Noun-Definiton, Rules, Types, And Usage in Sentences
What is a Noun?
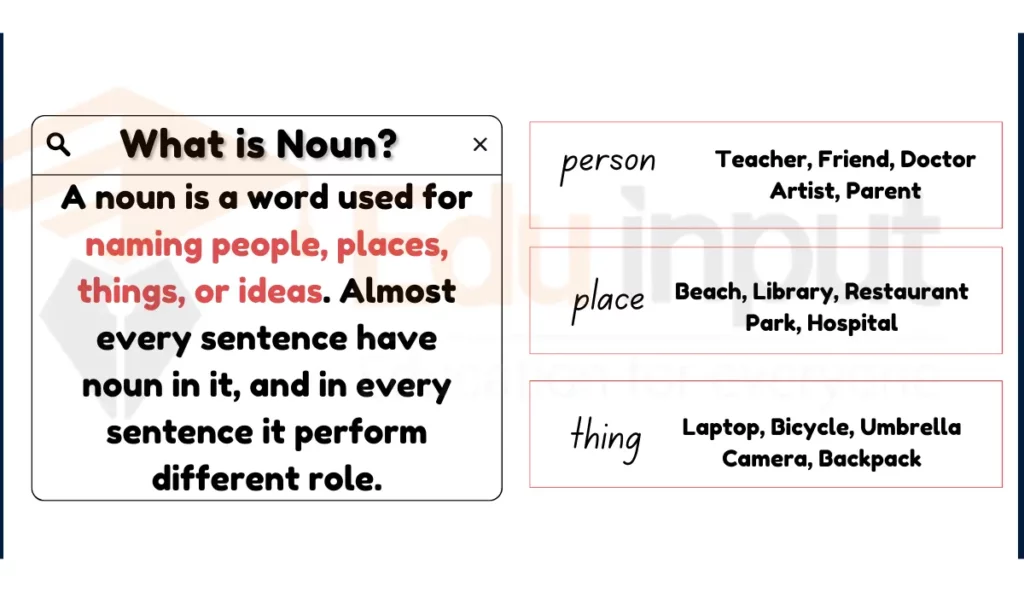
A noun is a word used for naming people, places, things, or ideas. Almost every sentence have noun in it, and in every sentence it perform different role.
It can act as the subject, an indirect object, a direct object, a subject complement and an object complement. It can also function as verb and adjective.
Commonly Used Nouns
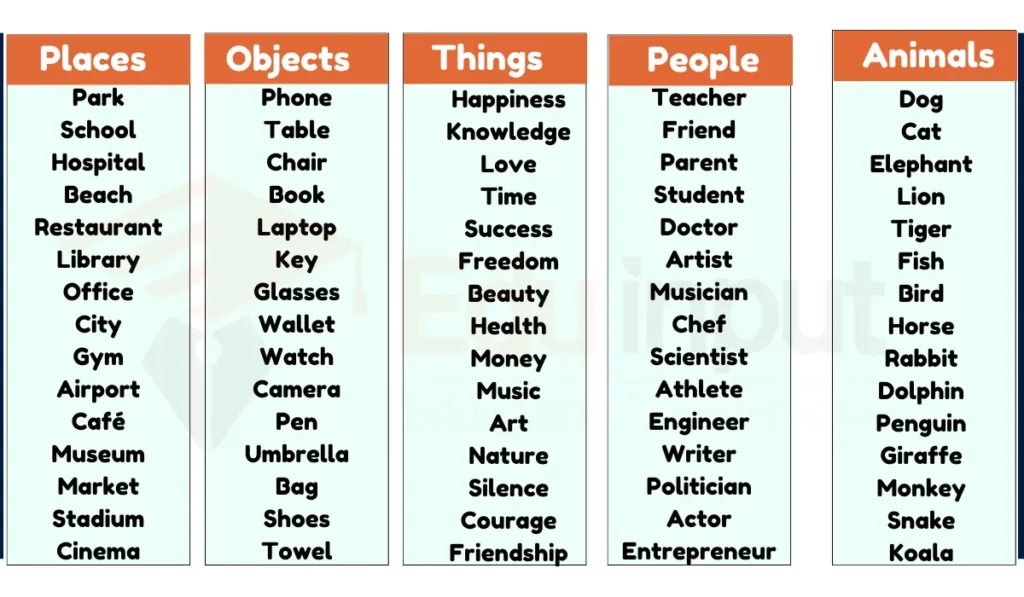
- Person – Mom, Dad, friend, teacher, athlete, singer, doctor, artist, neighbor, classmate.
- Places – Park, school, home, beach, city, mountain, forest, ocean, library, museum.
- Things – Book, pen, phone, car, bike, ball, shirt, hat, pizza, flower.
- Ideas – Love, happiness, fun, music, peace, freedom, kindness, courage, truth, imagination.
