Transport Across Plasma Membrane
Cytoplasm communicates with the outer environment by the means of the cell membrane. This communication or movement of molecules occurs through different mechanisms. Transport across plasma membrane occurs through diffusion, facilitated diffusion, osmosis, and many others.
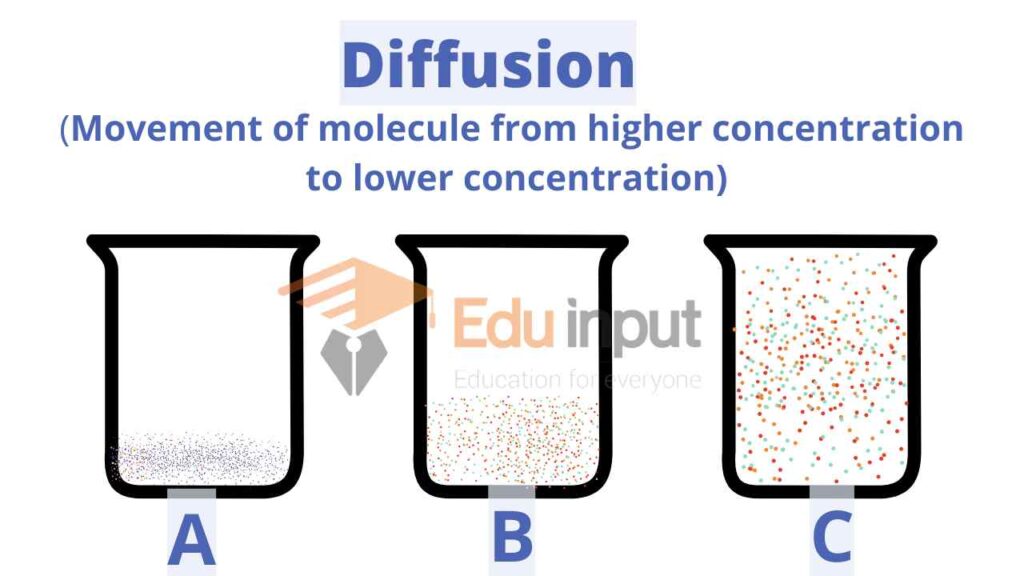
Diffusion:
The movement of molecules in or outside the cell from higher concentration to lower concentration is called simple diffusion.
In diffusion, the molecules move randomly. They keep moving randomly until they are distributed in the cell evenly. They come in a state of dynamic equilibrium. Most of the short-distance transport takes place by simple diffusion.
Facilitated Diffusion:
The movement of molecules through the assistance of protein molecules from higher concentration to lower concentration is called facilitated Diffusion.
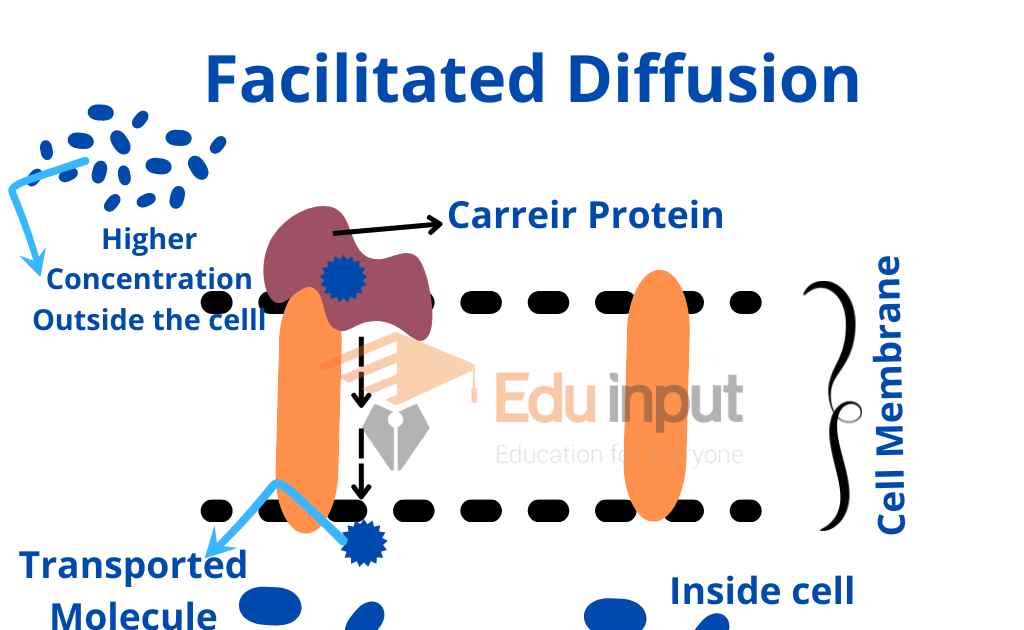
Polar molecules are insoluble in lipids. So their diffusion takes place by the means of protein channel pores. The protein channels provide a pathway for the movement of specific molecules across the membrane. Thus these molecules do not come in contact with the hydrophobic layer.
