Tactic Movement in Plants-Definition and Examples
The movement of higher plants is mainly manifested in the bending, twisting, and stretching of certain plant parts or organs. There are other plant movements that occur spontaneously without external stimuli.
These movements are called spontaneous or voluntary movements. Some plant movements are caused in response to some or specific stimuli and are said to be induced or plant movements that occur spontaneously, without the irritation and sensitivity of protoplasm.
Types Of Movements
There are two types of movements;
- Autonomic movements
- Paratonic movements
Autonomic Movements
The spontaneous movement due to internal causes is called autonomic movement. The stimulus for autonomic movements may be internal or external. There are three types of autonomic movement.
These are:
• Tactic Movements
• Growth Movement
Tactic Movements
Plants are the kingdom of multicellular eukaryotes. Unlike animals, they are capable of photosynthesis. They are major players in photosynthesis in terrestrial ecosystems.
Tactical movement is a movement in plants towards (positive) or away from (negative) stimuli. For example, phototaxis is the response of plants to light. Positive phototaxis occurs when plants move or orient toward a light source.
This type of exercise allows the plant to maximize its photosynthetic range, which helps it grow. Phototaxis can also be negative, meaning that plants move away from light sources to minimize light-induced damage. Other stimuli that can trigger tactical movements in plants are gravity and touch.
These are movements of the whole cell, its organelles, or the organism due to external stimuli. Tactical action can be aggressive when targeting a stimulus. These can be positive or negative when removed from the stimulus.
The tactic movements are further classified based on the nature of the stimulus:
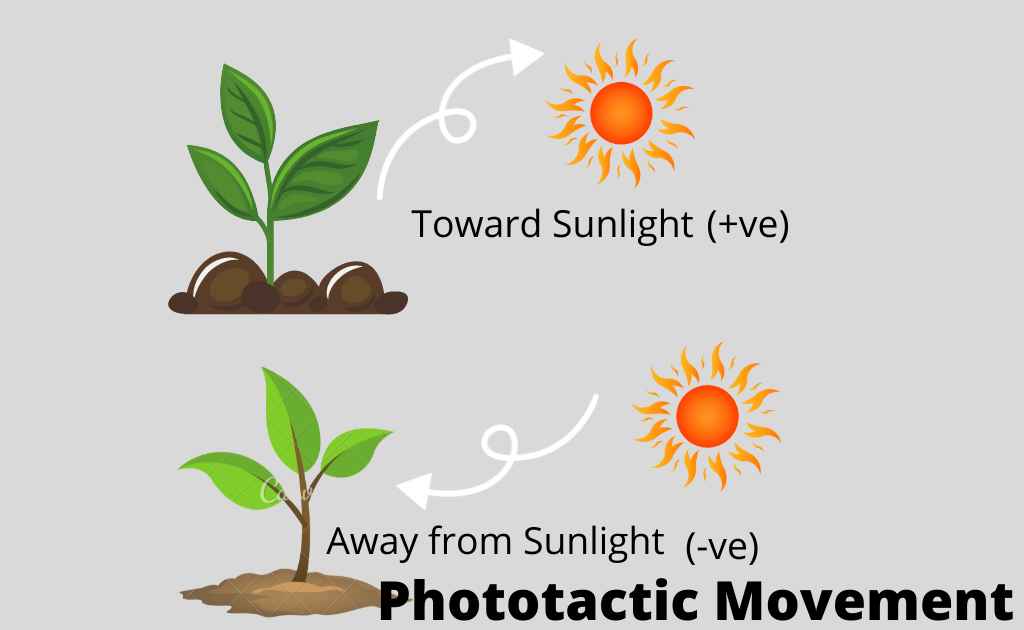
Phototactic Movement:
The tactic movement in response to the stimulus of light is called phototactic. The movement may be toward the source of light, called positive phototactic movement. For example, positive movement of chloroplast due to cyclosis.
