Difference between Nervous Coordination and Chemical Coordination
Nervous Coordination and Chemical Coordination share some characteristics, as both hormone-producing cells and nerve cells (neurons) synthesize chemical messengers. Both release the messenger chemicals in extra-cellular spaces of the body, help in the coordination of the body, and function in response to specific stimuli. These stimuli may be from within the body or from the external environment. Both are homeostatic in function.
Nervous Coordination
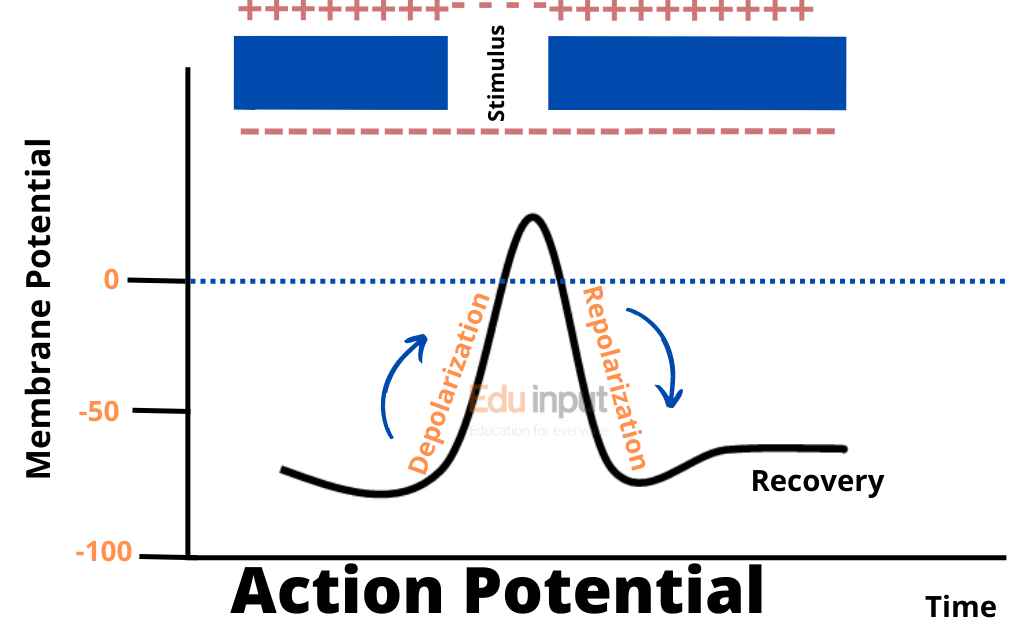
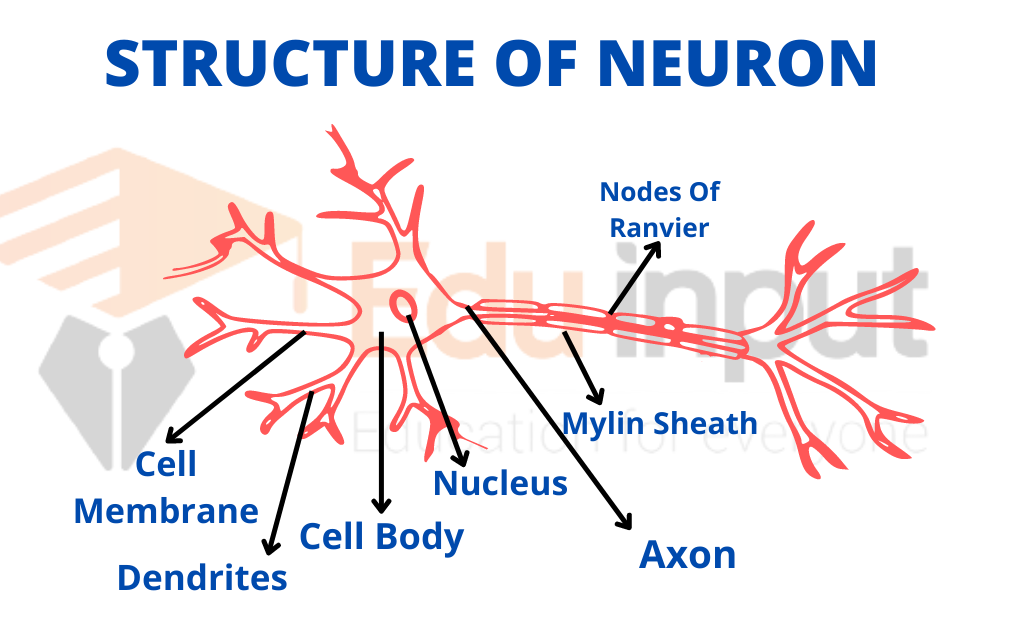
The coordination involves specialized cells or neurons is called nervous coordination. These neurons are linked together directly. Or they are linked by the central nervous system. The neurons form a network. They connect the receptors and effectors. The receptors are the cells or organs. They receive stimuli.
