Stages and Significance of Meiosis II | What happens in Meiosis II?
The cell cycle involves two stages Meiosis and Mitosis. Meiosis is a type of cell division in which the number of chromosomes remains half in daughter cells. In Sexual reproduction, the genetic contribution from two different sex cells is required. It resembles Mitosis.
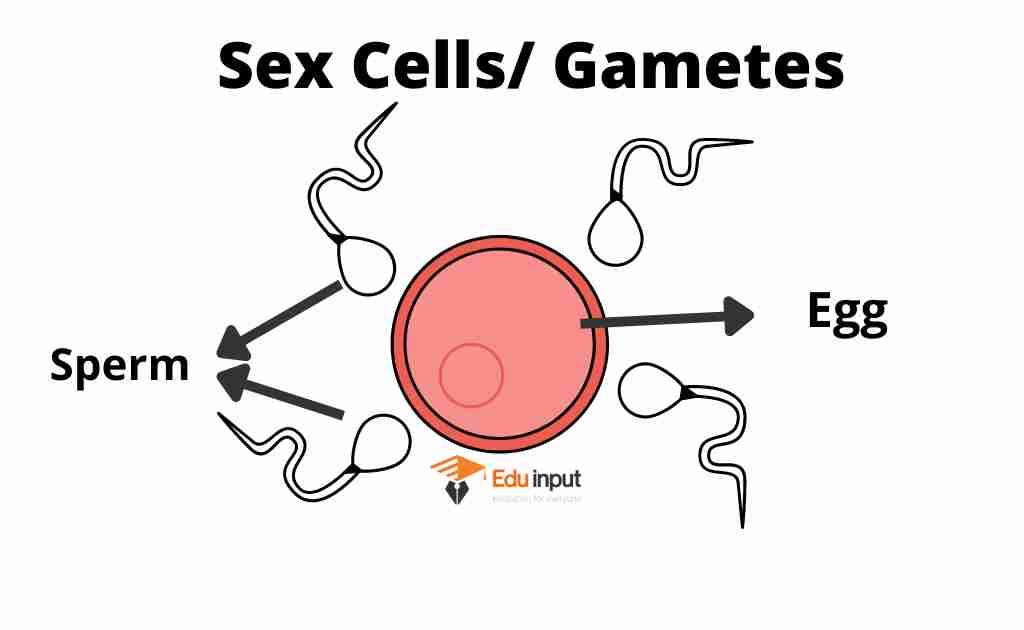
Sex cell or gamete
There are two specified sex cells named egg (Ovam) and sperm. These sex cells are called gametes. During fertilization, A male gamete (sperm) unites with a female gamete (egg) to form a zygote.
syngamy
The fusion of gametes is called syngamy. The zygote is the first cell of the newly producing animal. Both gametes contribute half of the genetic information to the zygote. The sexually reproducing animals produce gametes by meiosis.
Where does meiosis occur?
