Neuron Diagram and Functions
February 14, 2024
Neuron Diagram Labelled
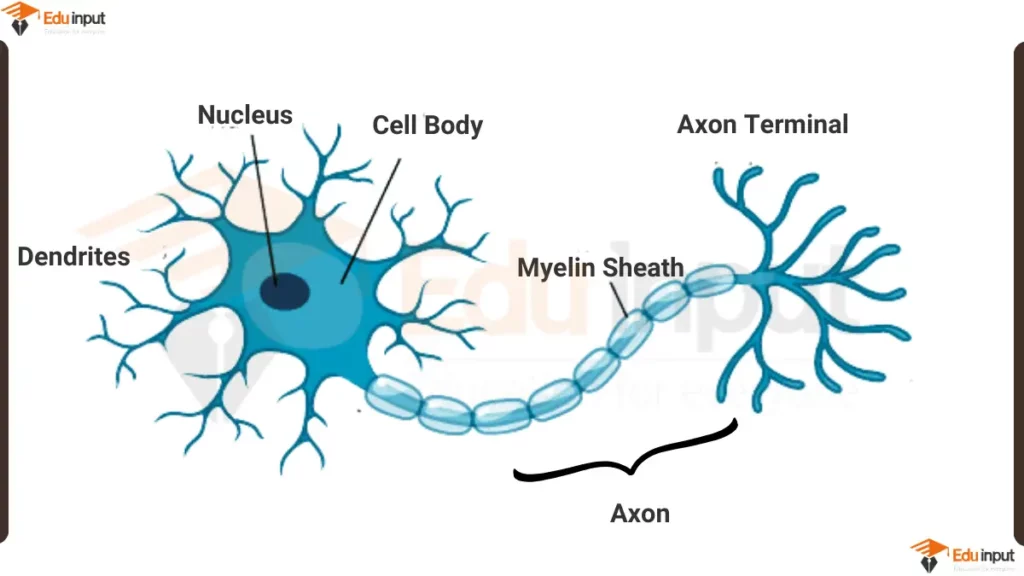
Here are the main parts of a neuron and their functions:
- Cell body (soma): This is the main part of the neuron, containing the nucleus, which houses the cell’s genetic material. The cell body also contains organelles that produce energy for the neuron and other molecules needed for its function.
- Nucleus: The nucleus contains the cell’s DNA, which holds the instructions for building and maintaining the cell.
- Dendrites: These are short, branched extensions that reach out from the cell body. They receive signals from other neurons and transmit them towards the cell body.
- Axon: This is a long, thin fiber that carries electrical signals away from the cell body. The axon is covered in a fatty substance called myelin, which helps to insulate the axon and speed up the transmission of signals.
- Myelin sheath: This is a fatty substance that surrounds the axon and helps to insulate it. The myelin sheath speeds up the transmission of electrical signals by preventing them from leaking out of the axon.
- Axon terminal: This is the end of the axon, where it forms connections with other neurons. The axon terminal contains neurotransmitters, which are chemical messengers that transmit signals to other cells.
- Synapse: Synapse is the junction between the axon terminal of one neuron and the dendrites or cell body of another neuron. When an electrical signal reaches the axon terminal, it triggers the release of neurotransmitters. These neurotransmitters bind to receptors on the other neuron, and this can either excite or inhibit the other neuron.
File Under:



Leave a Reply