Difference between Longitudinal and Transverse Wave
The key difference between longitudinal and transverse wave lies in the direction of oscillation with respect to the direction of propagation.
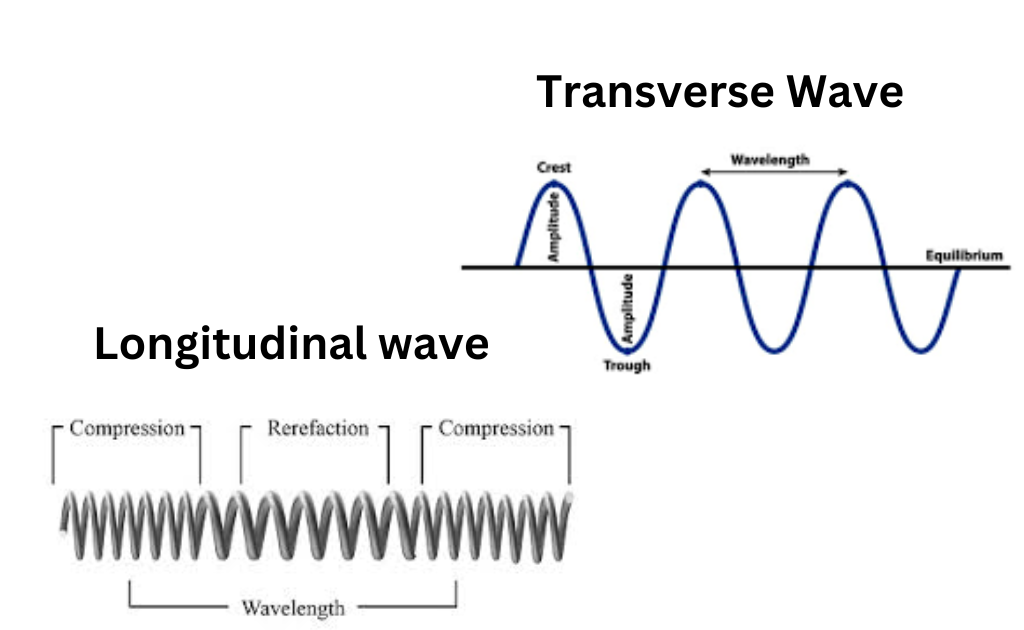
The displacement of the particles in a longitudinal wave occurs parallel to the wave’s path of propagation. On the other hand, the transverse wave’s particle displacement is perpendicular to the wave’s path of propagation.
Read Real-life examples of transverse waves
Transverse vs longitudinal waves
The important difference between longitudinal and transverse wave is given below.
| Transverse wave | Longitudinal Wave |
|---|---|
| The medium is traveling in a direction that is perpendicular to the waves. | In the case of a longitudinal wave, the medium travels parallel to the wave direction. |
| There is no polarisation or alignment of this wave. | It is undoubtedly conceivable for this wave to be polarised or aligned. |
| It acts in one dimension | It acts in two dimensions |
| There are crests and troughs in this wave. | This wave is made up of compressions and rarefactions |
| The only media in which this wave may be produced are liquid and gas | This wave may form in any media, including solids, gases, and liquids. |
| The earthquake S wave is an illustration of a transverse wave. | The earthquake P wave is a prime illustration of a longitudinal wave. |
Related FAQs
What is the difference between longitudinal and transverse Wave?
The main difference between longitudinal and transverse Wave lies in the direction of the wave motion relative to the direction of oscillation of the particles within the wave.
Are sound waves longitudinal or transverse?
Sound waves are longitudinal waves. In a sound wave, the particles of the medium (such as air, water, or solids) vibrate parallel to the direction of wave propagation. This means that the particles move back and forth in the same direction as the sound wave is traveling.
Difference between longitudinal and transverse wave with examples
The main difference between longitudinal and transverse wave is the direction in which the particles of the medium oscillate relative to the direction of wave propagation. Longitudinal wave examples include sound waves and seismic waves.
Transverse wave examples include light waves, water waves, and electromagnetic waves.

 written by
written by 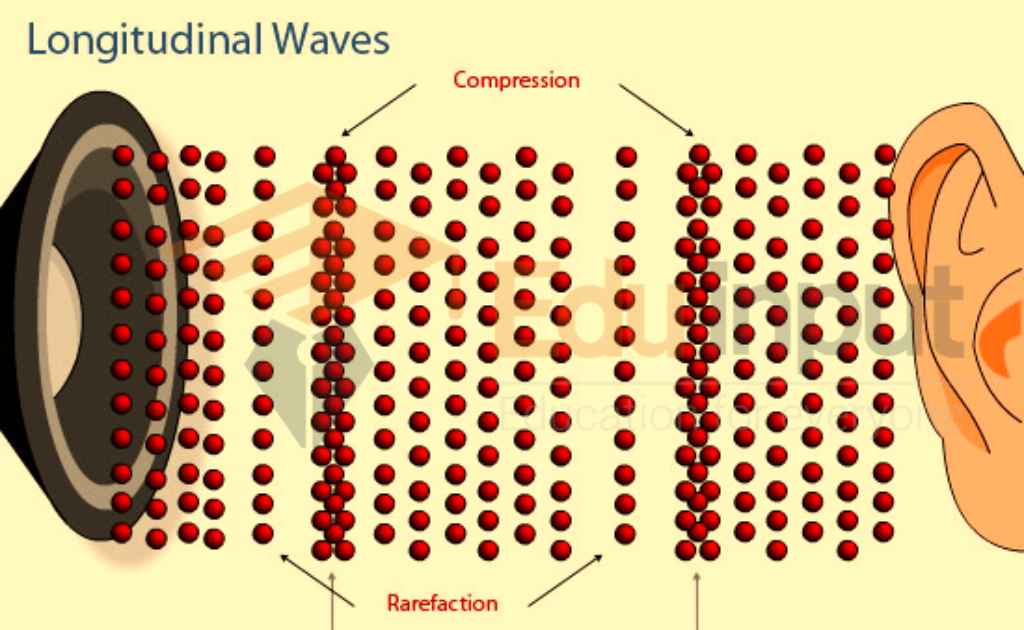


Leave a Reply