Meiosis occurs in specialized cells of the ovaries and testes. It reduces the number of chromosomes to the haploid (1N) number.
Meiosis II
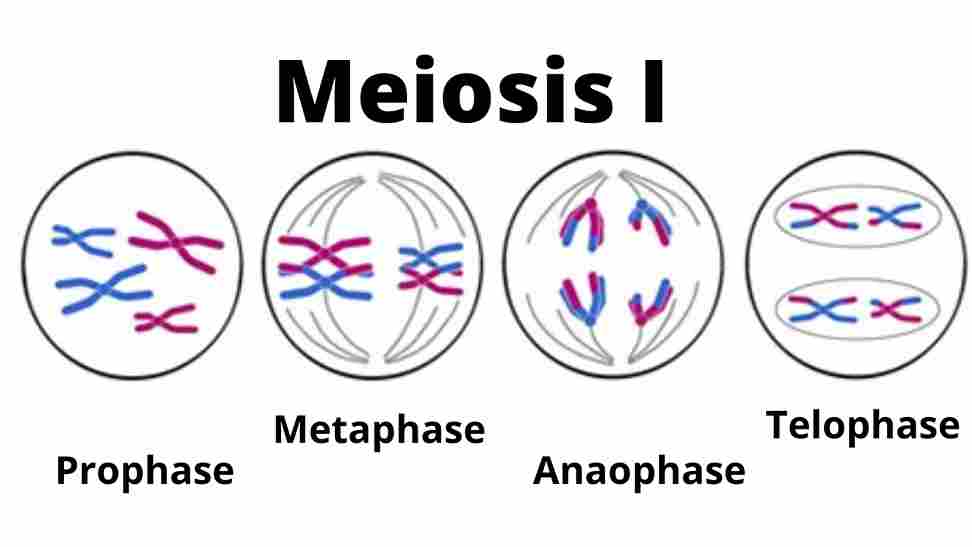
Meiosis is a continuous process. It is divided into two phases:
- Meiosis I
- Meiosis II
Stages of Meiosis II
Here is a detailed description of meiosis II:
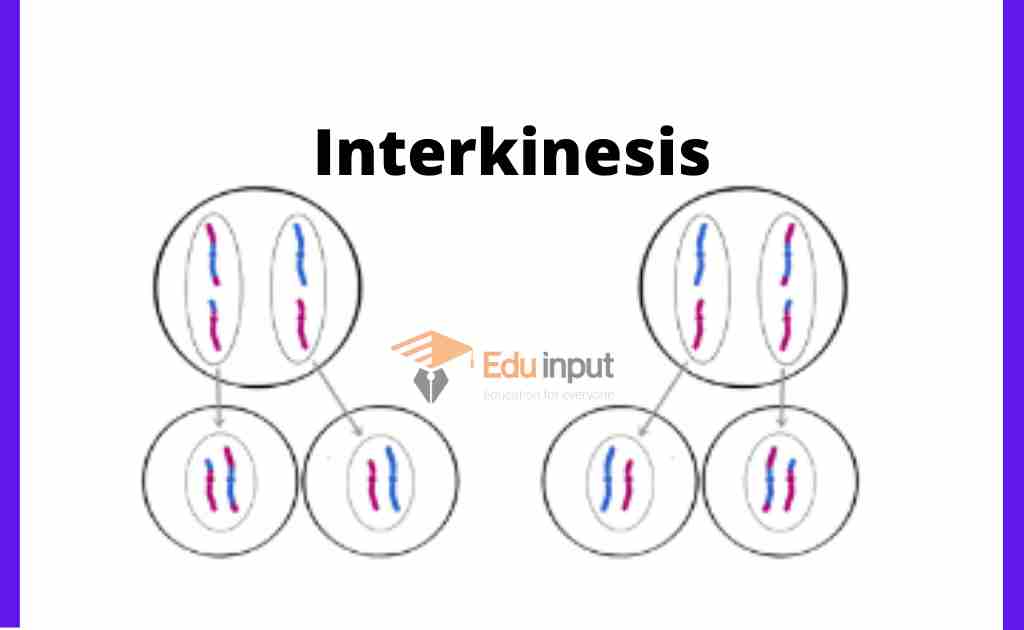
The progression to the second division of the nucleus is called interkinesis. The DNA does not replicate during interkinesis.
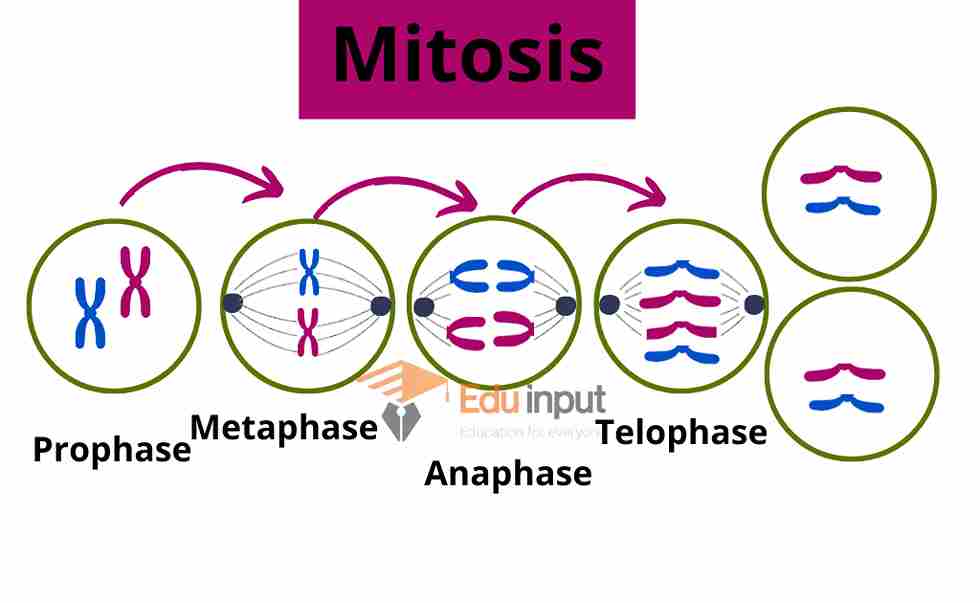
The second meiotic division resembles an ordinary mitotic division. Meiosis II is divided into sub-stages. The sub-stages of meiosis are just like the stages of mitosis. The number of chromosomes has been reduced by half. The phases are
- Prophase II
- Metaphase II
- Anaphase II
- Telophase II
The final products of these divisions of meiosis are four haploid cells. These cells finally form gametes (sex cells).
