What is Cell Death?-Apoptosis and Necrosis
Cell death is a natural part of life. It helps us eliminate unhealthy cells and prevents diseases from spreading. Necrosis and apostasies are types of cell death. Cells in an organism depend upon various extracellular and intracellular signals. These signals regulate and control the activities like cell division, pattern formation, differentiation, morphogenesis, and motility.
The fate of each cell is predestined. These fates are the future responsibilities of the cells. Even the death of the cell is programmed.
What Is Cell Death?
Cell death is the process of dying cells. In biology, cell death is defined as the irreversible cessation of cellular functions. The term was coined by Dr. Robert Adelberg in the early 1960s.
Cell death plays a critical role in maintaining tissue homeostasis. It also has important implications for human health and disease.
Cell death has the following importance:
1. Programmed cell death control of multicellular development of the body.
2. This cell death may remove the entire structure (e.g. the tail of developing human embryos) or part of the structure (e.g., the tissue between developing digits).
3. Most of the neurons in the human body die during development. So cell death also controls the number of neurons.
Control Of Cell Death
Two fundamentally different factors control cell deaths in multicellular organisms.
These two factors are:
The cell commits suicide in the absence of survival signals (trophic factors) The cells are murdered by killing signals from other cells.
Types of Cell Death
There are two types of processes which causes the death of cells:
- Apoptosis
- Necrosis
Apoptosis
Apoptosis is a Greek word that means dropping off or falling off. Apoptosis is a natural cell death process that occurs during development and growth. Apoptosis is also responsible for eliminating unwanted cells from our bodies.
The term apoptosis was coined by Dr. Bruce Beutler in 1972. He defined apoptosis as “programmed cell death”. In other words, apoptosis is a normal part of life and helps us eliminate damaged or harmful cells.
Apoptosis is a type of programmed cell death that happens in response to stress signals. This form of cell death is often associated with aging, cancer, neurodegenerative diseases, and autoimmune disorders.
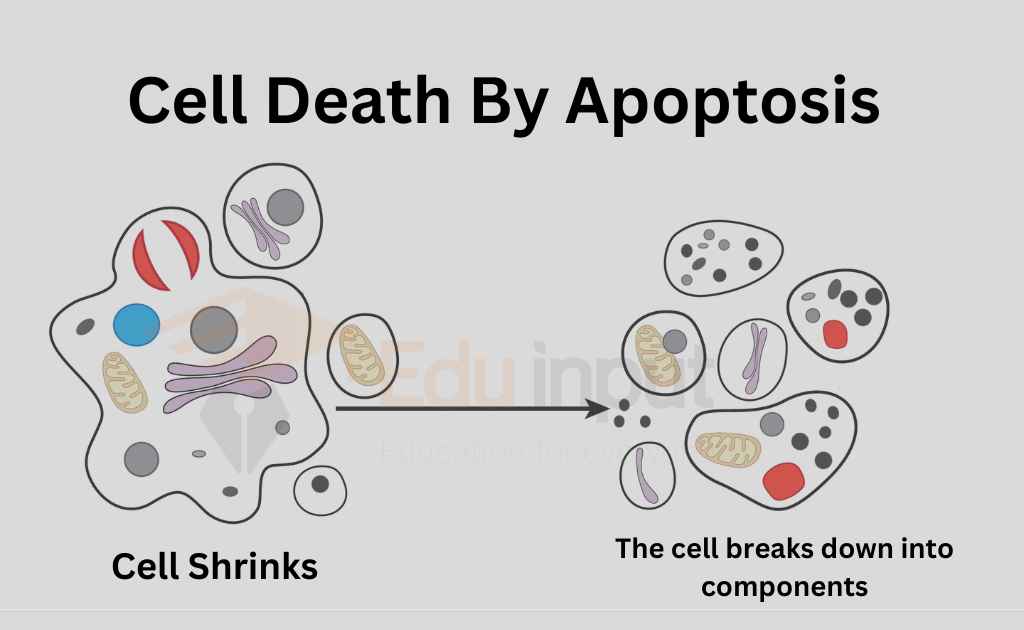
The events of the internal program and sequence of morphological changes by which cell commits suicide are collectively called apoptosis. The dying cells shrink during apoptosis. It then condenses and ultimately split up.