Types of Nouns
Here are the main types of noun:
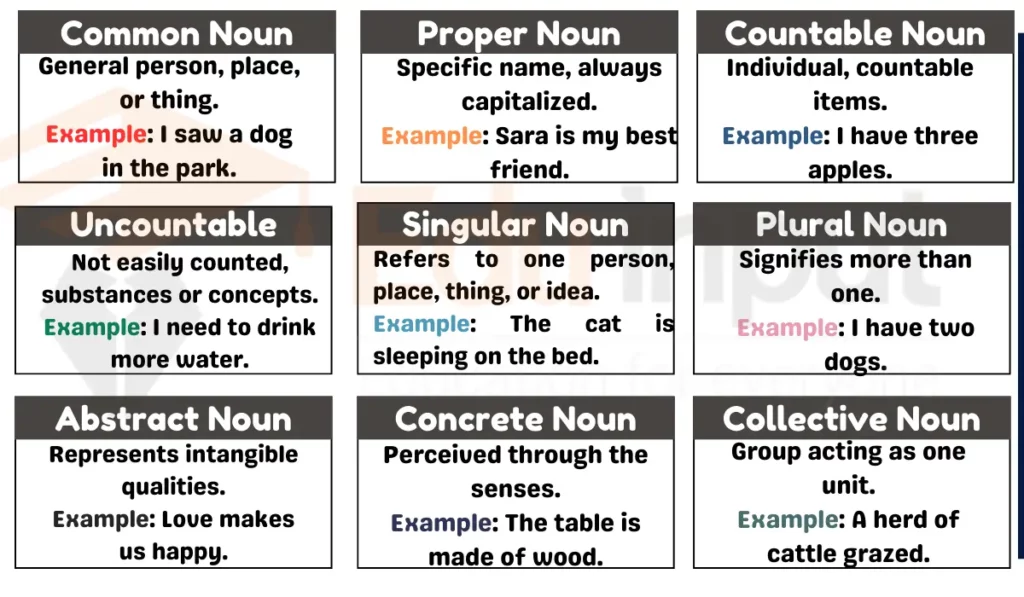
1. Common Noun
A common noun refers to a general, non-specific person, place, or thing. It refers to generic term. It is not capitalized unless it begins a sentence.
Example
- I saw a dog in the park.
- The book on the shelf is interesting.
- The city is busy with people.
2. Proper Noun
A proper noun is a specific and unique name given to a particular person, place, or thing. It always starts with a capital letter.
Example
- Sara is my best friend.
- We visited Paris during our vacation.
- Mount Everest is very tall.
3. Countable Noun
A countable noun refers to individual, distinct items that can be counted as discrete units.
Example
- I have three apples.
- There are five cars on the street.
- The teacher praised the students.
4. Uncountable Noun
An uncountable noun denotes something that cannot be easily counted as separate units, usually substances, concepts, or qualities. These type of nouns includes both abstract and concrete noun.
Example
- I need to drink more water.
- Knowledge is important for learning.
- The room has beautiful furniture.
5. Singular Noun
A singular noun refers to one person, place, thing, or idea.
Example
- The cat is sleeping on the bed.
- Earth is our home planet.
- An idea can be powerful.
6. Plural Noun
A plural noun signifies more than one person, place, thing, or idea. These nouns are made by adding ‘s’, ‘es’ and ‘ies’ to singular noun. Some noun remains same in their singular and plural form. Some noun in their plural form has totally different spelling.
Example
- I have two dogs.
- The mountains are beautiful.
- The concepts were interesting.
7. Abstract Noun
An abstract noun represents a quality, state, or concept that cannot be perceived through the senses.
Example
- Love makes us happy.
- Freedom is important for everyone.
- Happiness comes from small things.
8. Concrete Noun
A concrete noun refers to something that can be perceived through the senses.
Example
- The table is made of wood.
- A tree stands in the backyard.
- My phone fell and cracked.
9. Collective noun
A collective noun refers to a group of people, animals, or things considered as a single unit. It represents a collection of individuals, acting as one unit.
Example
- A herd of cattle grazed in the meadow.
- The team played exceptionally well in the tournament.
- A flock of birds filled the sky with their graceful flight.
10. Possessive Noun
A possessive noun indicates ownership or possession of a particular person, entity, or thing. It is formed by adding an apostrophe (‘), followed by an “s” (or just an apostrophe after plural nouns ending in “s”), to the noun.
Examples
- The dog’s collar was bright red.
- Maria’s car is parked in the driveway.
- The students’ books were neatly arranged on the shelf.
Noun usage in sentences
Noun can be used as different components of sentence. It can be used as subject, object, subject compliment and object compliment. Some nouns are multifunctional. They can be used as adjective and verb.
1. Noun as Subject
A noun can act as the subject of a sentence, indicating what the sentence is about and performing the action. When noun act as subject, it mostly begins the sentence.
Examples
- Dogs bark loudly in the park.
- Children enjoy playing in the snow.
2. Noun as Object
A noun can serve as the object of a verb, receiving the action of the subject. Here, the noun functions as the recipient of the action performed by the subject. It completes the meaning of the verb.
Examples
- She loves flowers.
- The chef cooked dinner for the guests.
3. Noun as Subject Complement
A noun can be used as a subject complement, providing additional information about the subject. It is often linked by a linking verb.
Examples
- The winner is John.
- The weather today seems perfect.
4. Noun as Object Complement
A noun can function as an object complement, giving more information about the direct object. . It is also linked by a linking verb.
Examples
- They declared him captain.
- She considers the movie a masterpiece.
5. Noun as Verb
Some nouns can be transformed into verbs. This involves using a noun to represent an action or process.
Examples
- I need a hammer to fix the shelf.(Noun)
- I’ll hammer the nail into the wall.(Verb)
6. Noun as Adjective
Nouns can function as adjectives when they modify or describe other nouns. This provides additional information about the noun they are associated with.
Examples
- The mountain is covered in snow. (Noun)
- We went on a mountain hike. (Adjective)

 written by
written by 


Leave a Reply