This movement helps the plants to absorb maximum light for photosynthesis. The light intensity and direction of light affect the intracellular distribution of chloroplast. It may move away from the source of light called negative phototactic movement.
Chemotactic Movements:
The movement in response to the stimulus of a chemical is called chemotactic movement. For example, the movement shown by sperm of liver-worts, mosses, and ferns. The sperm moves towards archegonia in response to a nucleic acid stimulus.
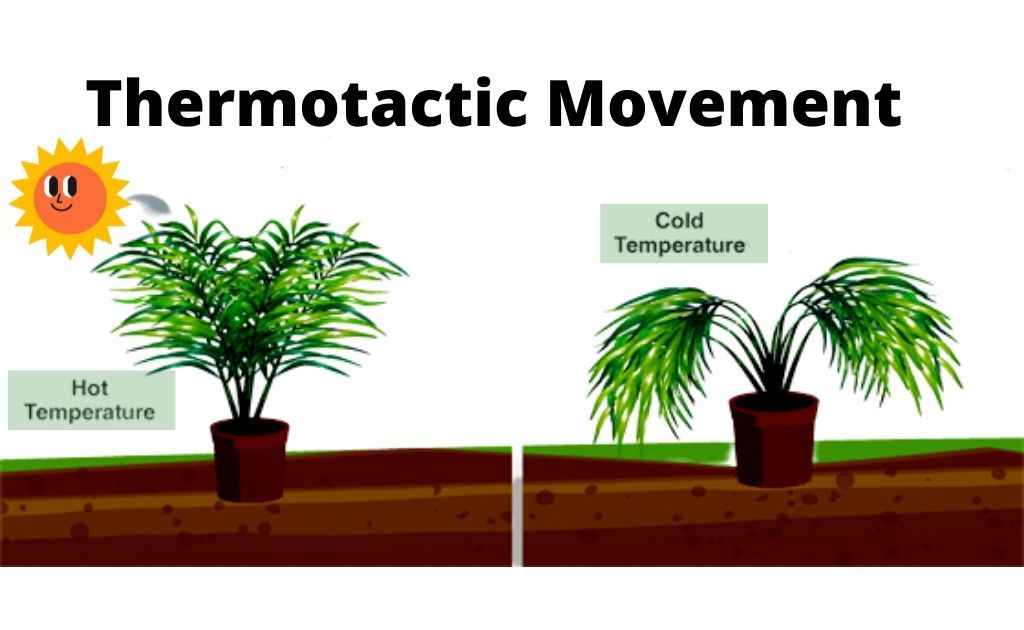
Thermotactic Movement
The movement of locomotion in response to certain unidirectional temperature stimuli. It can be positive or negative according to the direction (towards or away from stimuli).
Examples of Tactic Movement
- Movement of Chlamydomonas towards the light. It is an example of Phototactic movement.
- Movement of Male gamete of Bryophyte from antheridium to archegonium. This movement is caused due to chemicals secreted by archegonium. It is an example of the Chemotactic movement.
- Chlamydomonas move towards the warmer side (positive thermotaxis) and if the temperature is higher than the required level, it will move away from the high temperature (negative thermotaxis). It moves because the enzymatic activity is optimum in warmer conditions. This is an example of thermotactic movement.
Is tactic movement directional?
Tactic movement is the movement in response to different stimuli (temperature, chemical, or light). So it is controlled by the direction of the stimulus, it is happening in response to.
What are positive and negative phototaxis?
Phototaxis is a type of tactic movement, which occurs in response to light. The movement is called phototaxis, if it is in direction of stimulus (light),
, and if the movement is opposite to the direction of stimuli, it is known as negative phototaxis.
What is the most common example of Tactic Movement?
The movement of the Male gamete of Bryophyte from antheridium to archegonium is an example of tactic movement in plants.
Why is the movement in plants important?
Plant movement is important for the growth, survival, and reproduction of plants. For example phototaxis help plants to carry photosynthesis, as the plant moves toward light.

 written by
written by 

Leave a Reply