Pronoun-Definition, Types, and Usage
What is Pronoun?
A pronoun is a word or phrase that takes the place of a noun. It helps to avoid repetition and make the language more efficient.

Pronouns are often used to refer to people, places, things, or ideas without having to repeat the specific noun they represent. Examples of pronouns include “he,” “she,” “it,” “they,” “we,” and “you.”
Instead of repeating the same noun over and over, you can use a pronoun to refer back to it. For example, instead of saying “The dog chased the ball. The dog caught the ball.”, you can say “The dog chased the ball. It caught the ball.”
Types of Pronoun
Here are the main types of pronoun:
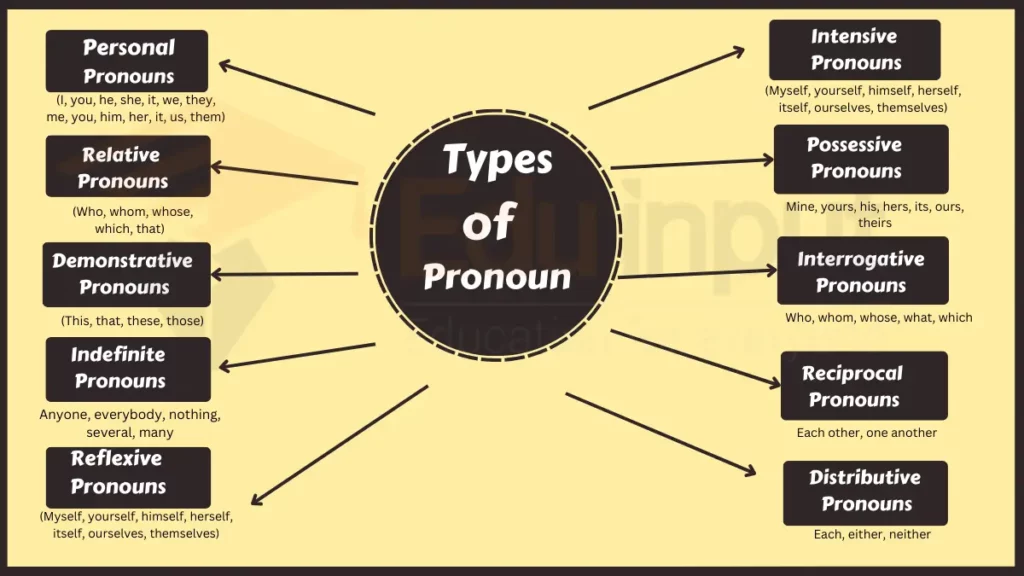
1: Personal Pronouns
Personal pronouns are words that replace specific people or things in a sentence. They include different forms for the subject, object, possessive, and emphatic, serving various functions in communication.
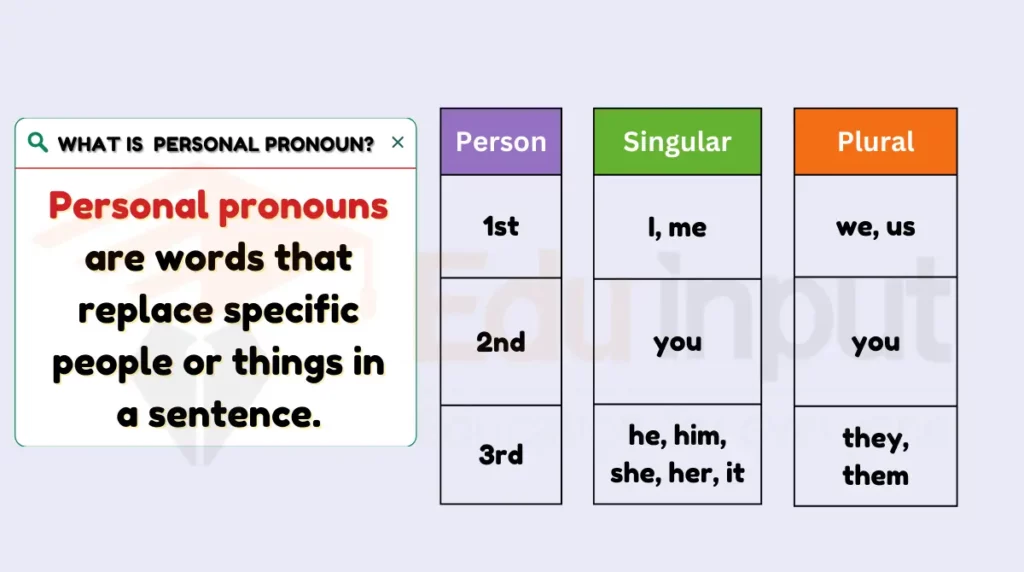
Types
- Subject: I, you, he, she, it, we, they (refer to the subject of the sentence)
- Object: me, you, him, her, it, us, them (refer to the object of the sentence)
- Possessive: mine, yours, his, hers, its, ours, theirs (show ownership)
- Emphatic: myself, yourself, himself, herself, itself, ourselves, yourselves, themselves (emphasize the subject)
Usage
- Subject: “I went to the store.”
