Types of Solvent Extraction | Solvent Extraction Techniques
Solvent extraction is a widely used method to separate compounds from various matrices based on their solubility in different solvents. This technique is commonly used in chemistry, biology, and industry for applications ranging from pharmaceuticals to environmental analysis.

In this article, we will explore some of the main types of solvent extraction methods based on diffrent techniques, focusing on Liquid-Liquid Extraction (LLE), Solid-Liquid Extraction (SLE), Supercritical Fluid Extraction (SFE), Pressurized Liquid Extraction (PLE), Microwave-Assisted Extraction (MAE), Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction (UAE), and Soxhlet Extraction.
Types of Solvent Extraction
Solvent extraction uses a range of methods to selectively separate compounds from complex mixtures based on differences in solubility.
Here are some common types of solvent extraction based on diffrent techniques being used for solvent extraction.
1. Liquid-Liquid Extraction (LLE)
Liquid-Liquid Extraction (LLE), also known as solvent extraction, separates compounds based on their differential solubility in two immiscible liquids. One liquid phase (the extractant) selectively dissolves analytes of interest. The partition coefficient describes how a compound distributes between the solvent and original phase. LLE is applied for purifying pharmaceuticals, alkaloid isolation, and wastewater treatment.
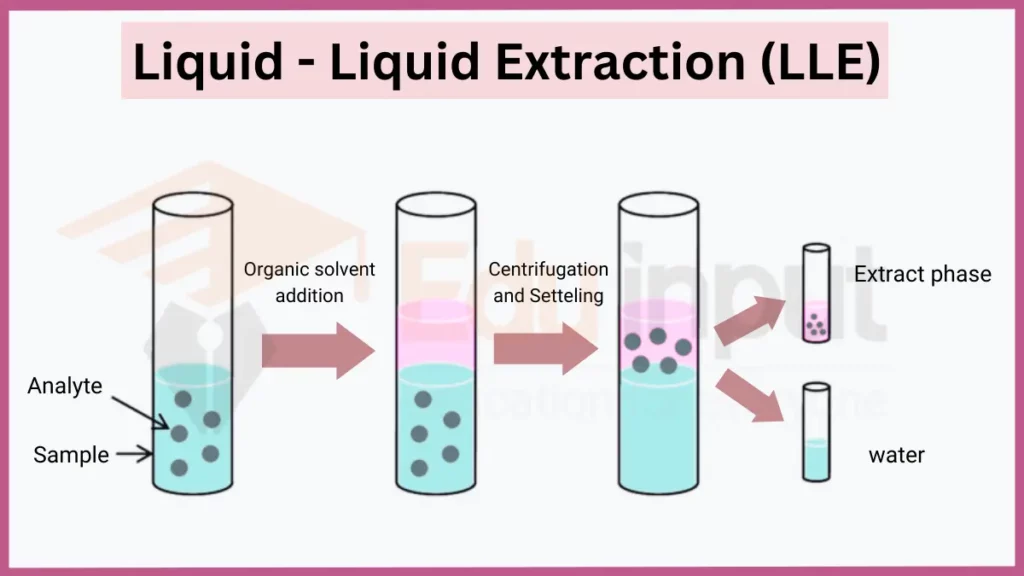
- Key principles: Differential partitioning, immiscible extractant, partition coefficient
- Applications: Drug purification, metal extraction, pollutant removal
- Safety: Proper venting for volatile solvents, personal protective equipment
Read Which Properties of Solvents are Useful for Solvent Extraction
2. Solid-Liquid Extraction (SLE)
Solid-Liquid Extraction (SLE) dissolves components of a solid matrix using a liquid solvent. Compounds with higher solubility in the solvent will be extracted, leaving behind insoluble material. SLE is extensively used for sample preparation, natural product isolation, and analyzing contaminants in soil, toys, and food.