There is small interphase in two daughter cells after telophase I. But replication of chromosomes does not take place during this interphase.
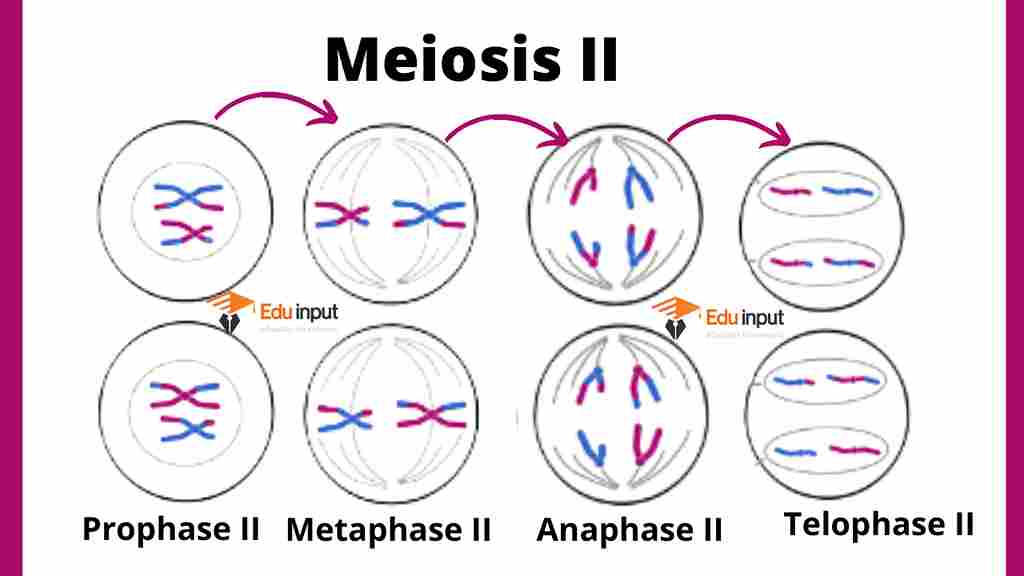
Prophase II
The chromosomes condense and the mitotic apparatus appears.
Metaphase II
The chromosomes are arranged at the equators.
Anaphase II
The sister chromatids of the chromosomes move towards the pole.
Telophase II
The chromosomes de-condense. Cytokinesis takes place. Thus each cell divides and forms four haploid daughter cells.
Importance of Meiosis
Meiosis is important because of some significant processes that take place during meiosis. These are;
Variations
Two significant processes happen to cause variations.
Crossing over
The parental chromosomes exchange segments with each other during crossing over others. It results in a large number of re-combinations.
Random assortment of chromosomes
The separation of homologous chromosomes is random during anaphase. It gives a large variety of gametes.
Both these phenomena cause variations and modifications in the genome. These variations are individual specific, particular, and unique in their characteristics. Even the progeny of every parent, i.e. Brothers and sisters are not identical to each other.
A Constant number of chromosomes in each generation
Meiosis takes place during sexual cell (gamete) formation and spore formation in plants. Thus it reduces the number of chromosomes to one-half in each gamete or spore.
The original number of the chromosome is restored after fertilization. So it maintains chromosome number constant generation after generation. The chromosome number will become double after every generation without meiosis.
Related FAQs
What is meiosis?
Meiosis is a type of cell division in which the number of chromosomes remains half in daughter cells.
Where does meiosis occur?
Meiosis occurs in specialized cells of the ovaries and testes.
What are the steps of Meiosis I?
Meiosis is the reduction phase where the diploid cell becomes haploid. It has the following stages;
Prophase II
Metaphase II
Anaphase II
Telophase II
Why Meiosis is Important?
Meiosis is important because of some significant processes that take place during meiosis. Crossing over occurs during meiosis causes variation and increases the diversity of genetic makeup.
What is Syngamy?
The fusion of gametes is called syngamy. Both gametes contribute half of the genetic information to the zygote.





Leave a Reply