Definition and Explanation of Figure of Speech
Have you ever heard someone say, “Time is a thief” or “The world is a stage”? These phrases show the expression of speech meaning, which makes language more creative and interesting. A figure of speech means words go beyond their usual meaning to create strong images and emotions.
A figure of speech is a way of using words in a non-literal sense to make ideas clearer and more engaging. Instead of saying something directly, it adds creativity and makes language more powerful. Figurative of speech definition refers to special ways of using words, like comparisons, exaggerations, or symbolic meanings.
The expression of speech is important in stories, poems, speeches, and everyday conversations. Figurative language with meaning helps people express ideas in a more vivid and memorable way. From metaphors and similes to personification and hyperbole, these tools make communication more effective and engaging.
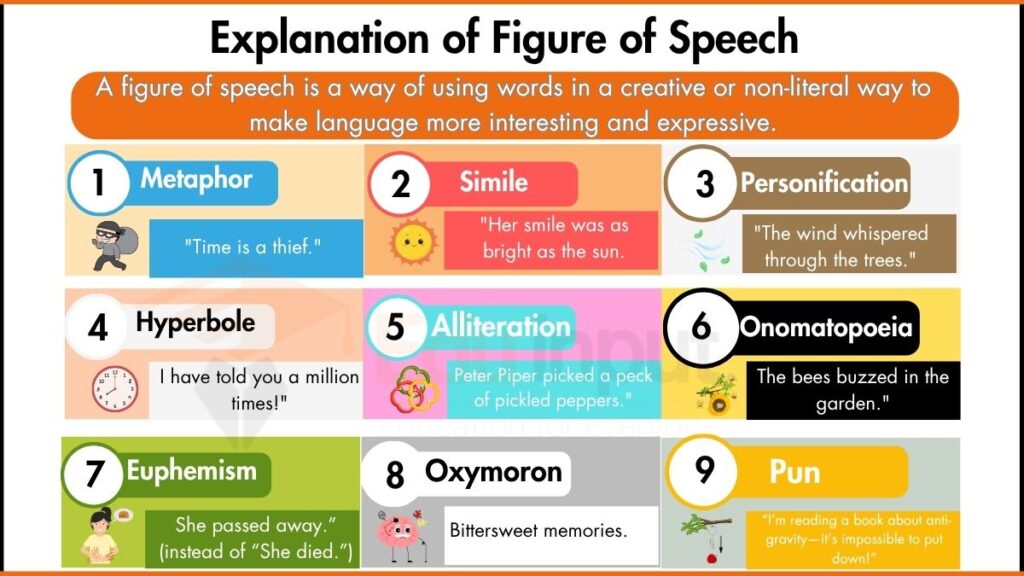
What is Figure of Speech?
A figure of speech is a way of using words in a creative or non-literal way to make language more interesting and expressive. The Oxford Dictionary defines it as “a word or phrase used in a non-literal sense for rhetorical or vivid effect.” Merriam-Webster says it is “an expression that uses language in a special way to create a particular effect.”
According to the Cambridge Dictionary, it is “an expression that is different from the usual way of saying something.” While the definitions vary, they all agree that figurative language and figure of speech go beyond literal meanings to make communication more powerful.
Figures of speech rely on key ideas. They use non-literal language, meaning words do not always mean exactly what they say. They act as rhetorical devices, helping to make speech and writing more persuasive, clear, or entertaining. They also add style, making language more engaging with emphasis, humor, or vivid descriptions.
The difference between literal and figurative language is important—literal language states things directly, while figurative language with meaning uses comparisons, symbolism, or exaggerations to create a stronger effect.
The study of figures of speech dates back to ancient Greece and Rome. Scholars like Aristotle and Quintilian explored how rhetorical techniques improve communication.
- Greek Influence: Aristotle defined rhetoric as “the faculty of observing in any given case the available means of persuasion.” He introduced logos (logic), pathos (emotion), and ethos (credibility) as key elements in effective speech.
- Roman Influence: Quintilian refined rhetorical principles, emphasizing style, structure, and delivery in persuasive communication.
Figures of speech have remained essential in literature, speeches, and daily conversations, making language more engaging and impactful.
Core Concepts
Figures of speech help make language more interesting, creative, and expressive. They use non-literal language, meaning words go beyond their usual meaning to add depth. As rhetorical devices, they make speech and writing more engaging by helping to persuade, inform, or entertain. They also act as stylistic tools, allowing writers and speakers to add emphasis, humor, or vivid imagery.
Understanding the difference between literal and figurative language is key. Literal language means exactly what it says, while figurative language uses comparisons, exaggerations, or symbolism to create a stronger effect.
Figures of speech have been studied since ancient times. Greek and Roman scholars like Aristotle and Quintilian explored how they could improve communication. Over the centuries, they have remained an important part of literature, speeches, and everyday conversations, making language more expressive and engaging.
How Figures of Speech Improve Communication
Figures of speech make communication more effective and engaging. They enhance meaning by making statements more precise and impactful. Instead of simply saying, “He is very smart,” using a phrase like “He is a walking encyclopedia” creates a stronger image.
They also add emotion and imagery to language, which makes it more powerful. For example, saying “The wind whispered through the trees” creates a more emotional and visual experience for the listener or reader.
Additionally, figures of speech bring variety and uniqueness to writing and speech. They allow writers and speakers to highlight key ideas and develop a distinctive voice. Their use can also depend on culture and context—different cultures have unique ways of using figurative language, and the meaning of a phrase can change depending on how and where it is used.
Misconceptions About Figures of Speech
People sometimes confuse figures of speech with idioms and clichés.
- Figures of speech use creative language techniques, such as “Life is a rollercoaster.”
- Idioms have meanings that are different from the actual words, like “Break a leg” (which means good luck).
- Clichés are overused phrases that have lost impact, such as “Only time will tell.”
Using too many figures of speech can make writing unclear. The key is to find balance—use them where they add value, but don’t overuse them. To be effective, they should match the tone and message, not be mixed too much in one sentence, and be easy to understand.






Leave a Reply