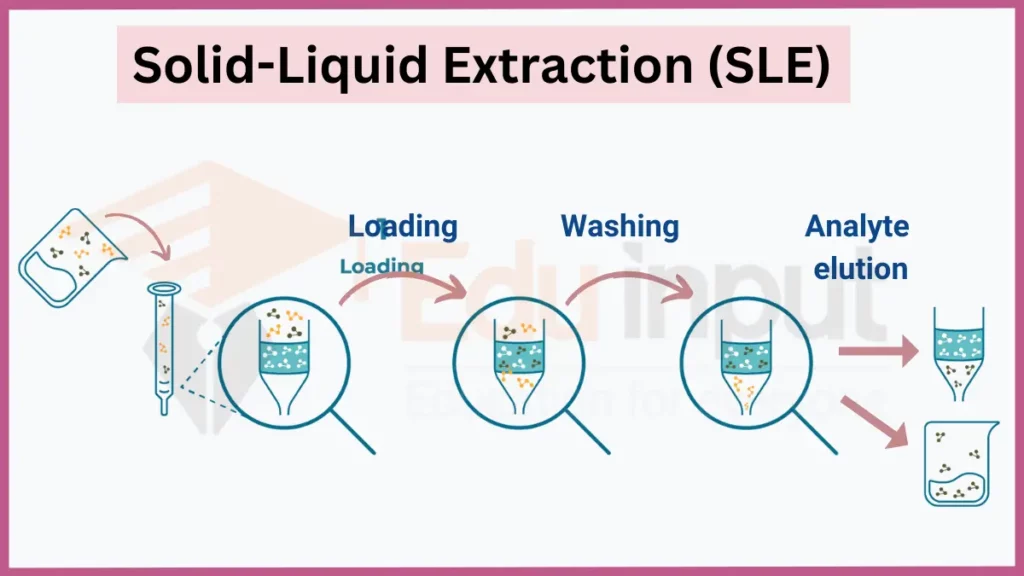
- Key principles: Solubility, mass transfer
- Applications: Herbal medicine, infused oils, environmental analysis
- Safety: Flammability warnings for organic solvents
3. Supercritical Fluid Extraction (SFE)
Supercritical Fluid Extraction (SFE) employs fluids above their critical temperature and pressure as extractants. Under supercritical conditions, fluids possess low viscosity and high diffusivity, allowing deep penetration into solids. SFE avoids organic solvents, enabling non-toxic, efficient extraction suitable for products like decaffeinated coffee or cannabinoid oils.
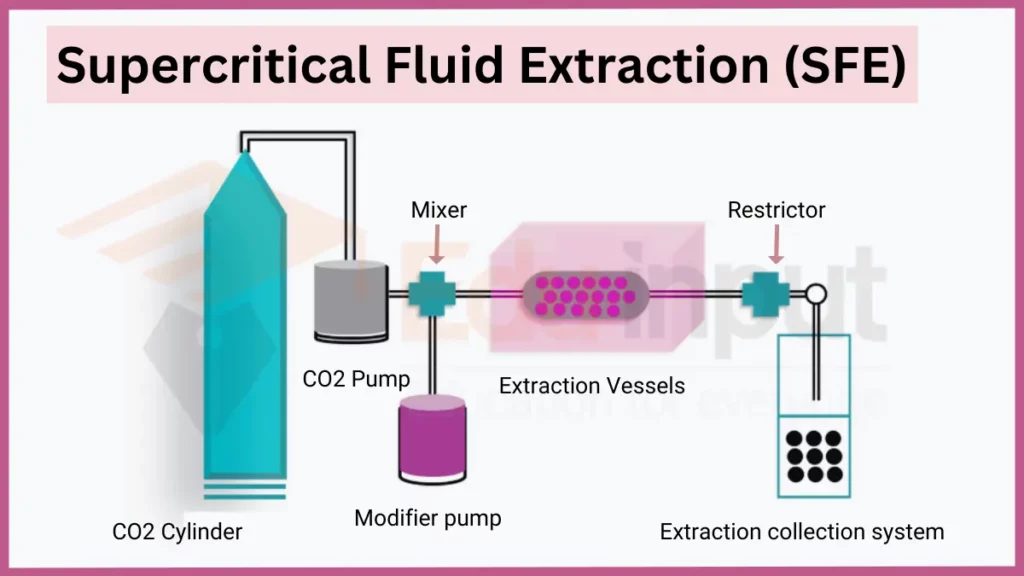
- Key principles: Supercritical state, tunable solubility
- Applications: Food and flavor extraction, pharmaceutical processing, analytical sample preparation
- Safety: High pressure equipment safety protocols
4. Pressurized Liquid Extraction (PLE)
Pressurized Liquid Extraction (PLE) operates at high temperatures and pressures to enhance solubility and mass transfer. Increased solubility improves extraction efficiency compared to ambient conditions. PLE efficiently extracts pollutants from soil, drugs from biologic fluids, and pesticide residues from food.