- Object: “They helped me find the book.”
- Possessive: “This is my pen.”
- Emphatic: “I did it myself.”
2: Possessive Pronouns
Possessive pronouns indicate ownership or possession of a particular person or thing. They eliminate the need for repeating nouns and show who or what something belongs to.
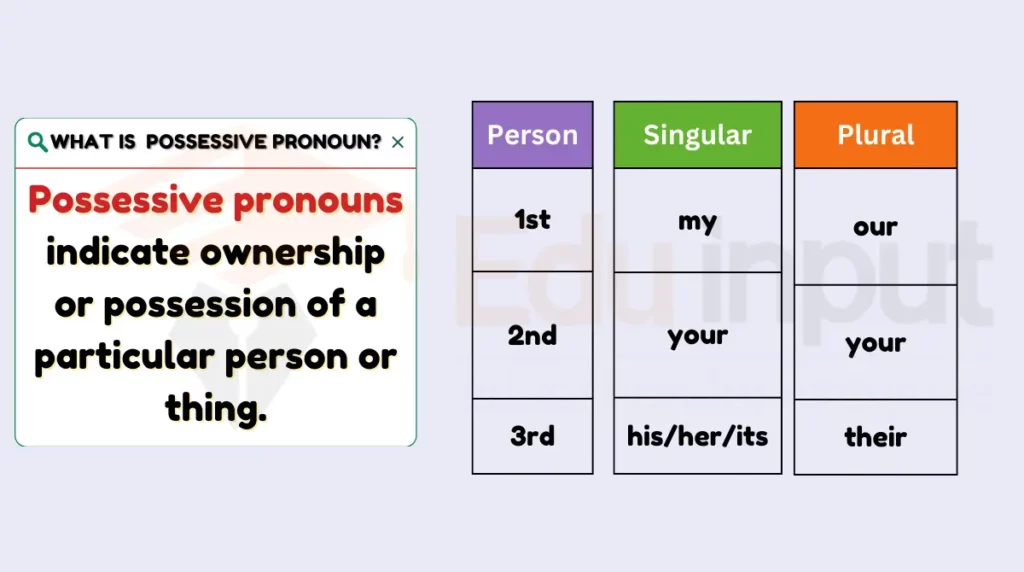
Types
- Singular: mine, yours, his, hers, its
- Plural: ours, yours, theirs
Usage
- “This phone is mine.”
- “The book is theirs.”
3: Demonstrative Pronouns
Demonstrative pronouns point to specific things or places, helping to identify or distinguish them in a conversation. They include both singular and plural forms.
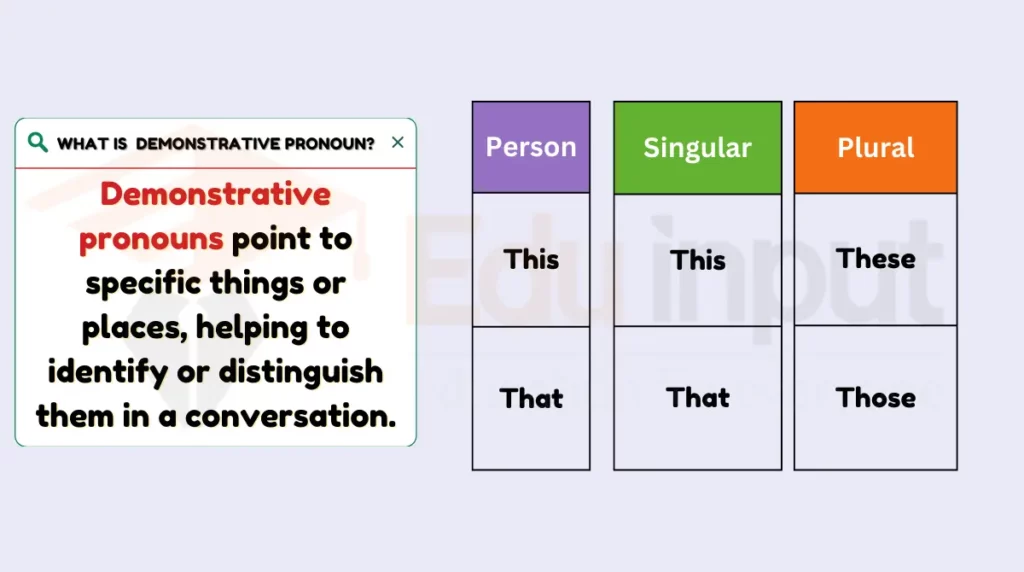
Types
- Singular: this, that
- Plural: these, those
Usage
- “This is the book you wanted.”
