What is Synapse? – Parts, Types, and Mechanism
The junction between the axon of one neuron and the dendrite of another neuron or effector (glands or muscle cell) cell is called the synapse. It is the site where electric nerve impulses are transmitted between two neurons.
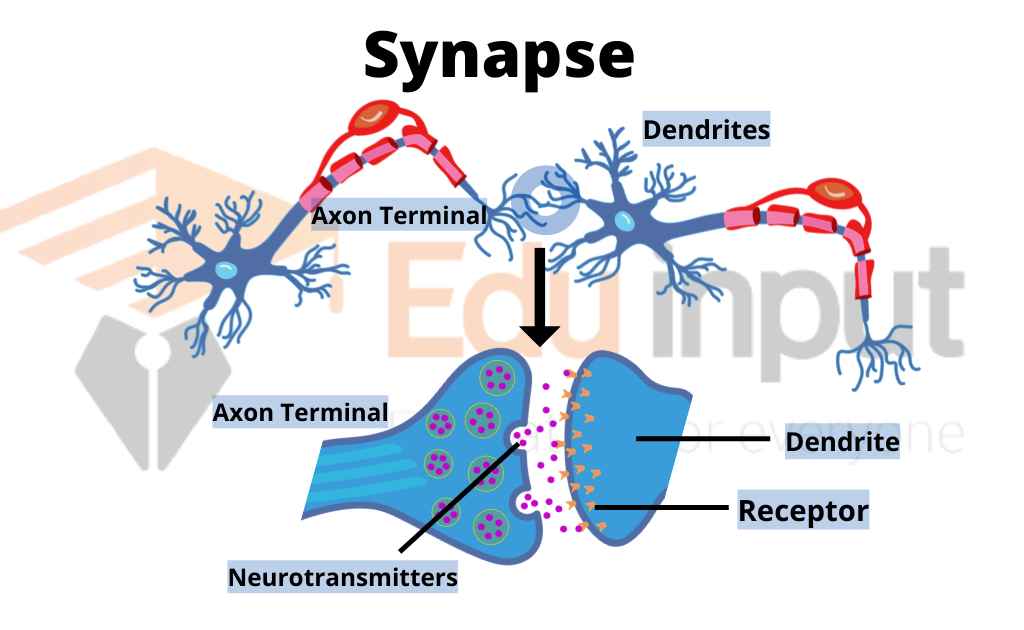
Also learn When Transmission Occurs at a Synapse?
Parts Of Synapse
It has the following part:
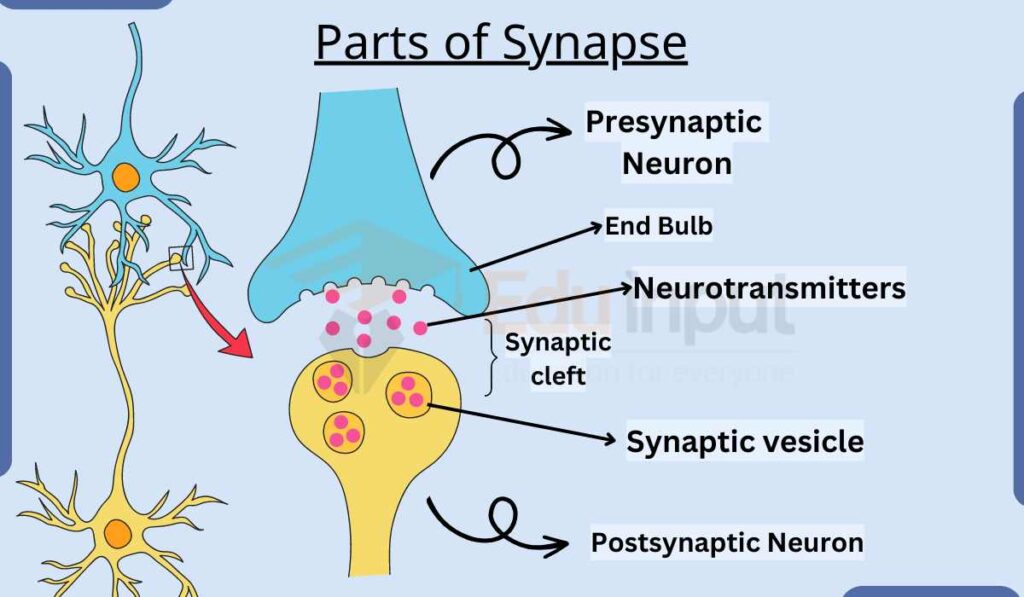
1. End bulb: an action potential travels along an axon. It reaches the end of a branching axon terminal called the end bulb.
