What is an Avometer?-History, Circuit, and Applications
What is an Avometer?
An avometer also known as an AVO meter is a portable electrical measuring instrument. It combines the functionalities of an ammeter, voltmeter, and ohmmeter. This versatile device allows users to measure direct current (DC), alternating current (AC), voltage, and resistance.
You can choose what you want to measure by using the function selector switch. For example, if you want to measure current, you set it to the current measuring mode. If you want to measure voltage, you set it to the voltage measuring mode. And if you want to measure resistance, you set it to the resistance measuring mode.
Also Read Difference Between Ohmmeter And Avometer
History of Avometers
The avometer has a rich history dating back to the early 20th century. It was invented by British engineer Donald Macadie in the 1920s. Macadie’s innovative design revolutionized electrical testing, providing a compact and portable solution for measuring current and voltage. Since then, Avometers has evolved significantly, incorporating digital technology and additional features.
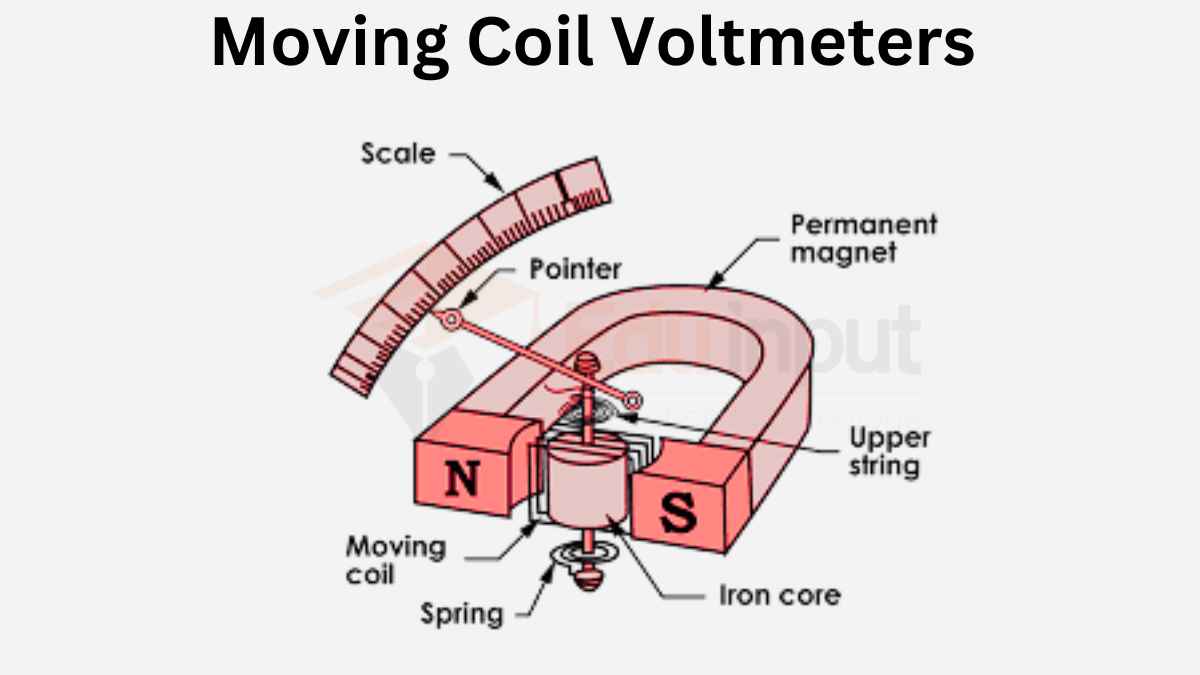
Avometer Circuit
An AVO meter primarily comprises a highly sensitive moving coil galvanometer. It can be transformed into a versatile instrument capable of measuring current, voltage, or resistance based on the specific circuit connected to the galvanometer through a function selector switch, commonly known as FS.
This switch allows users to select the desired measurement function, enabling the AVO meter to fulfill the role of an ammeter, voltmeter, or ohmmeter with different measurement ranges.

