Verb-Definiton, Types, Examples, and Usage in Sentences
What is Verb?
A word which shows an action, state, condition, possession or presence of a thing/person called verb.
A verb is an important part of speech that tells us what someone or something does. In simple words, if you ever wonder what is verb, it is a word that shows an action like run or eat, or a state like is or seems. The most basic verb definition is that it helps us understand what is happening in a sentence.
So, what is a verb? It is the word that tells us what is happening. What are verbs? They are words like run, think, have, and is, each one helping us understand what someone is doing or what condition they are in. This clear definition of verb makes it easy to recognize verbs whenever you read or write.

What is Meaning Of Verb?
To understand verb meaning, it helps to know where the word comes from. The word “verb” comes from the Latin word “verbum”, which means “word.” In English, a verb is a part of speech that expresses the existence, action, or occurrence of a subject or an object. In simple terms, the verb word meaning is linked to what someone or something does or is.
When we talk about a verb with meaning, we refer to words like eat, sleep, write, or is, because each one shows an action or a state. So, verbs meaning actions or conditions are essential in every sentence. The verb is the heart of a sentence and forms an important part of the predicate, giving life and meaning to the subject.

What are Verb Examples?
Verbs are essential for making sentences meaningful. The use of verb in a sentence shows what the subject does, what condition it is in, or what it owns. To understand what are verb examples, we can look at how verbs appear in real sentences. Verb sentences help show actions, states, possession, and even the presence or absence of something. These verb examples make it easier to understand how verbs work in everyday language.
Here are some simple action verb examples, sentences, and other types of verbs in use:
- He is writing a letter. (Action)
- Karachi is a beautiful city. (State)
- She has a car. (Possession)
- There is milk in the jug. (Presence)
- There wasn’t milk in the jug. (Absence)
Each sentence shows how verbs give meaning and complete the idea in a sentence.
Verb Usage Rules
Here are some essential Verb Usage Rules:
| Rule Category | Description | Incorrect Example | Correct Example |
| Subject-Verb Agreement | The verb must match its subject in number (singular subjects take singular verbs; plural subjects take plural verbs). | The cat chase the mouse. | The cat chases the mouse. |
| Consistency in Tense | Maintain the same verb tense when describing actions within the same time frame or sequence. | She opened the door and sees him. | She opened the door and saw him. |
| Use Correct Form | Use the appropriate principal form of the verb (base, simple past, or past participle) for the sentence’s structure. | I have went to the store. | I have gone to the store. |
| Watch for Irregular Verbs | Pay attention to verbs whose past tense and past participle forms do not end in -ed. | He seed the ball and runned fast. | He saw the ball and ran fast. |
| Avoid Double Negatives | Using two negative words in the same clause creates a positive statement, often unintentionally. Use only one negative word. | I don’t have none of that candy. | I don’t have any of that candy. |
| Mindful of Verb Phrases | Ensure the helping verb (auxiliary verb) in a verb phrase agrees with the subject in number. | The students is studying hard. | The students are studying hard. |
| Use Modal Verbs Wisely | Use modal verbs (e.g., can, should, must, might) precisely to convey ability, necessity, possibility, or permission. | You must can finish the work today. | You can finish the work today. |
- Subject-Verb Agreement – The verb must agree with its subject in number (singular or plural). For example, “She runs” but “They run.”
- Consistency in Tense – Keep verb tenses consistent within the same time frame. Don’t shift randomly between past, present, and future tenses.
- Use Correct Form – Use the correct form of the verb for its context. For example, “I have gone” not “I have went.”
- Avoid Double Negatives – Two negatives make a positive, so avoid using two negatives in the same clause. For example, say “I don’t have any” instead of “I don’t have none.”
- Watch for Irregular Verbs – Some verbs have irregular past tense or past participle forms that don’t follow the regular -ed pattern. For example, “went” not “goed” for the past tense of “go.”
- Mindful of Verb Phrases – Verb phrases use helping verbs like “is,” “have,” “will” along with the main verb. Make sure these agree in number.
- Use Modal Verbs Wisely – Modal auxiliary verbs like “can,” “should,” “must” change the meaning, so use them precisely based on intended meaning.
Types of Verb
A verb is a part of speech that shows action, state, condition, possession, or presence. Understanding what is verb and its types helps identify how verbs work in sentences. There are several types of verbs used depending on their function.
1. What Are Action Verbs and Mental Action Verbs?
Action verbs express physical or mental actions. They describe what the subject is doing or what is happening. Mental action verbs show thinking, feeling, or deciding.