2. Synaptic cleft: the space between the end bulb and the dendrite of the next neuron is called the synaptic cleft.
3. Presynaptic neuron: the neuron carrying the action potential toward a synapse is the presynaptic neuron.
4. Postsynaptic neuron: the receptive segment of the second neuron is called the postsynaptic neuron. The presynaptic cell is always a neuron. But the postsynaptic cell can be a neuron, muscle cell, or gland cell.
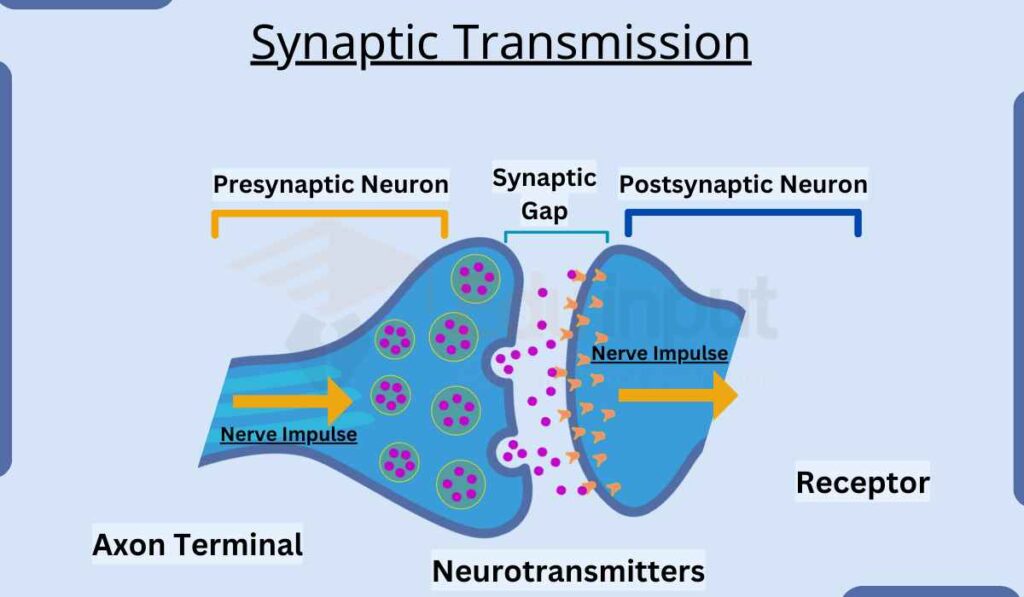
Synapse Diagram
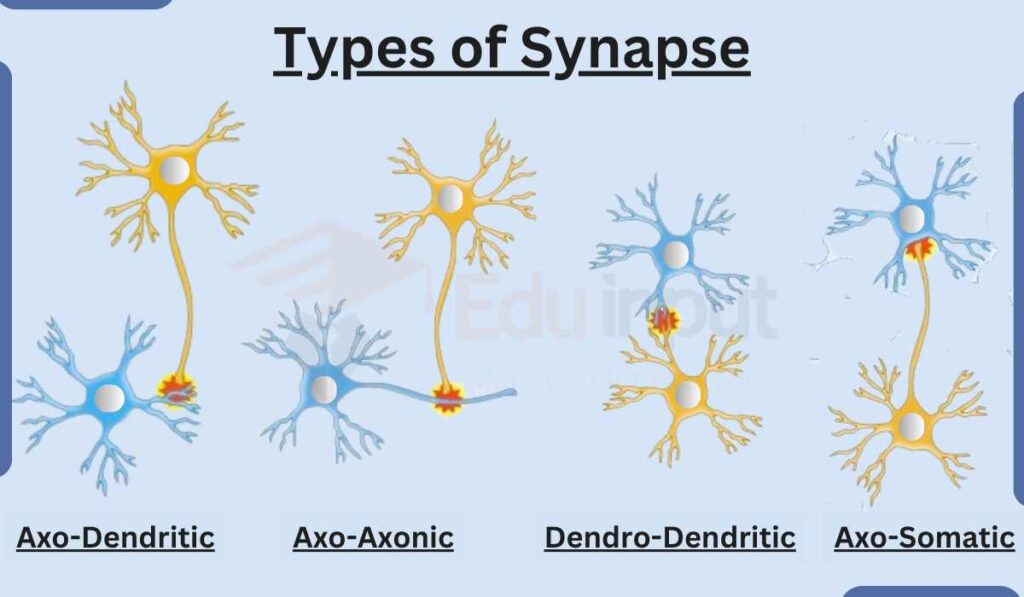
Types of Synapse
There are following main types of synapse:
- Chemical Synapse (Where neurons communicate by communicate with each other by transmitting chemical signals)
- Electrical Synapse (Where neurons communicate by communicate with each other by transmitting electrical signals)
- Axo-Dendritic Synapse (Between the axon of one neuron and the dendrite of another neuron)
- Axo-Somatic Synapse (Between the axon of one neuron and the soma (cell body) of another neuron)
- Axo-Axonic Synapse (Between axon of one neuron communicating with the axon of another neuron)
- Dendro-Dendritic Synapse (Between the dendrites of two different neurons)
Learn Detailed article on types of synapse
Nature Of Synapses
Synapses can be electrical or chemical.
