The skin of Birds-Features and Structure
The skin of birds is called plumage. This refers to the feathers covering the bird’s head, neck, back, wings, tail, legs, feet, and breast.
It is estimated that there are more than 300 different types of bird feathers, with each type of feather having its unique shape and color. There are two main types of feathers on a bird’s body:
Features Of Bird’s Skin
The skin of birds shows many reptilian features. It has the following features
1. It has no epidermal glands. The only epidermal gland of birds is uropygial or preen gland.
2. The epidermis is thin over most of the bird’s body. It is only two or three cell layers thick. Therefore, birds are also called thin-skinned, animals
3. The outer layer is keratinized. It is often quite soft.
4. Epidermis contains feathers. Feathers are the most prominent parts of the epidermis. Feathers are derived from the scales of reptilian ancestors. These are the most complex keratinized epidermal structures.
5. The dermis of birds is similar to the dermis of reptiles. It contains blood, lymphatic vessels, and nerves. It also contains sensory bodies. These bodies are epidermally derived Air spaces are part of the avian respiratory system. These air spaces extend into the dermis. The air spaces are involved in thermal regulation.
6. Smooth-muscle fibers are present in the dermis. They have a complex arrangement. They are associated with feathers. They control the position of the feathers. Feather position is important in thermal regulation, flying, and behavior.
7. Aquatic birds may also have fat deposits in the hypodermal layer. It stores energy and insulates the body.
Structure of Skin of Birds
Avian integument consists of an outer layer of dead cells and an inner layer of living cells. The outer layer is called the stratum corneum, and the inner layer is called the dermis. Both layers contain hair follicles, sweat glands, blood vessels, nerve endings, and lymphatic vessels. The stratum corneum protects the bird from injury and dehydration.
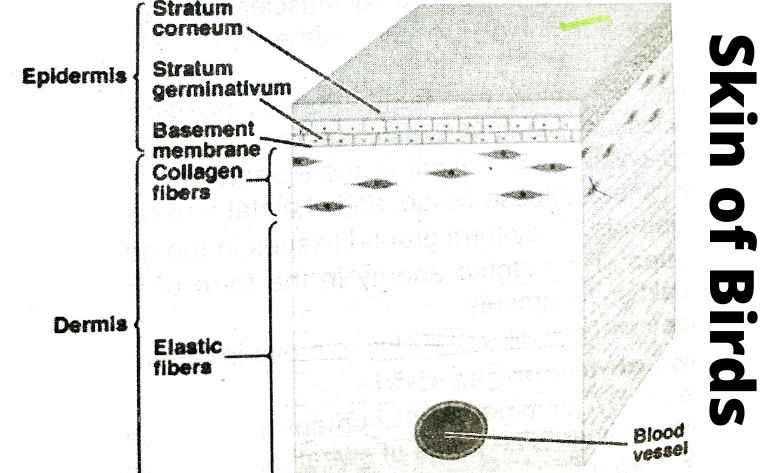
Birds also produce oils and waxes through the sebaceous gland. These substances lubricate the feathers and keep them smooth. They also help waterproof the feathers. The dermis contains collagen fibers and elastin fibers. Collagen provides strength to the dermis, while elastin gives flexibility to the dermis.



Leave a Reply