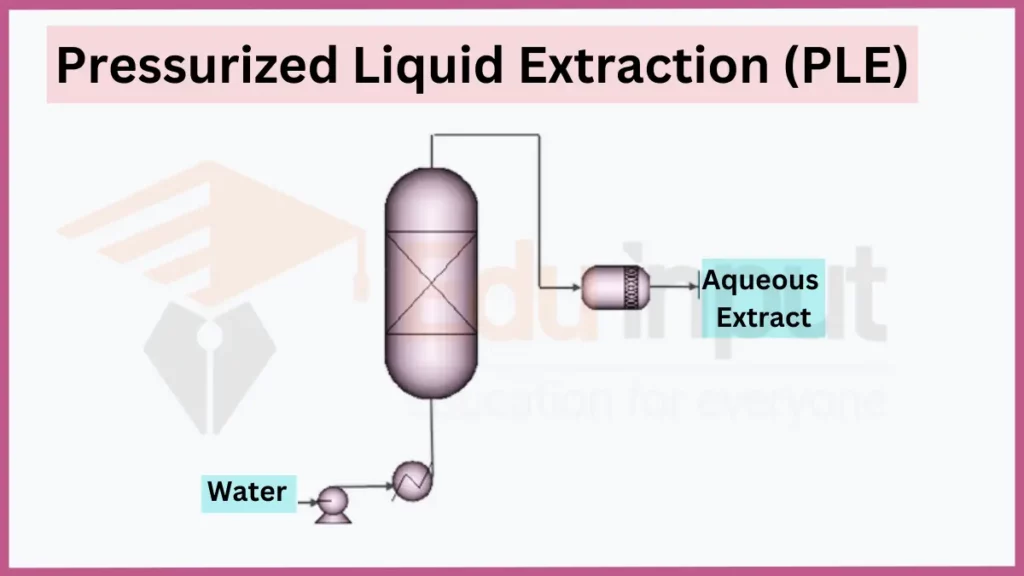
- Key principles: Temperature, pressure, solubility
- Applications: Environmental analysis, toxin detection
- Safety: Proper training for high pressure equipment
5. Microwave-Assisted Extraction (MAE)
Microwave-Assisted Extraction (MAE) uses microwave irradiation to rapidly heat solvent and solid matrix. Localized heating accelerates extraction kinetics compared to traditional methods. MAE is a green technique applied in analytical labs for pharmaceutical, environmental, and food testing.
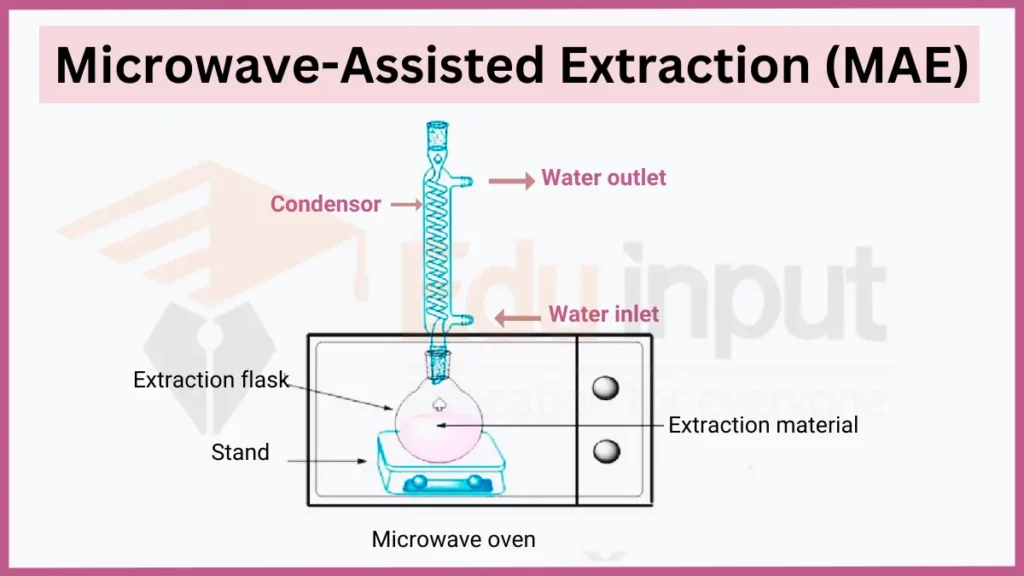
- Key principles: Dielectric heating, extraction kinetics
- Applications: Drug tablet analysis, pesticide residue testing
- Safety: Microwave radiation safety protocols
6. Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction (UAE)
Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction (UAE) utilizes high frequency ultrasonic waves to enhance mass transfer between samples and solvents. Waves create cavitation bubbles which collapse, generating shockwaves and local heating that accelerate extraction. UAE efficiently extracts antibiotics, antioxidants, and other natural products.
