Gaseous Exchange In Plants | Structures Involved In Gaseous Exchanges In Plants
Gaseous Exchange In Plants occurs through stomata and lenticels. The epidermis has minuscule pores, called stomata (singular stoma), that manage transpiration and gas exchange with the air. When photosynthesis happens during the day, the oxygen released from the process is used for respiration.
Plants get their free energy from respiration. There are no special organs or systems present for the exchange of gases in plants. Every cell of the plant cares for the exchange of gases according to its need The transport system of plants is composed of large conducting vessels xylem and the phloem. The transport system is not involved in the transport of gases in plants.
Structures Involved In Gaseous Exchanges In Plants
The following structures and methods are involved in the exchanges of gases.
Air Spaces
Air spaces are present between mesophyll cells. The mesophyll cells of the leaves are specialized for photosynthesis. Large air spaces are present between these mesophyll cells. These spaces are directly involved in the exchange of gases. The air spaces are like a honeycomb.
The air spaces are up to 40% of the total volume of the leaf.
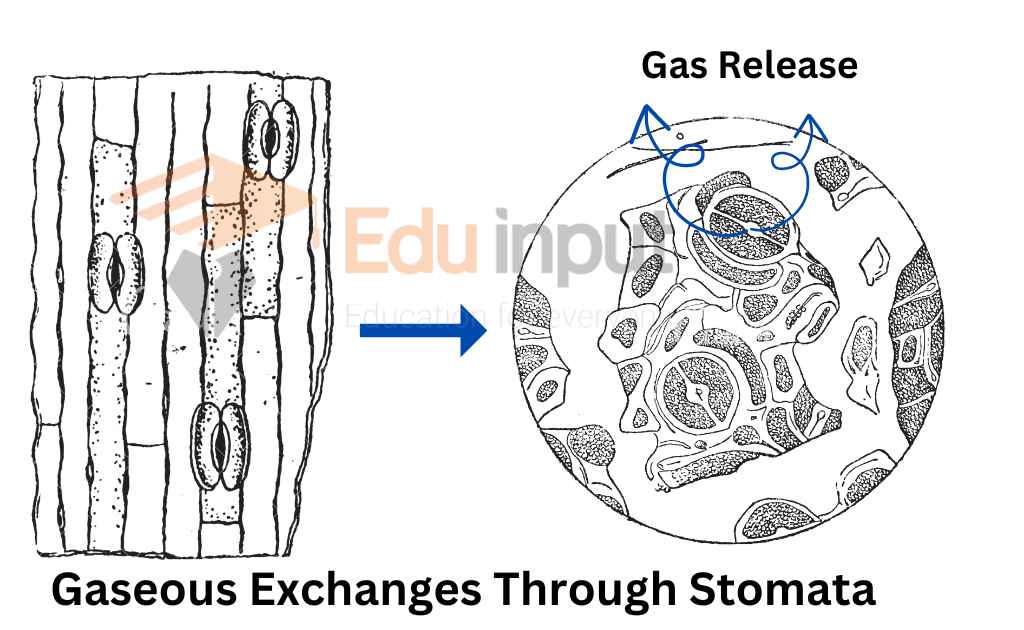
Stomata
Stomata are the main source of the exchange of gases. Stomata are present in the leaves and the young stem. The land plants get their oxygen directly from the air. This air enters through the stomata into the plants
A large number of stomata are present on the leaves It is estimated that there are 12000 stomata per square centimeter of leaf surface in Tobacco plants. These stomata lead into intracellular space between the mesophyll cells.
Lenticels
The cork tissues have special pores called lenticels. Cork tissues are present in the older stems. These cork tissues are formed from dead tissues The lenticels are also involved in the exchange of gases.
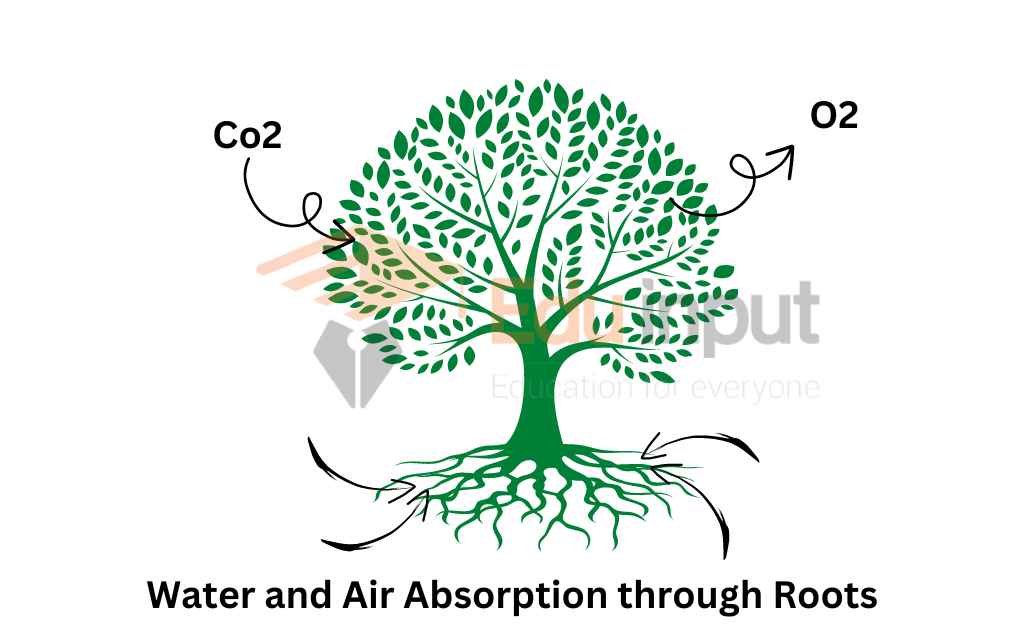
Roots
Air is present in the spaces between the soil particles. The roots of the plants absorb air from the surroundings.
Gaseous Exchange Aquatic Plants
The water contains dissolved oxygen. The aquatic plants absorb this oxygen. In aquatic plants, water passes between the tissues and provides the medium for gas exchange. In terrestrial plants, air enters the tissues and the gases diffuse into the moisture bathing the internal cells.
Related FAQs
How does gaseous exchange occur in plants?
Plants exchange gases through diffusion, where they absorb gases from the surroundings and release carbon dioxide into the outer environment.
Which structures are involved in the gaseous exchange of plants?
Plants exchange gases through;
Stomata
Lenticels
Roots
Air spaces
How do aquatic plants exchange gases?
In aquatic plants, water passes between the tissues and provides the medium for gas exchange. In terrestrial plants, air enters the tissues and the gases diffuse into the moisture bathing the internal cells.

 written by
written by 

Leave a Reply