Electrical Synapse
In this case, positively charged ions move from one neuron to the next. Therefore, nerve impulses transmit directly from neuron to neuron. This is because the electric synapses permit ions to flow between cells through gap junctions.
An electrical synapse can rapidly transmit impulses in both directions. Electrical synapses are common in fishes.
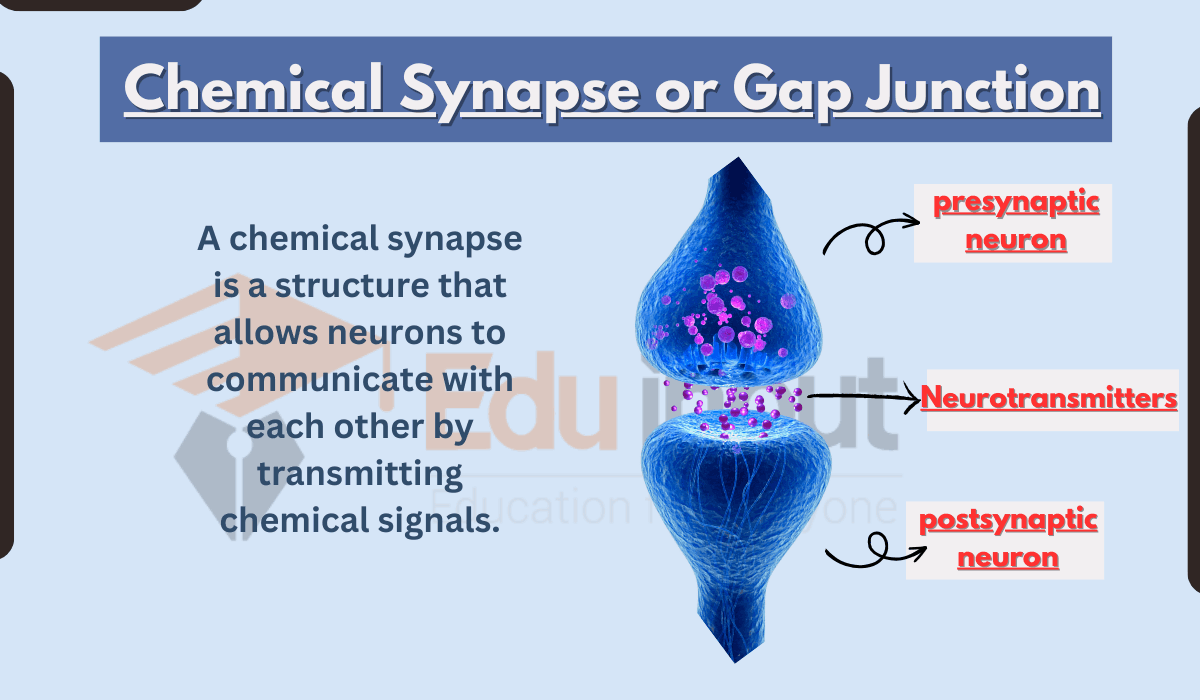
Chemical Synapse
In this case, two cells communicate using a chemical agent called a neurotransmitter. It is released by the presynaptic neuron.
A neurotransmitter changes the resting potential in the plasma membrane of the post-synaptic cell. It creates an action potential in the next cell. This cell continues the transmission of the impulse.