Large molecules and lipid insoluble molecules need assistance for movement which is provided by protein carriers. It does not need energy. A carrier protein binds with a molecule in the plasma membrane. It is transported from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.
Osmosis:
The diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane from higher concentration to lower concentration is called osmosis.
Osmosis is a particular type of diffusion.
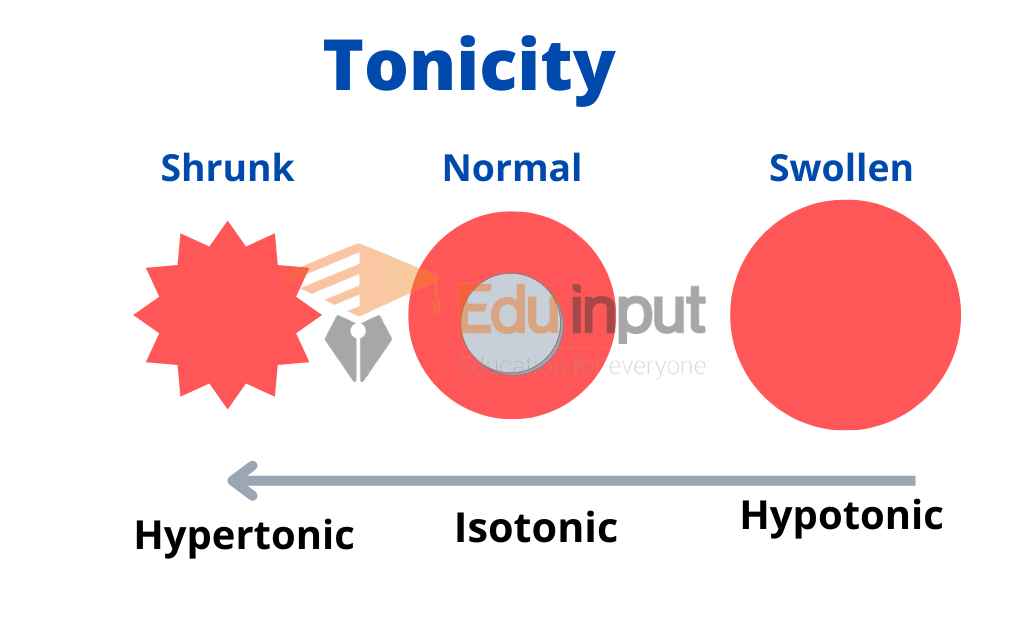
What is Tonicity?
The relative concentration of solutes in the water inside and outside the cell is called tonicity.
There are three different types of tonicity based on solvent and solute concentration.
(a) Isotonic solution:
The concentration of solute and solvent is the same inside and outside the cell.
(b) Hypertonic solution:
When the solute concentration is higher outside the cell than inside, this is called a hypertonic solution.
