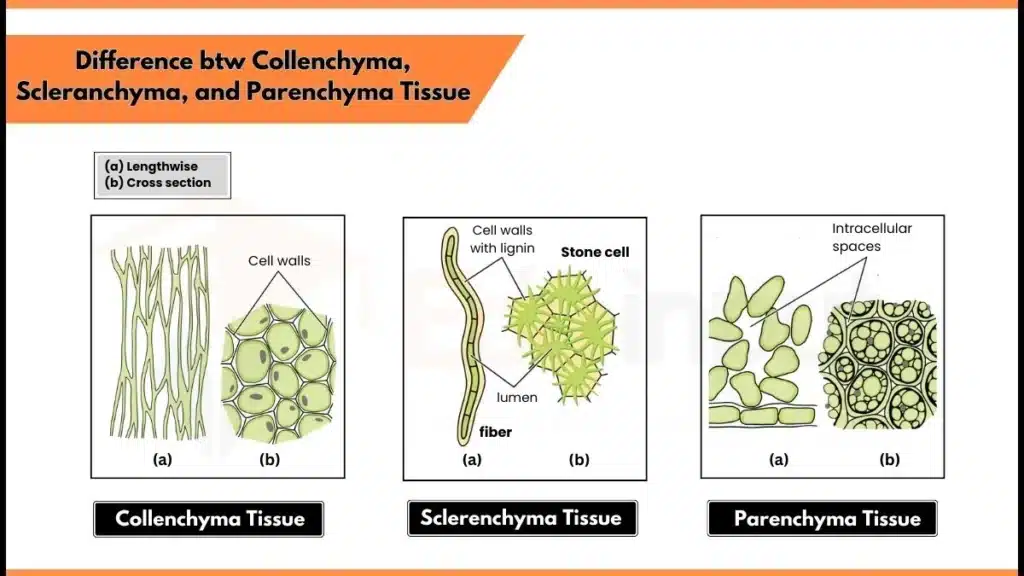
Collenchyma, sclerenchyma, and parenchyma are the three main types of plants simple tissues. Among these, every tissue has a unique structure and performs a different function. To get a list of key difference between these three tissues, a table is given below.
Difference between Collenchyma, Sclerenchyma, and Parenchyma
Here’s a list of key differences between Collenchyma, Sclerenchyma, and Parenchyma:
| Characters | Collenchyma | Sclerenchyma | Parenchyma |
| Definition | Collenchyma is a type of plant tissue with cell walls having irregular thickness. It provides support and flexibility to plants. | Sclerenchyma is a plant tissue made up of thick and lignified secondary cell walls. It supports the structure of plant by providing strength. | Parenchyma is a plant tissue with living, thin wall. It forms the soft interior of plants and helps in storage, support, and metabolic activities. |
| Origin | Originates from apical meristem or lateral meristem. | Arises from meristematic tissues, essentially procambium or ground meristem. | Arise from the ground and protoderm meristems. |
| Cell Type | living and specialized cells | Dead cells | living and unspecialized cells |
| Location | Mainly found in growing parts like stems, leaves, and petioles | Found in mature parts such as stems, hard fruits | Found in every soft part like roots, stems, leaves, and flowers |
| Cell Shape | Irregular, angular, and elongated | Long, narrow fibers. Thin at both ends | Round, spherical, isodiametric, or elongated |
| Cell Wall | Thick primary cell wall, made up of cellulose and pectin | Extremely thick secondary cell wall, composed of lignin | Thin cell wall, made up of cellulose |
| Intercellular Spaces | Small intercellular spaces between cells | Very small or absent intercellular spaces | Larger intercellular spaces. |
| Function | Provides mechanical support and elasticity | Gives structural support and strength to plants | Helps nutrient storage, photosynthesis, and damage healing |
File Under:




Leave a Reply