Nucleic Acid- Discovery and Types Of Nucleic Acid
Nucleic acids are macromolecules that are present in all living organisms. That’s why they are also known as biopolymers. They are composed of nucleotides. Nucleic acids are polymers of a unit called a nucleotide.
Most of the nucleic acid (DNA) is present in the nucleus. Some of them are present in the cytoplasm (DNA in chloroplast and mitochondria). While RNA is present in the nucleolus, Ribosome, and cytosol. Ribosomes use this RNA in the synthesis of proteins.
They serve as the primary information-carrying molecules in the cell and make up the genetic material, Which is responsible for heredity. DNA is a type of nucleic acid that acts as hereditary material.

Discovery of Nucleic Acids
Nucleic acids have been characterized as large biological molecules that are made up of smaller subunits called nucleotides. Nucleic acids were discovered in 1868 by a Swiss physician named Friedrich Miescher while he was studying white blood cells.
He later determined that the substance he discovered was neither protein, lipid nor carbohydrate and therefore could be described as an altogether different type of biological molecule.
They were isolated from nuclei and they were acidic in nature. Therefore, they were named as nucleic acid.
Types of Nucleic Acids
Let’s class up this biochemistry content by striking out the buzzwords and replacing them with simpler, more effective terminology.
There are two types of nucleic acids, based on their chemical composition and their role in cells. One is called RNA. It is responsible for providing a blueprint of an organism. The other is called DNA, it contains a complete copy of the blueprints that reside in the cell’s nucleus (where all the important stuff in your body happens).
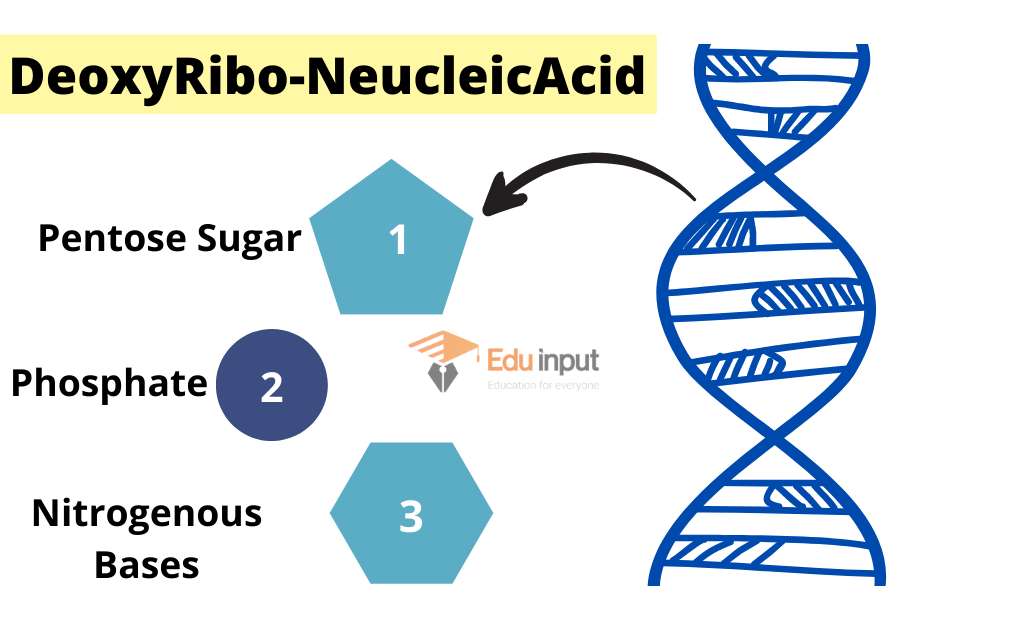
DNA or Deoxyribonucleic Acid
DNA is a type of Nucleic acid that is present in chromosomes, and the nucleus of the cells. A small amount of DNA is also present in mitochondria and chloroplast.
RNA or Ribonucleic Acid
RNA is a type of Nucleic acid that is present in the nucleolus, ribosome, Cytosol, and Cytoplasm. A small amount of RNA is also present in another part of the cell.
Structure of Nucleic Acid
Nucleic acids are complex substances. They are polymers of units called nucleotides.
DNA is composed of deoxyribonucleotides and RNA is composed of ribonucleotides.
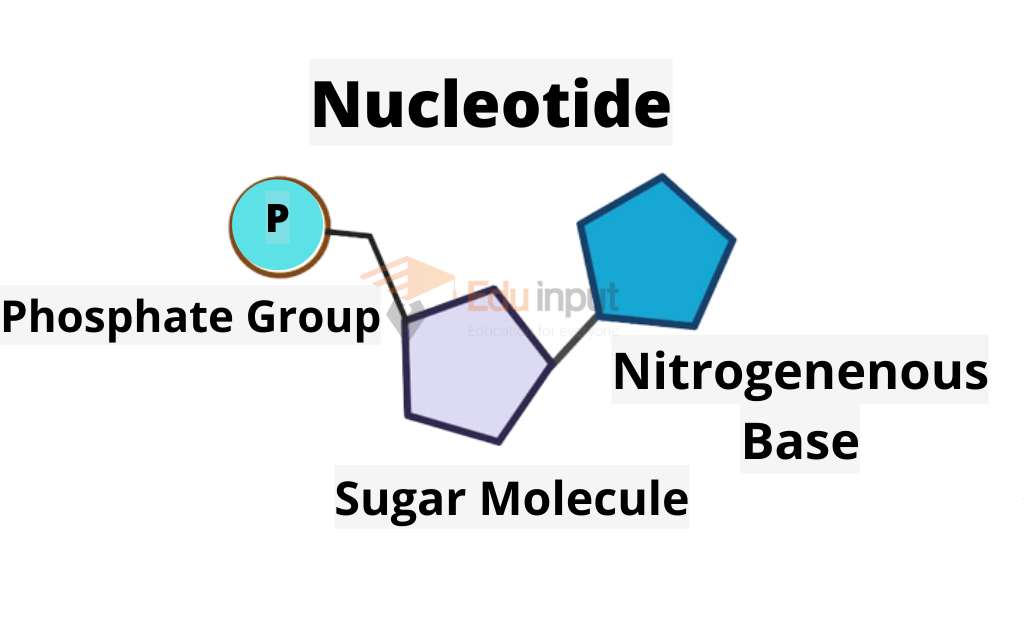
Nucleotides
Each nucleotide is made up of three subunits pentose sugar, nitrogen base and phosphoric acid.