Examples Of Action Verbs In Sentences
- John ran to the park.
- She studied for the exam.
- The dog barked at the squirrel.
- I love reading books.
- They decided to go on a trip.
2. What Are Compound Verbs?
Compound verbs are formed by combining a verb with one or more auxiliary verbs (helping verbs) to create a single verb phrase.
Usage of Compound Verbs in Sentences
- I have been working on this project for two weeks. (present perfect continuous)
- They will be leaving for vacation tomorrow. (future continuous)
- She had already finished her homework. (past perfect)
- We should have studied harder for the exam. (modal + perfect)
- He might have been waiting for us there. (modal + perfect continuous)
3. What Are Linking Verbs, State Verbs, and Presence Verbs?
Linking verbs connect the subject to a word or phrase that identifies or describes the subject. They do not express action but relate to the subject’s state of being.

Usage of Linking Verbs in Sentences
- She is a teacher.
- The cake looks delicious.
- The weather became sunny.
- His answer seemed correct.
- The room felt warm.

4. Helping Verbs
Helping verbs assist the main verb to show tense, mood, or voice. Alone, they have no meaning. Helping verbs (also called auxiliary verbs) are used with main verbs to express tense, mood, or voice. They have no meaning on their own, but help form the complete verb.
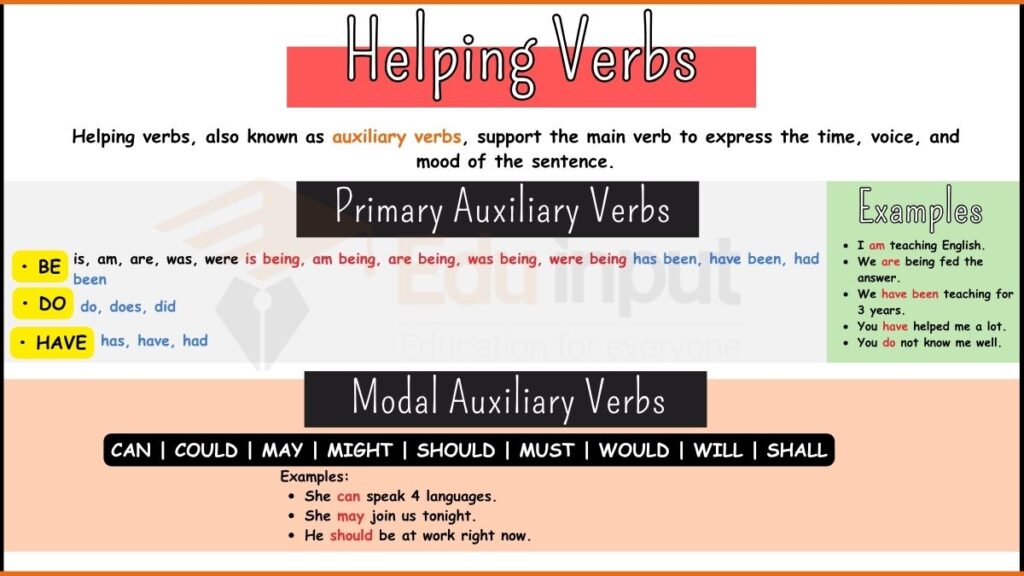
Usage in Sentences
- I have finished my homework.
- She will visit her grandparents.
- They should clean their room.
- We were playing outside.
- He can speak three languages.
5. What Are Phrasal Verbs?
Phrasal verbs are combinations of a verb and a preposition or adverb that have a meaning different from the individual words. They are idiomatic expressions.
Usage in Sentences
- She turned off the light.
- I ran into my old friend.
- They looked up the word in the dictionary.
- He put on his coat.
- We came across an interesting book.
6. What Are Regular Verbs?
Regular verbs form their past tense and past participle by adding “-ed” to the present tense form.
Usage in Sentences
- I walked to the store yesterday.
- She listened to the music carefully.
- They planned a surprise party.
- He watched a movie last night.
