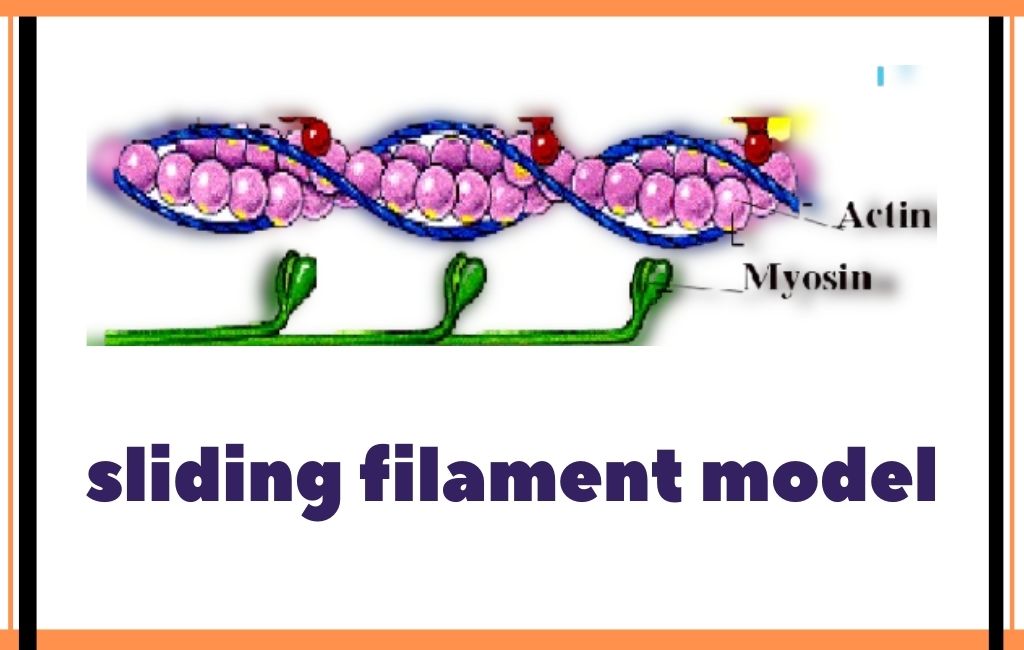
Sliding Filament Model of Muscle Contraction
H. Huxley and AH Huxley and their colleagues suggested a hypothesis named Sliding Filament Model. That model explains the mechanism of muscle contraction. This is called the sliding filament model of muscle contraction.
The filaments undergo shifting during the contraction of muscle fiber the I band reduces the length so the z line gets closed to each other.
sliding filament Model
The sliding filament model/theory explains the mechanism of contraction of muscles which is based on the sliding of muscle proteins that slide past each other to generate movement.
Steps Of sliding filament theory
There are the following steps involved in the contraction of a muscle:
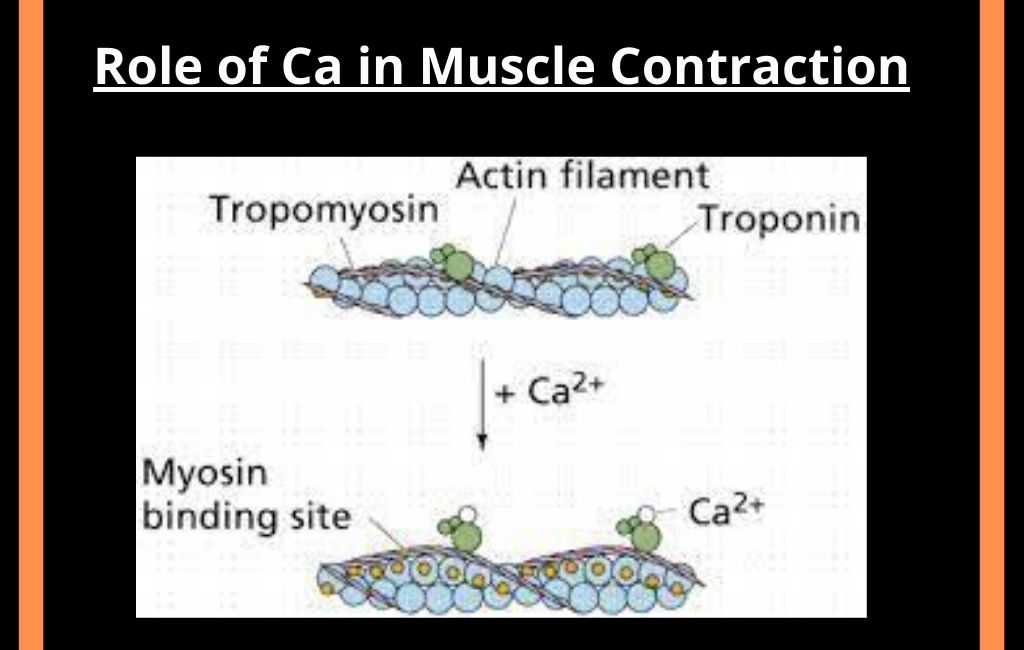
- The reticulum initiates the release of CA 2+ ions. The Z line is brought closer together.
- The I band shortens and the h zone disappears
- Binding of myosin and Actin site. The cross-bridges of thick filament become attached to binding sites on the Actin filament.
- Power supply by the release of ATP
- Hydrolyzation of ATP
- Ca+ are sent back to SR
- The cross-bridge then contracts to pull the actin filament towards the center of the sarcomere.
How The Cross Bridges Are Controlled?
At rest:
The Tropomyosin covers the sites on the Actin chain during rest. Thus the head of the Myosin cannot be attached to these sites.
During contraction:
Calcium ions bind with the Troponin molecule at the start of muscle contraction. The Troponin molecule moves slightly. This movement displaces the Tropomyosin. It exposes the binding sites for the Myosin head. The Myosin head is attached to the Actin filament. ATP is hydrolyzed and sliding of actin and myosin starts.
This ATP is provided by a large number of mitochondria present in each muscle cell.
Rigor mortis:
The stiffening of the body after death is called rigor mortis. ATP is required to break the link between the mass. The amount of ATP in the body falls after death. Thus the bridges cannot be broken. So this bridge remains firmly bound. As a result, the body becomes stiff after death.
Frequently Asked Questions-FAQs
What is the sliding filament Model?
The sliding filament model/theory explains the mechanism of contraction of muscles which is based on the sliding of muscle proteins that slide past each other to generate movement.
What are the steps Of sliding filament theory?
It involves the following steps:
Initiation of Ca Ions
Binding of myosin and Actin site
Hydrolyzation of ATP
Ca+ are sent back to SR
Contraction of cross-bridge to pull the actin filament
Why is it called a sliding filament model?
Actin and Myosin Filament slide in and out to make muscle contraction. That’s Why it is known as the sliding filament model.

 written by
written by 

Leave a Reply