How Does The Circulatory System Maintain Homeostasis?
The circulatory system maintains homeostasis by supplying blood and oxygen to all of the cells throughout the body, by regulating pH, osmotic balance, ion and water homeostasis, temperature, and blood sugar levels.
How Does The Circulatory System Maintain Homeostasis in Body?
Here are some specific ways of how the circulatory system maintains homeostasis:
1. Regulating pH
The circulatory system transports acids and bases from where they are produced to where they can be excreted or buffered. This helps to maintain the body’s pH within a narrow range.
2. Osmotic balance
The circulatory system transports water and electrolytes to maintain osmotic balance between the cells and the extracellular fluid. This is important for cell function.
3. Ion and water homeostasis
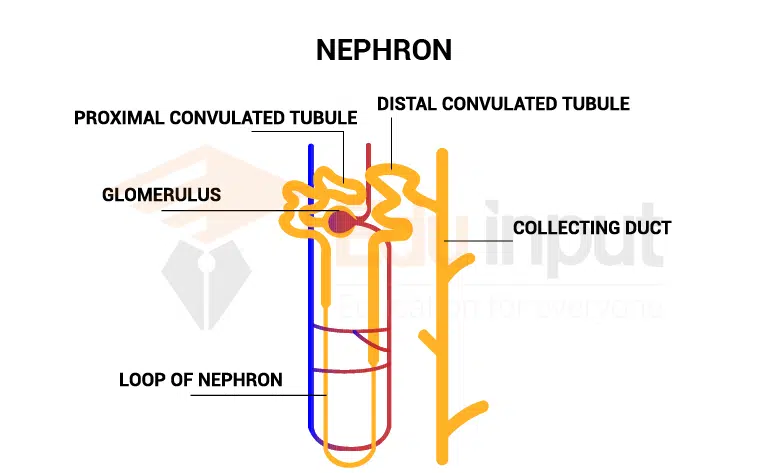
The circulatory system transports ions and water to maintain homeostasis in the body fluids. This is important for many physiological processes, such as nerve function and muscle contraction.
4. Temperature regulation
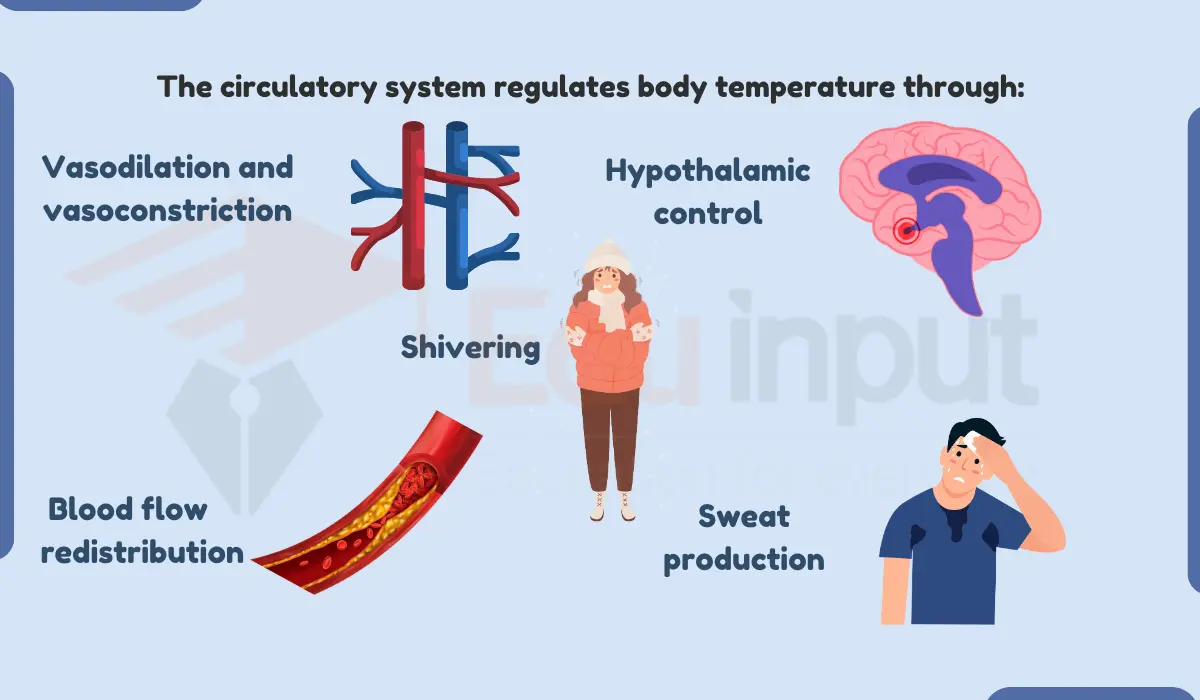
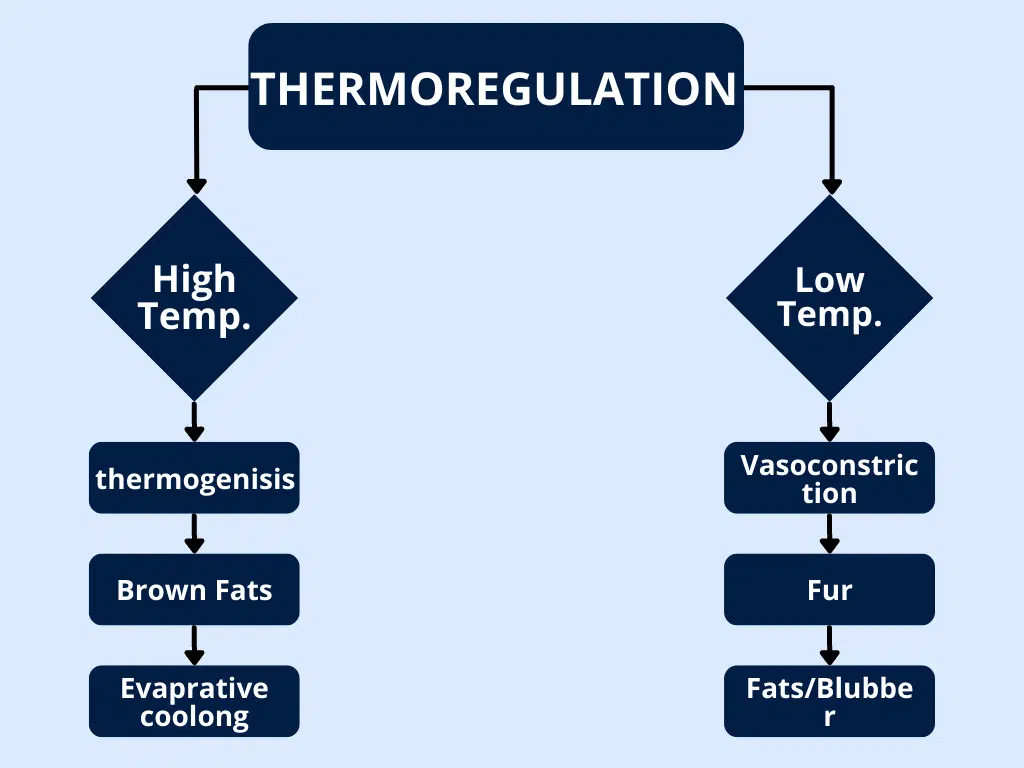
The circulatory system transports heat from the core of the body to the periphery, where it can be dissipated to the environment. This helps to maintain the body’s temperature within a narrow range.
5. Regulation of blood sugar levels
The circulatory system transports glucose from the liver to the tissues, where it can be used for energy. The circulatory system also transports hormones that help regulate blood sugar levels.



Leave a Reply