Thus it releases small membrane-bounded apoptotic bodies. These bodies are phagocytosed by other cells. The intracellular constituents of these bodies are not released freely in the extracellular atmosphere. This constituent may have deleterious effects.
Necrosis
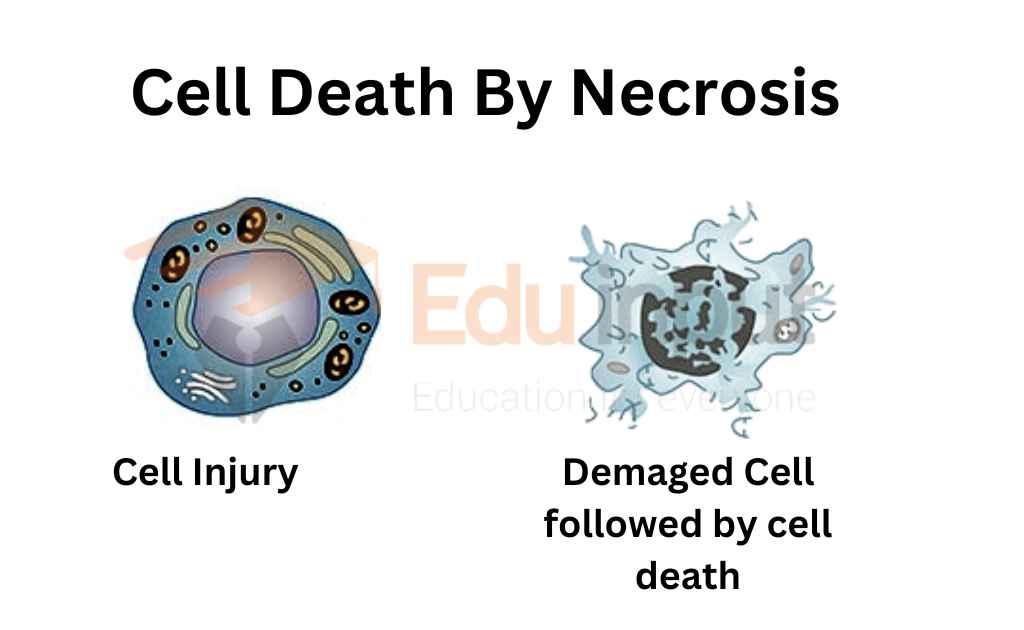
The cell death due to tissue damage is called necrosis. During this process, the typical cell swells, bursts, and releases the intracellular contents.
Necrosis is a process that causes cells to die off. The body usually tries to fight against necrosis by producing antibodies, but sometimes these fail to work properly. This leads to the death of the affected tissue. It occurs when cells stop dividing and start dying. When the immune system fails to recognize the dead cells, they become necrotic.
Necrosis is caused by damage to the tissues due to infection, trauma, cancer, or other diseases. It can occur anywhere in the body, but it is most common in the skin, bones, joints, heart, lungs, liver, kidneys, intestines, and brain.
Frequently Asked Questions-FAQs
What does it mean by cell death?
The fate of each cell is predestined. These fates are the future responsibilities of the cells. Even the death of the cell is programmed. Cells that are no longer needed or are on threat of death and can cause infection to lead to programmed death to prevent infection.
Where do dead cells go?
A dead cell is sent to the lysosome where the digestive enzyme disgests these components and makes them available for next use.
What is Apoptosis?
Apoptosis is a Greek word that means dropping off or falling off. Apoptosis is a natural cell death process that occurs during development and growth. Apoptosis is also responsible for eliminating unwanted cells from our bodies.
What is Necrosis?
The cell death due to tissue damage is called necrosis. During this process, the typical cell swells, bursts, and releases the intracellular contents.



Leave a Reply