- “Those are your shoes.”
4: Interrogative Pronouns
Interrogative pronouns are used to ask questions, seeking information about people, things, ideas, choices, or possession.
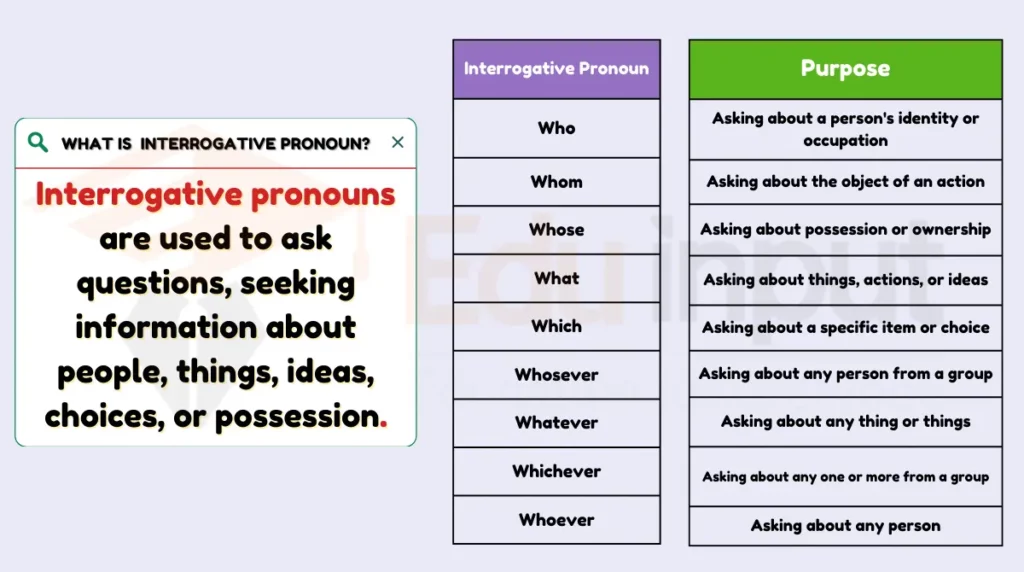
Types
- Who: refers to people
- What: refers to things
- Which: refers to a choice between two or more things
- Whom: refers to the object of a preposition (less common)
- Whose: shows ownership
Usage
- “Who wrote this book?”
- “What is your favorite color?”
- “Which one do you prefer?”
5: Reflexive Pronouns
Reflexive pronouns refer back to the subject of the sentence, emphasizing the action or expressing an action done to oneself.
Types
- Singular: myself, yourself, himself, herself, itself
- Plural: ourselves, yourselves, themselves
Usage
- “She hurt herself.”
- “We helped ourselves.”
6: Relative Pronouns
Relative pronouns connect clauses and introduce dependent clauses, providing additional information about a noun in the sentence.
Types
- Who: refers to people
- Which: refers to things
- That: refers to people or things
- Whose: shows ownership
Usage
- “The book that I read was amazing.”
- “The teacher who helped me is very kind.”
7: Indefinite Pronouns
Indefinite pronouns refer to nonspecific people, things, or amounts, conveying a sense of ambiguity or generality.
Types
- Singular: somebody, someone, anybody, everyone, nobody, anything, everything, something, nothing, each, either, neither, one, other, another
- Plural: few, many, several, all, most, some, none, any, both
Usage
- “Everyone likes ice cream.”
- “Few people came to the party.”
8: Reciprocal Pronouns
Reciprocal pronouns express a mutual relationship between two or more people, emphasizing the exchange of actions or feelings.
Types
- Singular (rare): each other
- Plural: one another
Usage
- “They love each other.”
- “We helped one another.”
9: Intensive Pronouns
Intensive pronouns emphasize the noun they refer to, adding emphasis to the subject or object in a sentence.
Usage
- “I, myself, did it.”
- “She painted the picture, herself.”
10: Dummy Pronouns (Expletives)
Dummy pronouns, like “there” and “it,” are used to introduce a sentence or clause without carrying specific meaning. They serve as placeholders or introductory elements.
Types
Singular: there, it
Usage
- “There is a book on the table.”
- “It is raining outside.”

 written by
written by 



Leave a Reply