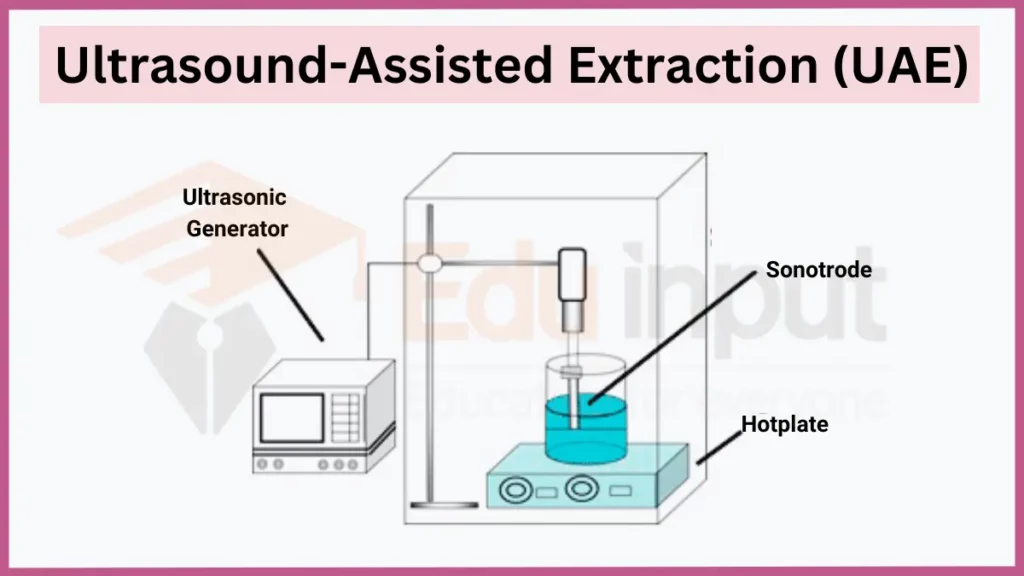
- Key principles: Cavitation, mass transfer
- Applications: Natural product isolation, food and flavor analysis
- Safety: Ensure safe ultrasound power levels
7. Soxhlet Extraction
Soxhlet extraction continuously drain off heated solvent through a solid sample. Fresh solvent contacts the sample, achieving efficient, automated extraction without extensively handling hot solvents. It is applied for lipid, fat and pesticide extractions requiring exhaustive sample extraction.
