Differences Between Fibrous Proteins And Globular Proteins
May 27, 2023
The main difference between fibrous proteins and globular proteins is their structure and function. Fibrous proteins are long and narrow strands, serving a structural role, while globular proteins have a more compact and rounded shape, performing functional roles.
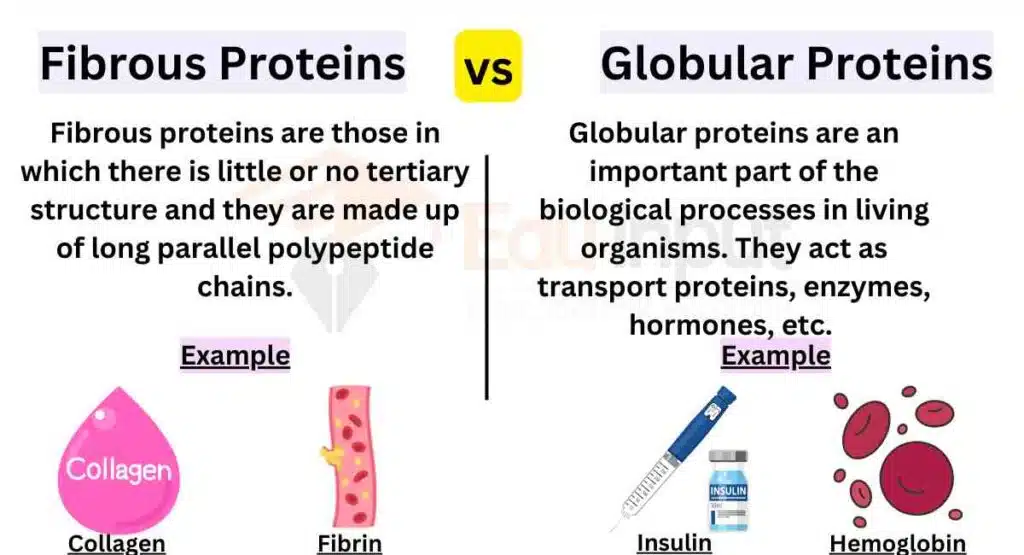
Fibrous Proteins vs. Globular Proteins
Here are the main Differences Between Fibrous Proteins And Globular Proteins:
| Factors | Fibrous Protein | Globular Protein |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose of Proteins | Structural – provides scaffolding for maintaining cell shape | Functional – carries out specific biological functions in the body |
| Examples | Keratin, collagen, elastin, fibrin | Hemoglobin, myoglobin, insulin, enzymes |
| Shape of Proteins | Usually long and narrow | Typically spherical in shape |
| Sequence of Amino Acids | Amino acid sequence is repetitive in nature | Amino acid sequence is irregular |
| Resilience | Less sensitive to factors such as changes in temperature and pH | More sensitive to temperature and pH |
| Solubility | Typically insoluble in water | Typically soluble in water |
| Location in Organisms | Found in connective tissues, tendons, and bones | Found in blood, enzymes, and hormones |
| Functionality | Provide mechanical strength and support | Perform enzymatic reactions, transport oxygen, regulate metabolism, and signaling |
| Structural Organization | Form long fibers or sheets | Folded into complex 3D structures |
| Stability | Highly stable and resistant to denaturation | Relatively less stable and prone to denaturation |
| Role in Body Processes | Structural integrity and movement | Enzymatic activity, transport, signaling, and regulation |
| Interaction with Environment | Less interactive with external environment | Highly interactive with external environment and other molecules |
File Under:





Leave a Reply