Transverse Waves in Electromagnetic Spectrum
Electromagnetic waves are a type of transverse wave. It means that the electric and magnetic fields within the electromagnetic wave oscillate in a plane that is perpendicular to the direction in which the wave is moving.
What is Transverse wave?
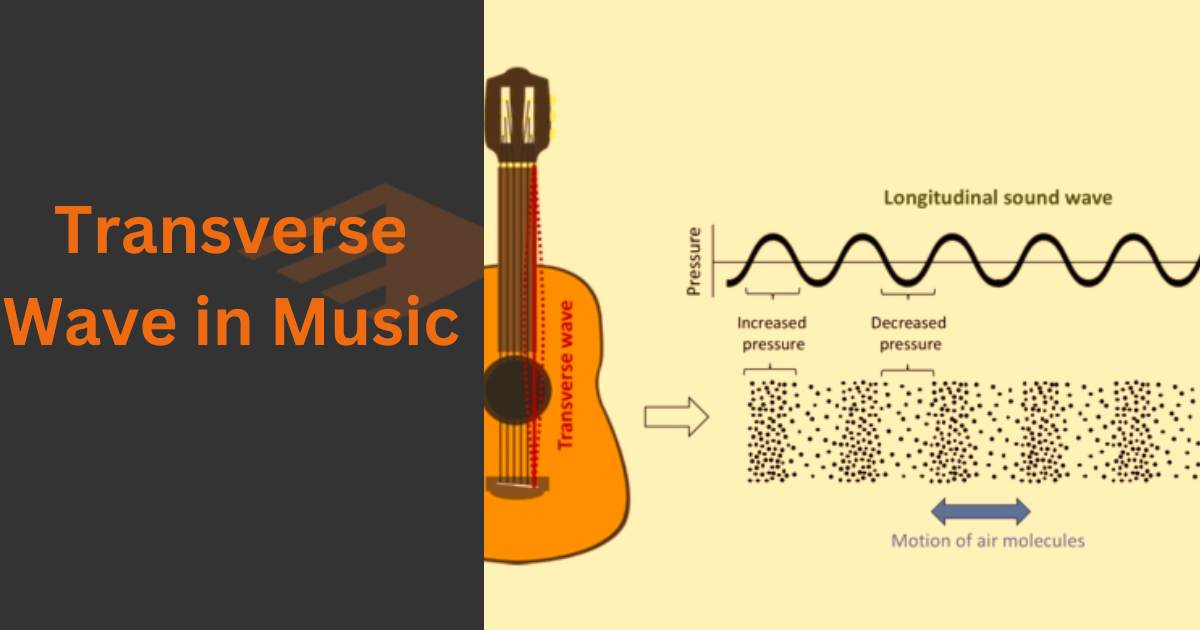
Transverse waves are a type of wave in which the particles of the medium vibrate perpendicular to the direction of the wave propagation.
Transverse waves possess distinct characteristics that differentiate them from other types of waves. Firstly, they exhibit oscillations perpendicular to the direction of energy transfer. This is in contrast to longitudinal waves, where the oscillations occur parallel to the direction of energy transfer.
Examples of transverse waves include the motion of a string when plucked or the ripples on the surface of the water.
What is an Electromagnetic Spectrum?
The electromagnetic spectrum refers to the continuum of all electromagnetic waves, ranging from low-frequency radio waves to high-frequency gamma rays. It has a vast range of wavelengths and frequencies, each corresponding to a unique region within the spectrum. These regions include radio waves, microwaves, infrared waves, visible light waves, ultraviolet waves, X-rays, and gamma rays.
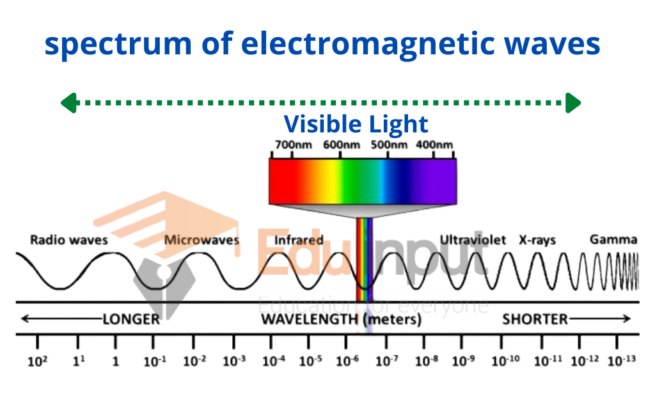
Different regions of the electromagnetic spectrum have distinct properties and applications. Radio waves, for instance, are used for communication and broadcasting, while X-rays find applications in medical imaging and scientific research. Understanding the characteristics and applications of each region is crucial for various technological advancements and scientific discoveries.
Types of Transverse Waves in the Electromagnetic Spectrum
Radio Waves
Radio waves have the longest wavelengths and lowest frequencies within the electromagnetic spectrum. They are widely used for broadcasting and communication, including television and radio signals. Additionally, radio waves are essential in wireless technologies like Wi-Fi and cellular networks.
Microwaves
Microwaves have shorter wavelengths and higher frequencies than radio waves. They find applications in microwave ovens, satellite communications, radar systems, and wireless communication technologies.
Infrared Waves
Infrared waves have longer wavelengths and lower frequencies than visible light waves. They are commonly used in heat detection, remote controls, and thermal imaging devices. Infrared radiation is also utilized in medical applications, such as infrared therapy and non-invasive diagnosis.
Visible Light Waves
Visible light waves are the portion of the electromagnetic spectrum that humans can perceive. They range from violet to red, with each color corresponding to a specific wavelength and frequency. Visible light is crucial for vision and plays a vital role in photography, optical communication, and various lighting applications.
Ultraviolet Waves
Ultraviolet waves have shorter wavelengths and higher frequencies than visible light waves. They have numerous applications, including sterilization, detection of counterfeit money, and forensic investigations. However, excessive exposure to ultraviolet radiation can be harmful to living organisms.
X-rays
X-rays have even shorter wavelengths and higher frequencies than ultraviolet waves. They are widely used in medical imaging, such as X-ray radiography and computed tomography (CT) scans. X-rays also have applications in materials testing and airport security scanning.
Gamma Rays
Gamma rays have the shortest wavelengths and highest frequencies within the electromagnetic spectrum. They are produced by radioactive materials and nuclear reactions. Gamma rays are used in cancer treatment (radiotherapy) and industrial applications like sterilization and imaging of dense materials.
Related FAQs
What are 4 types of transverse waves?
The four types of transverse waves are:
Light waves
Radio waves
X-rays
Gamma rays
What are transverse electromagnetic waves examples?
Transverse electromagnetic waves include examples such as radio waves, microwaves, infrared waves, visible light waves, ultraviolet waves, X-rays, and gamma rays.
Why is the electromagnetic spectrum a transverse wave?
The electromagnetic spectrum is considered a transverse wave because the electric and magnetic fields within the wave oscillate perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation.

 written by
written by 




Leave a Reply