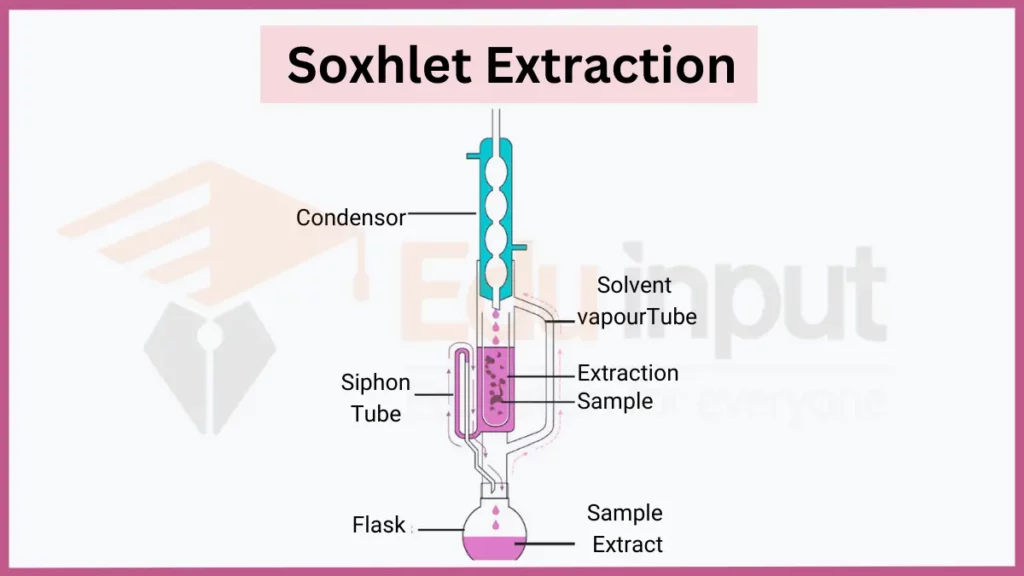
- Key principles: Continuous contact, automation
- Applications: Fat analysis, polymer purifications, environmental contaminant testing
- Safety: Proper ventilation and containment for large solvent volumes
8. Acid-Base Extraction (ABE)
Acid-Base Extraction is a technique that uses the differential solubility of compounds in an organic solvent with varying pH levels. By adjusting the pH of the solution, specific compounds can be selectively extracted.
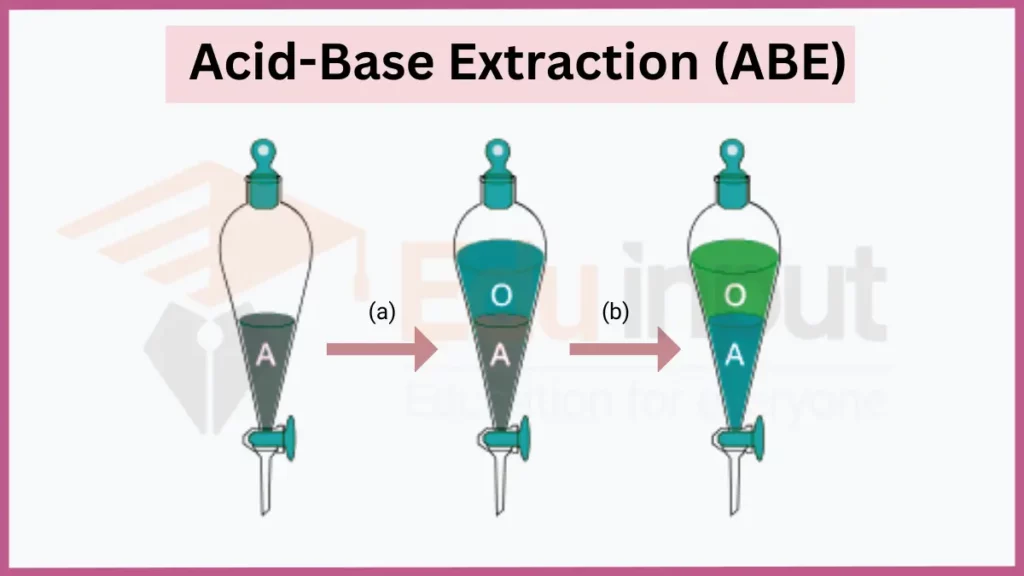
- Key Principles: pH Adjustment, Differential Solubility
- Applications: Separation of Alkaloids in Natural Products, Purification of Organic Compounds in Synthesis, Isolation of Acidic and Basic Components
- Safety: Controlled pH Conditions, Proper Handling of Organic Solvents
9. Mechanochemical Assisted Extraction (MAE)
Mechanochemical Assisted Extraction uses mechanical forces to facilitate the breakdown of cell structures. It promotes the release of target compounds from the matrix.