Action of Neurotransmitters
Nerve impulse is transmitted across synapse in the form of chemical messenger called neurotransmitters. It has following mechanism:
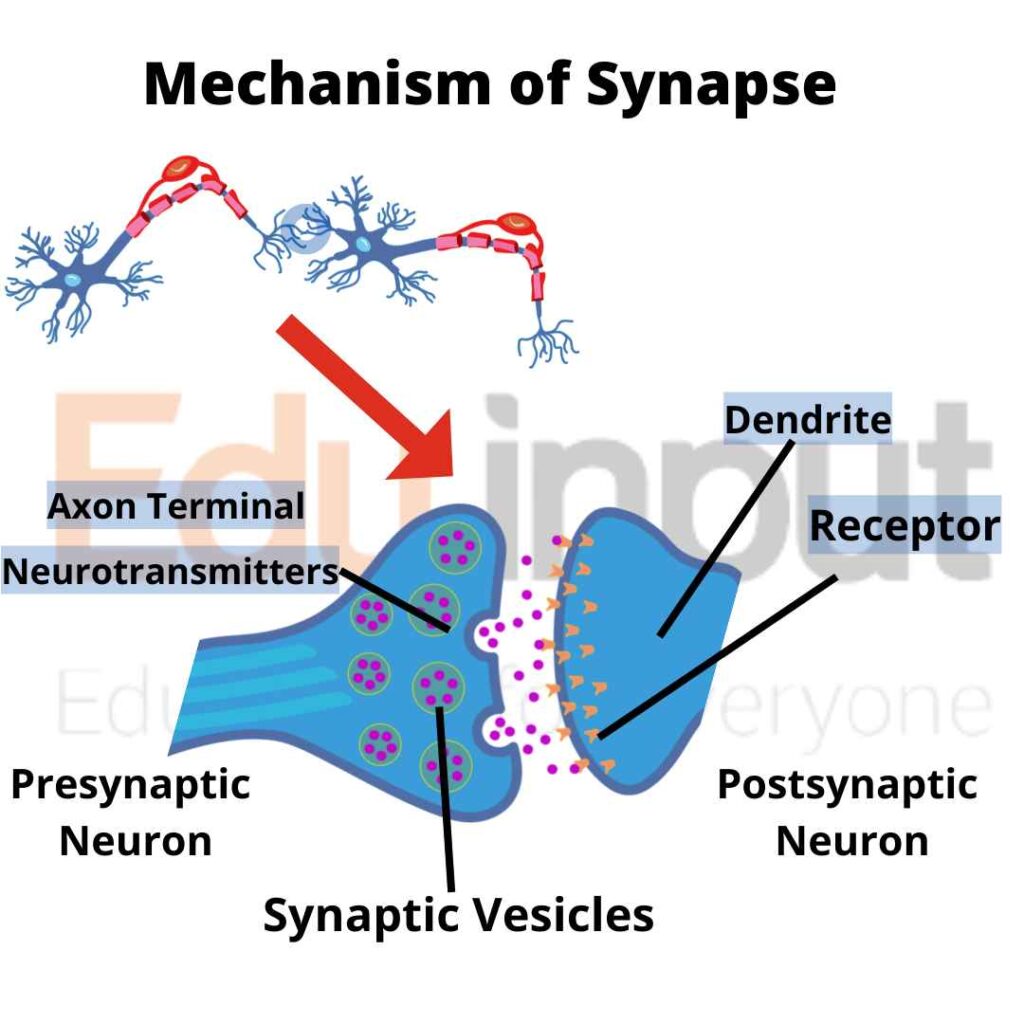
1. Release of neurotransmitter
Nerve impulse reaches the end bulb. It stimulates the storage of vesicles. These vesicles contain chemical neurotransmitters. These vesicles fuse with the plasma membrane. The vesicles release the neurotransmitter by exocytosis into the synaptic cleft.
The common neurotransmitter is acetylcholine and norepinephrine. More than 50 other transmitters are known.
2. Stimulation of postsynaptic membrane
The neurotransmitter binds with the receptor protein. These proteins are present in the postsynaptic membrane. It causes depolarization in the presynaptic cell. The enzyme acetylcholinesterase quickly inactivates acetylcholine.
If acetylcholine is not inactivated, it continuously produces nerve impulses. It causes disease. The active ingredient in most flea sprays and powders is parathion. It prevents the breakdown of acetylcholine in fleas. It causes disease in it and kills them.
Also learn about:

 written by
written by 

Leave a Reply