Manganese-Discovery, Properties, And Applications
Manganese is a chemical element with the atomic number 25 and the symbol Mn. It is a silvery-grey metal that is commonly found in minerals such as pyrolusite and rhodonite. Manganese is a versatile element that has many applications in various fields, including metallurgy, chemistry, and biology.
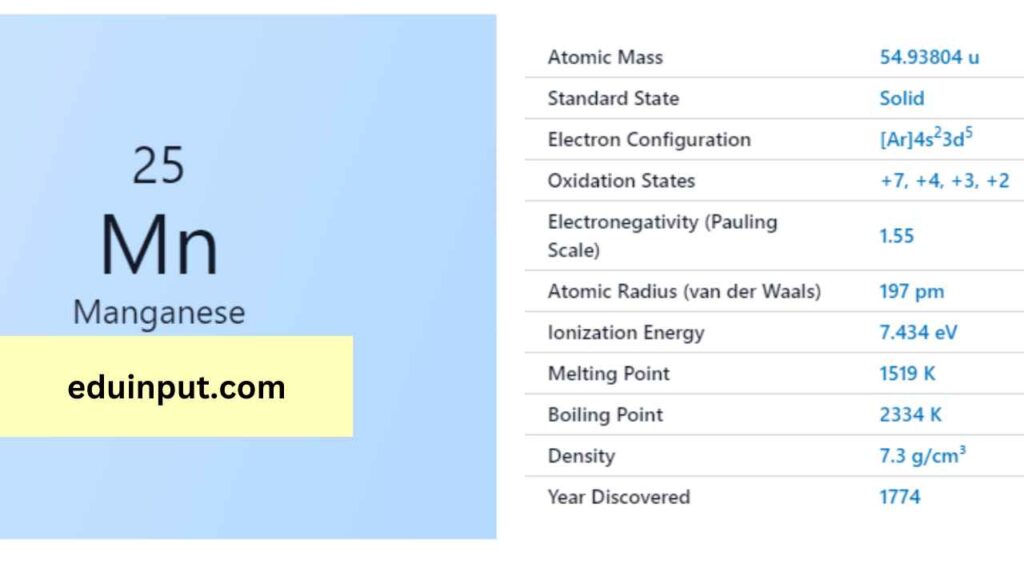
| Property | Value |
| Name | Manganese |
| Symbol | Mn |
| Atomic number | 25 |
| Relative atomic mass (Ar) | Block in the periodic table |
| Standard state | Solid at 298 K |
| Group in the periodic table | Silvery metallic |
| Classification | Metallic |
| Group in periodic table | 7 |
| Group name | (none) |
| Period in periodic table | 4 |
| Period in the periodic table | d |
| Shell structure | 2.8.13.2 |
| CAS Registry | 7439-96-5 |
Discovery
Manganese was first isolated by the Swedish chemist Johan Gottlieb Gahn in 1774. He discovered it while studying the mineral pyrolusite, which is a major source of manganese. The name “manganese” comes from the Latin word “magnes,” which means magnet, because the mineral pyrolusite was thought to have magnetic properties.
Physical Properties
Manganese is a silvery-grey metal that has a melting point of 1,246°C and a boiling point of 2,061°C. It is a hard, brittle metal that is easily oxidized, and it has a density of 7.21 g/cm³. Manganese is paramagnetic, which means it is attracted to magnetic fields but is not magnetic itself.
Chemical Properties
Manganese is a transition metal that can form compounds with a wide range of oxidation states, from -3 to +7. It has many chemical properties that make it useful in various applications. For example, it is a strong oxidizing agent that can react with oxygen to form manganese oxide, which is used in the production of batteries, ceramics, and glass. Manganese also plays a key role in photosynthesis and is an important nutrient for plants and animals.
Facts
- Manganese is the 12th most abundant element in the Earth’s crust, and it is commonly found in minerals such as pyrolusite, rhodonite, and braunite.
- Manganese is used in the production of steel, where it acts as a deoxidizing and desulfurizing agent.
- Manganese is a component of many enzymes that are essential for metabolism in animals and humans.
- Manganese is also used in the production of fertilizers, pigments, and disinfectants.
Applications
Manganese has many applications in various fields, including metallurgy, chemistry, and biology. Some of the most common applications of manganese include:
- Steel production: Manganese is used as a deoxidizing and desulfurizing agent in the production of steel, where it helps to remove impurities and improve the quality of the final product.
- Batteries: Manganese oxide is used as a cathode material in lithium-ion batteries, which are used in many portable electronic devices.
- Ceramics and glass: Manganese dioxide is used as a colorant in the production of ceramics and glass.
- Fertilizers: Manganese is a component of many fertilizers that are used to improve the growth and health of plants.
Manganese is a versatile element that has many applications in various fields. It is a key component of steel production, battery technology, and many other industrial processes. Manganese also plays a vital role in biology, where it is an important nutrient for plants and animals.






Leave a Reply