Respiration In Cockroach-Respiratory organs And Mechanism
Cellular respiration is the process of converting food into energy through chemical reactions. The main function of cellular respiration is to provide the body with energy.
This process takes place inside the mitochondria of each cell. Mitochondria are organelles found within eukaryotic cells that produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the molecule that powers our bodies. ATP is produced during cellular respiration.
This process involves the oxidation of organic compounds such as glucose, fatty acids, amino acids, and other molecules.
Respiration In Cockroach
The cockroach has specialized organs for respiration. Blood is not involved in the transport of gases. It respiratory system is called the tracheal system.
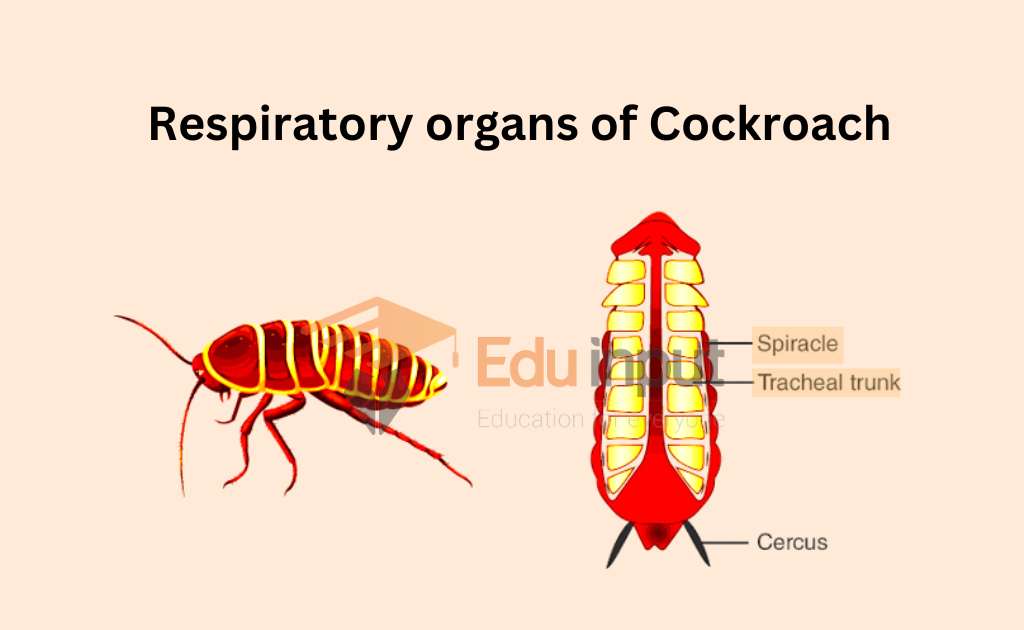
Respiratory organs
There are the following respiratory organs in cockroaches:
Trachea: The respiratory system of cockroaches is composed of a branching system or tubules called tracheae. These tracheae are lined by chitin.
Spiracles: The main tracheal trunk of a cockroach opens to the exterior by way of paired apertures, which are known as spiracles. These spiracles can be found on the lateral sides of the cockroach’s body.
In total, there are ten pairs of spiracles present in cockroaches – two pairs in the thorax and eight pairs in each of the eight abdominal segments.
Tracheoles: The main tracheae divide and subdivide to form tracheoles. Tracheoles are thin-walled tubules.
Fluid-filled ducts: The tracheoles end in small, blind ducts that are filled with fluid. Oxygen dissolves in this fluid and these blind ducts surround tissues and organs, supplying oxygen to cells directly.
Mechanism of respiration
Air is pumped in and out of the body by the expansion and relaxation of the abdominal muscles. The process of respiration is divided into inspiration (inhalation), and expiration (exhalation)
Inspiration
The abdomen expands and the first four pairs of spiracles open. Air rushes into the tracheae through these spiracles, filling the lungs and allowing the creature to breathe.
The concentration gradient between the tracheae and spiracular openings sets up a diffusion pathway for oxygen to travel from the outer air into the tracheae.
The air enters the tracheoles from the tracheae. Then, oxygen is supplied to the cells through an exchange of gases between the tracheoles and tissues.
Expiration
Air enters the tracheoles from the tracheae and oxygen is supplied to cells by the exchange of gases between the tracheoles and tissues.
Related FAQs
What is cellular respiration?
Cellular respiration is the process of converting food into energy through chemical reactions. The main function of cellular respiration is to provide the body with energy.
What are the respiratory organs in cockroaches?
There are the following respiratory organs in cockroaches:
Trachea
Spiracles
Tracheoles
Fluid filled ducts
What is Spiracles?
The main tracheal trunk of a cockroach opens to the exterior by way of paired apertures, which are known as spiracles. These spiracles can be found on the lateral sides of the cockroach’s body.
Where does cellular respiration occur?
Cellular respiration takes place in the mitochondria of each cell.

 written by
written by 


Leave a Reply