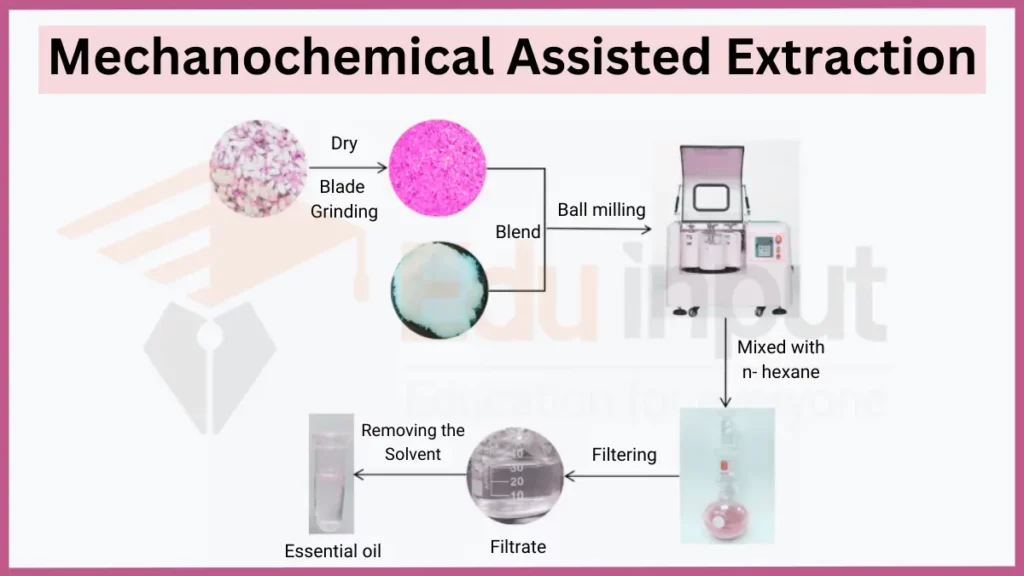
- Key Principles: Mechanical Disruption, Enhanced Mass Transfer
- Applications: Extraction of Proteins from Microorganisms, Isolation of Bioactive Compounds from Algae, Extraction of Essential Oils from Seeds
- Safety: Equipment Safety, Dust Control, Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
10. Heat Reflux Extraction (HRE)
Heat Reflux Extraction involves continuous boiling and condensation of the solvent to create a cyclic extraction process. This method enhances the extraction efficiency by maintaining a consistent temperature.
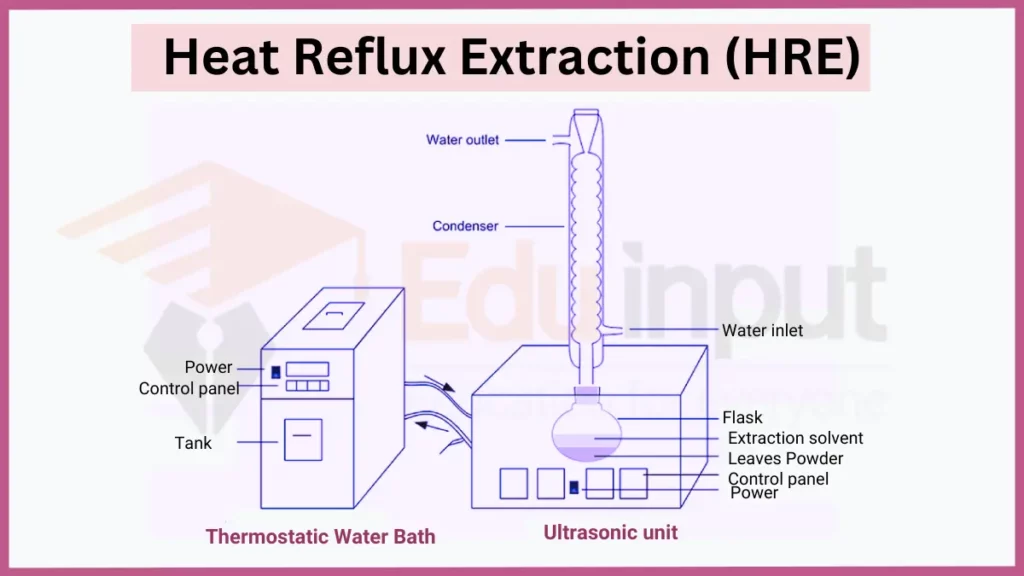
- Key Principles: Continuous Boiling and Condensation, Consistent Temperature Control
- Applications: Reflux Extraction in the Synthesis of Pharmaceutical Intermediates, Purification of Chemical Compounds through Distillation, Recovery of High-Purity Solvents in Industrial Processes
- Safety: Thermal Control and Monitoring, Proper Ventilation, Equipment Safety and Maintenance

 written by
written by 




Leave a Reply