- We cleaned the house on the weekend.
7. What Are Irregular Verbs?
Irregular verbs don’t follow a set rule for forming the past tense and past participle. They have their own unique forms that need to be memorized.
Usage in Sentences
- She sang a beautiful song.
- They ate the entire cake.
- The glass broke when it fell.
- He forgot to bring his keys.
- I saw a shooting star last night.
8. What Are Stative Verbs?
Stative verbs describe a state or condition rather than an action. They express emotions, senses, possession, or mental states.
Usage in Sentences
- I like chocolate.
- She knows the answer.
- The room smells nice.
- They own a house.
- He appears tired.
9. What Are Modal Verbs?
Modal verbs express ideas such as ability, permission, possibility, obligation, or necessity. They are used with other verbs to modify their meaning.
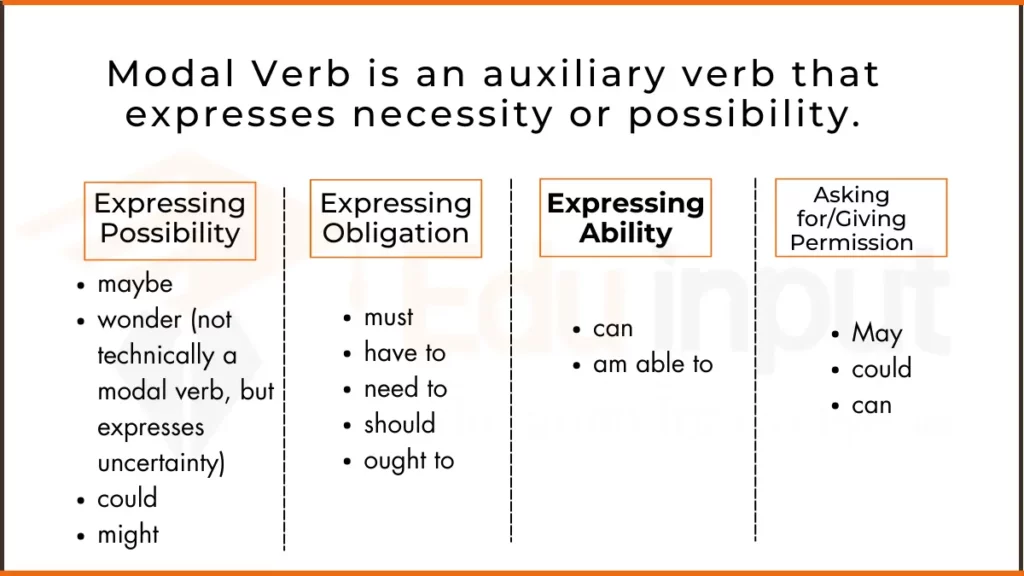
Usage in Sentences
- You can use my pen.
- We must follow the rules.
- They might visit us next week.
- I should study harder.
- He would like to travel abroad.

10. What Are Infinitive Verbs?
Infinitive verbs are the base form of verbs, usually preceded by “to.” They can function as nouns, adjectives, or adverbs in a sentence.
Usage of Infinitive Verbs in Sentences
- I want to learn a new language.
- His desire to succeed motivated him.
- They have the ability to adapt quickly.
- The best way to solve the problem is to work together.
- She promised to help us.
11. What Are Gerund Verbs?
Gerunds are the –ing form of verbs that function as nouns in a sentence.
Usage of Gerund Verbs in Sentences
- Reading is one of her hobbies.
- He enjoys hiking in the mountains.
- Cooking requires patience.
- Swimming is a great exercise.
- They discussed starting a new business.
12. Participle Verbs
Participles are verb forms that function as adjectives. They can be present participles (-ing) or past participles (-ed, -en, -d, -t, -n).
Usage Participle Verbs in Sentences
- The barking dog woke me up. (present participle)
- The broken vase was on the floor. (past participle)
- The running stream was refreshing. (present participle)
- She ate the baked cookies. (past participle)
- The falling leaves covered the ground. (present participle)



Leave a Reply