Avometer Functions
Avometers offer a range of functions, enabling users to perform diverse electrical measurements accurately. These functions typically include:
- Current Measurement: Avometers allow users to measure current flow in circuits, providing valuable information about the operational characteristics of electrical systems.
- Voltage Measurement: Avometers are capable of measuring both AC and DC voltage, aiding in the assessment of power supply levels and circuit conditions.
- Resistance Measurement: By measuring resistance, Avometers enable users to evaluate the integrity of components and identify faulty connections.
Types of Avometers
Avometers come in two main types:
- Analog Avometers
- Digital Avometers
Each type has its own set of advantages and considerations, catering to different user preferences and requirements.
Analog Avometers
Analog Avometers feature a needle or pointer that moves across a scale to indicate measurements. These traditional Avometers provide a visual representation of the measured quantity. They are often favored by experienced professionals for their simplicity, durability, and analog aesthetics.
Digital Avometers
Digital Avometers, on the other hand, utilize digital displays to present measurements numerically. These modern devices offer precise readings and enhanced functionality. They often come equipped with additional features such as auto-ranging, data hold, and backlighting for improved visibility.
How to Use an Avometer
Using an avometer requires adherence to safety precautions and an understanding of the various measurement techniques. Here are the essential steps for utilizing an avometer effectively:
Safety Precautions
Before proceeding with any electrical measurements, it is crucial to prioritize safety. Ensure that the power supply is switched off, and the circuits are de-energized. Wear appropriate personal protective equipment, such as insulated gloves, to minimize the risk of electrical shock.
Measuring Voltage
To measure voltage, connect the avometer’s probes to the appropriate points in the circuit. Select the voltage range suitable for the expected measurement and read the displayed value on the avometer’s scale or digital screen.
Measuring Current
When measuring current, the avometer is placed in series with the circuit. Carefully follow the avometer’s user manual for the correct current measurement setup. Select the appropriate range and record the measured value.
Measuring Resistance
To measure resistance, disconnect the component from the circuit or power source. Connect the avometer’s probes to the component’s terminals and set the avometer to the resistance measurement mode. Read the displayed resistance value on the scale or digital screen.
Applications of Avometers
The versatility of avometers makes them invaluable in various applications across multiple industries. Some common applications include:
Electrical Engineering
Avometers are extensively used by electrical engineers to troubleshoot electrical systems, test circuits, and validate the performance of components. These instruments aid in diagnosing faults, ensuring accurate measurements, and maintaining the integrity of electrical installations.
Automotive Maintenance
In the automotive industry, avometers play a vital role in diagnosing electrical issues in vehicles. From testing batteries and alternators to assessing wiring integrity, avometers assist technicians in identifying and resolving electrical problems efficiently.
Home Repairs
Avometers also find utility in home repairs and DIY projects. Whether you’re fixing a malfunctioning appliance or checking the continuity of wires, avometers empower homeowners to conduct electrical measurements safely and accurately.
Advantages of Avometer
- Versatility: Avometers combine multiple measurement functions into a single device, eliminating the need for separate instruments.
- Portability: Avometers are compact and portable, allowing users to carry them conveniently to different locations.
- Accurate Measurements: Avometers provide accurate and reliable measurements, ensuring precision in electrical testing and troubleshooting.
Disadvantages
- Learning Curve: Utilizing Avometers effectively may require some learning and practice, especially for beginners.
- Limited Specialized Features: Avometers may lack certain advanced features that are specific to specialized instruments used in niche applications.
Related FAQs
What is the use of Avometer?
The avometer is used for measuring electrical quantities such as current, voltage, and resistance in electrical circuits.
What is the full form of Avometer?
The full form of the Avometer is “Ampere-Volt-Ohm Meter.”
Why is the multimeter also called Avometer?
The multimeter is also called an avometer because it combines the functions of measuring current (amperes), voltage (volts), and resistance (ohms) in a single device.
What is the resistance measuring part of the Avometer?
The resistance-measuring part of the avometer is the component that allows the device to measure the resistance of electrical components or circuits.





Leave a Reply