Difference Between Peripheral Blood Smear and Bone Marrow Smear
Key Difference
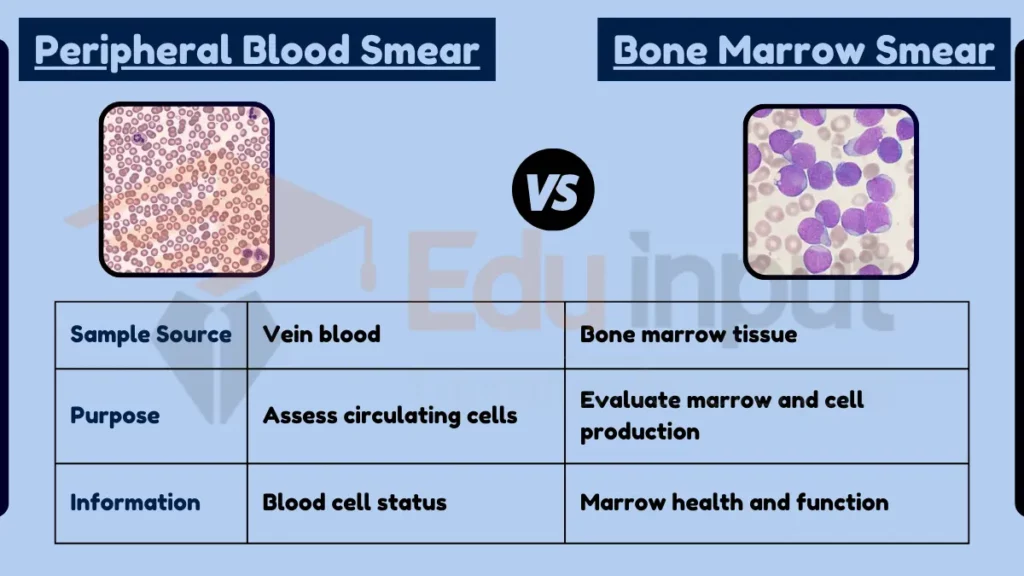
Peripheral blood smears and bone marrow smears are diagnostic tools used in hematology, but they differ in the source of the sample and the information they provide. A peripheral blood smear involves examining a sample of blood taken from a vein, typically to evaluate the different types of cells circulating in the bloodstream. A bone marrow smear involves examining a sample of bone marrow, usually extracted from the pelvic bone, to evaluate the blood cell production process and detect abnormalities in the bone marrow.
Comparative Analysis
- Sample Source:
- Peripheral Blood Smear: Blood from a vein.
- Bone Marrow Smear: Bone marrow tissue.
- Purpose and Use:
- Peripheral Blood Smear: Assess blood cell count, morphology.
- Bone Marrow Smear: Evaluate cell production, marrow pathology.
- Information Obtained:
- Peripheral Blood Smear: Status of circulating blood cells.
- Bone Marrow Smear: Health and function of bone marrow.
- Diagnostic Application:
- Peripheral Blood Smear: Anemia, infections, blood disorders.
- Bone Marrow Smear: Leukemia, marrow dysfunctions, metastasis.
- Procedure:
- Peripheral Blood Smear: Less invasive, simple blood draw.
- Bone Marrow Smear: More invasive, requires aspiration.
Table Summary
| Feature | Peripheral Blood Smear | Bone Marrow Smear |
|---|---|---|
| Sample Source | Vein blood | Bone marrow tissue |
| Purpose | Assess circulating cells | Evaluate marrow and cell production |
| Information | Blood cell status | Marrow health and function |
| Diagnostic Use | Blood disorders, anemia | Leukemia, marrow diseases |
| Procedure | Less invasive | More invasive |
Peripheral blood smears and bone marrow smears are essential diagnostic tools in hematology, each providing unique insights: the former offers information about circulating blood cells, while the latter gives a detailed view of the bone marrow and blood cell production process.



Leave a Reply