The cells or organs which carry out actions or responses are called effectors. The neuron can generate and conduct impulses. This impulse travels across the synapse. It is passed from the receptors to the effectors. Thus it brings about nervous coordination. The nervous system which helps in coordination is composed of three elements: Receptors, neurons, and effectors.
Chemical Coordination
The coordination which involves the endocrine system in animals is called chemical coordination. The endocrine system is composed of endocrine glands. These glands are present in various parts of the body. The ductless glands are called endocrine glands. These glands secrete hormones. They are composed of discrete groups of cells. These cells make specific chemical compounds called hormones. The endocrine system consists of endocrine glands/tissues.
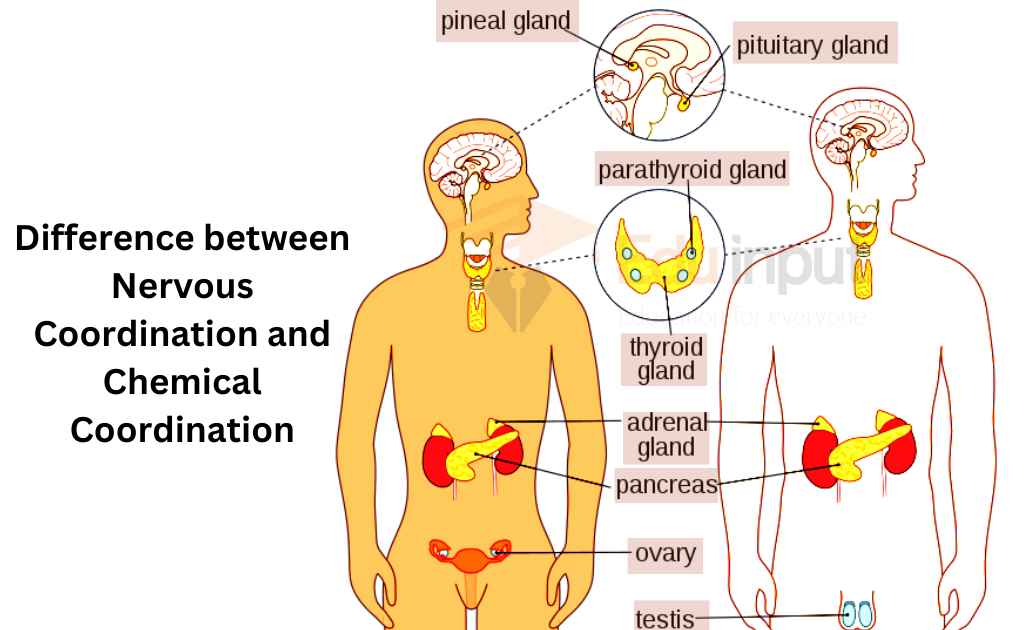
Difference between Nervous Coordination and Chemical Coordination
Here are the key differences between difference between nervous coordination and chemical coordination:
| Nervous Coordination | Chemical Coordination |
| Neurons are the basic units of structure and function of the nervous system. The nervous system also has neuroglial cells. These cells provide nutrition and protection to neurons. | Hormone-producing cells and neuro-secretary cells (in the hypothalamus) are units of structure and function of chemic coordination. They release hormones. |
| Hormones are transported by blood. These hormones affect the target cells. The target cells are far away from where the hormones are produced. For example, ADH is produced from the posterior lobe of the pituitary gland. However it affects the target cells present in the nephron and collecting tubule of the kidney. It controls the re-absorption of water. | There may be immediate effects (e.g. insulin). But mostly hormones have prolonged or delayed effects. For example growth hormone. |
| The neurons release their neuro-transmitter into one or a small group of specific cells. | Blood moves through the body. It bathes millions of cells indiscriminately. Only a few cells respond to these hormones. |
| The nervous system shows immediate effect or show a response to a stimulus instantly. | The nervous system shows effect through the electrical signals (nerve impulses). It travels within the cell itself and it releases its neurotransmitters at the synapse. |
| Hormones are transported by blood. These hormones affect the target cells. The target cells are far away from where the hormones are produced. For example, ADH is produced from the posterior lobe of the pituitary gland. However, it affects the target cells present in the nephron and collecting tubule of the kidney. It controls the re-absorption of water. | This control involves only chemical stimulation and the target cells are far away from them. |
| It shows a faster or more rapid effect. The speed of impulse in meters/second: but the maximum speed in most cases is 100 nerve impulse recorded in the human is 120 meters/second: | It is not very rapid. It shows slow but prolonged effects. |
| The hormones are short-lived. They are broken neurotransmitters or neurons shortly after their release. Thus the own effects of neurons duration. are much shorter | The hormones remain active for a much longer duration within the blood. Thus they have a much longer duration of actions. |



Leave a Reply