Plastids -Definition, Importance and Diversity in Plant Cells
What are Plastids?
The membranous bound and pigment-containing bodies present in the cell are called plastids. Plastids are special structures found in certain eukaryotic cells, including plants, algae, and some other organisms. They are responsible for various important functions, such as photosynthesis and storage of important molecules.
They are present in the cytoplasm. Chloroplasts and other plastids of plant cells contain their genome’s double-stranded DNA.
That is involved in the genetic anchoring of at least some of these processes, such as photo-autotrophy. DNA present in chloroplast and mitochondria differ from the DNA (heredity material) found in the nucleus.
Discovery of Plastids
Plastids, like chloroplasts in plants, are thought to have originated from engulfed cyanobacteria in an ancient event. Plastids are originated through a process called endosymbiosis. In this process, one organism engulfs and incorporates another organism into its cells.
There are two main types of plastids: primary plastids and secondary plastids.
Primary plastids arose from a single endosymbiotic event where a type of bacteria called cyanobacteria was engulfed by a primitive eukaryotic organism, eventually evolving into plastids found in plants and algae.
Secondary plastids are more complex, with additional membrane layers, and formed when an organism with primary plastids is itself engulfed by another organism. The origin of secondary plastids is debated, with the chromalveolate hypothesis. This suggests a single endosymbiosis event with a red alga, while the independent acquisition hypothesis proposes multiple endosymbiosis events with different eukaryotes.
Types of Plastids
Here are the main types of plastids:
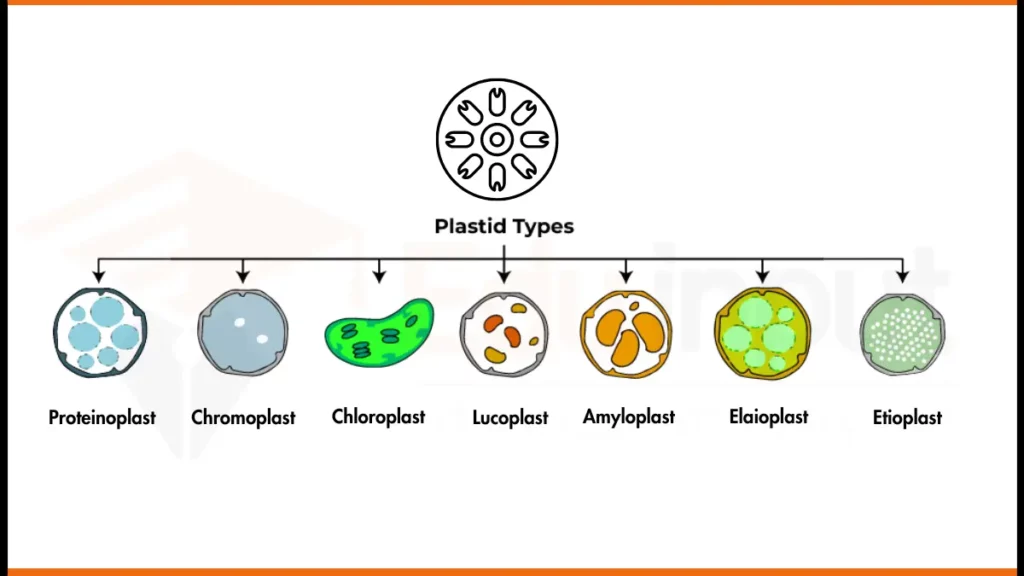
1. Leukoplasts
Leukoplasts are non-pigmented (colorless) plastids.. Their shapes may be triangular, tubular, or some other. They are found in various plant cells, such as root cells, tubers, and non-photosynthetic tissues. They act as storage organelles for starch, lipids, and protein reserves.
2. Chloroplasts
Chloroplasts are the most common type of plastids. They are found in the cells of green plant tissues. They contain chlorophyll and other pigments that make plants able to carry out photosynthesis and convert light energy into chemical energy.
3. Chromoplasts
Chromoplasts give color to plants other than green. They are responsible for the different colors found in many fruits, flowers, and other plant structures. They accumulate and store carotenoid pigments, such as carotenes and xanthophylls. These carotenoid pigments contribute to the yellow, orange, and red hues.
4. Amyloplasts
Amyloplasts are specialized plastids found in certain plant cells, such as tubers, roots, and seeds. They act as energy reserves for the plant. They are involved in the synthesis and storage of starch granules.
5. Elaioplasts
Elaioplasts are plastids involved in the synthesis and storage of lipids (fats) in plant cells. They are commonly found in seeds, fruits, and other lipid-rich plant tissues. They are also involved in energy storage in plants.
6. Proteinoplasts
Proteinoplasts are a type of plastid found in certain plant cells. They are primarily responsible for the synthesis and storage of protein reserves. They are commonly found in seeds and other storage tissues.
Importance Of Plastids In Plant Cells
Plastids are multifunctional organelles that are essential for plant survival, growth, reproduction, and adaptation to various environmental conditions. Their various roles show their importance in maintaining the overall health and productivity of plants. Here is why Plastids are important for plant cells:
- Photosynthesis – Chloroplasts are the site of photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert light energy from the sun into chemical energy in the form of carbohydrates. This process is crucial for the plant’s survival and growth, as well as for sustaining life on Earth by producing oxygen and food.
- Storage of nutrients – Plastids like amyloplasts, elaioplasts, and proteinoplasts serve as storage organelles for important nutrients such as starch, lipids, and proteins, respectively. These stored nutrients can be used by the plant during periods of growth, development, or stress.
- Pigment production – Chromoplasts are responsible for the synthesis and accumulation of carotenoid pigments, which contribute to the vibrant colors of fruits, flowers, and other plant structures. These pigments not only attract pollinators and seed dispersers but also have antioxidant properties and potential health benefits.
- Metabolic pathways – Plastids are involved in various metabolic pathways, including the synthesis of amino acids, fatty acids, and other important biomolecules essential for plant growth and development.
- Environmental responses – Plastids play a role in plant responses to environmental cues, such as light intensity, temperature, and stress conditions. They can adjust their structure, composition, and functions accordingly. It contributes to the plant’s ability to adapt and survive in different environments.
- Inheritance – In some plant species, plastids can be inherited from both maternal and paternal lineages. It contributes to the genetic diversity and potential adaptations of offspring.
Where are plastids found?
Primary plastids are found in Algae and Plants. Secondary plastids are found in phytoplankton (Diatoms).
Do all plastids have DNA?
Chloroplast is a type of plastid that possesses its genomic material.
Which animals have plastids?
Generally, animal cells do not have chloroplast. But a group of multicellular animals called sea slugs contain plastids. They feed on saponaceous algae.
Do plastids contain RNA?
Plastids possess RNA polymerase complexes.

 written by
written by 





Leave a Reply