(c) Hypotonic solution:
In this case. The solute concentration is lower outside the cell than inside.
Filtration:
Filtration is a process that pushes small molecules across selectively permeable membranes by using hydrostatic pressure.
What is hydrostatic pressure?
The pressure generated due to water in the cell is called hydrostatic pressure.
For example, in the kidney blood pressure forces water and dissolved wastes out of the blood vessels and into the kidney tubules. This is the first step in urine formation.
Active transport:
The movement of molecules from lower concentration to higher concentration by the expenditure of energy is called active transport.
It takes place against the concentration gradient. That’s why movement against the concentration gradient requires ATP energy. The active transport process resembles facilitated diffusion. But this carrier protein in the plasma membrane uses ATP to move the molecules against a concentration gradient.
The sodium-potassium pump is an example of active transport.
Endocytosis:
The movement of bulky material into the cell by the formation of the vesicle is called endocytosis.
The movement of molecules does not take place individually. Different types of molecules like cholesterol are brought into cells in this manner.
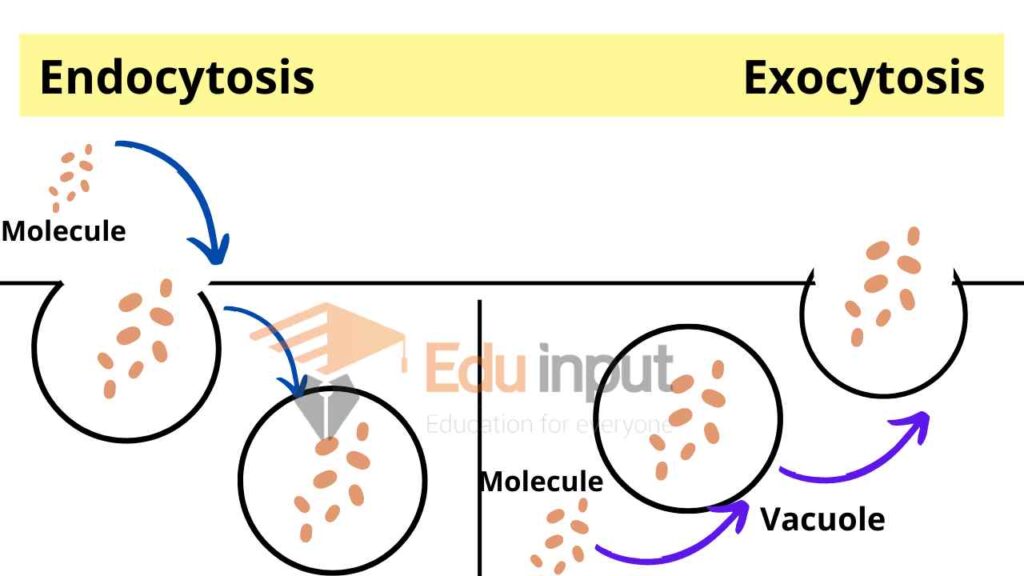
Exocytosis:
The removal of cell secretions from the cells by out folding is called exocytosis. The Golgi apparatus box up cholesterol, proteins, and other molecules into vesicles for secretion. These secretory vesicles fuse with the cell membrane and release their constituents into the outer environment. This process adds new membrane material. This material replaces the plasma membrane lost during endocytosis.
Frequently Asked Questions-FAQs
What are the modes of transport across the cell membrane?
There are the following modes of transport across the cell membrane;
Diffusion
Facilitated diffusion
Active transport
Osmosis
Exocytosis (type of active transport)
Endocytosis (type of active transport)
What id diffusion?
The movement of molecules from higher concentration to lower concentration is called diffusion.
What is Active Transport?
The movement of molecules from lower concentration to higher concentration by the usage of energy.
What is the difference between active transport and passive transport?
Active transport uses energy to transport molecules, whereas passive transport does not use energy for the movement of the molecule.

 written by
written by 



Leave a Reply