1- Pentose sugar:
It is five-carbon monosaccharide. The nucleotides of RNA contain ribose sugar. On the other hand, the nucleotides of DNA contain deoxyribose sugar.
2- Nitrogen bases:
Nitrogen bases are of two types.
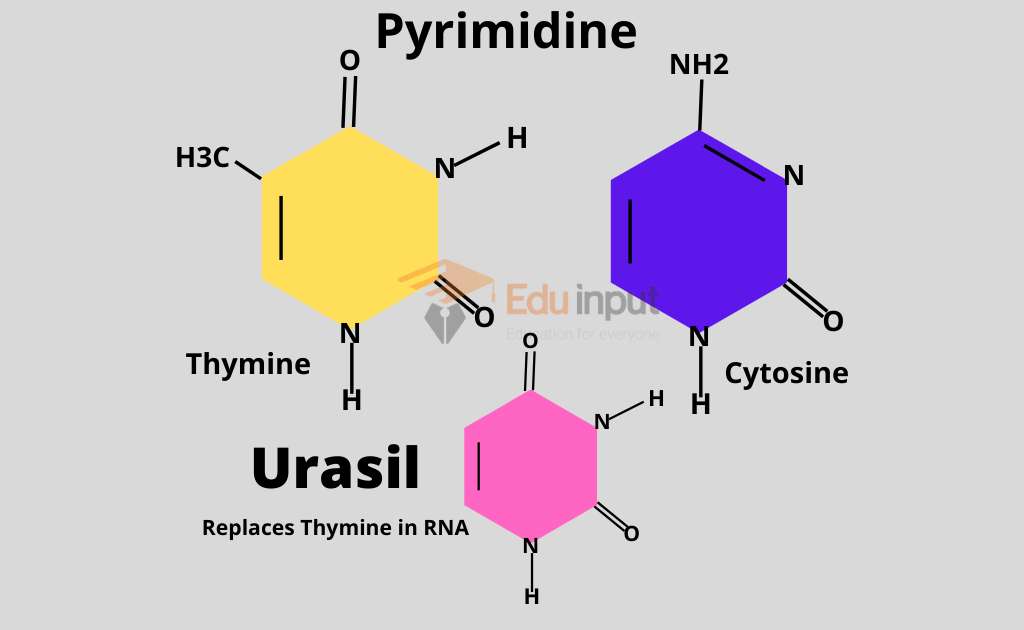
Pyrimidines:
These are composed of single ring. These are Cytosine (C), Thymine (T) and Uracil (U).
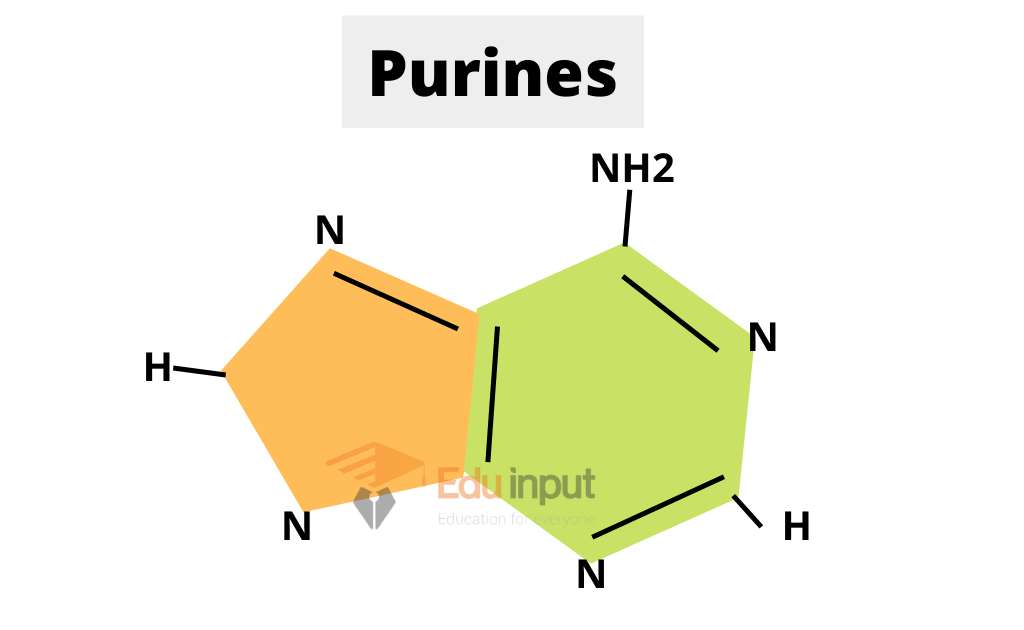
Purines:
These are composed of double rings. These are Adenine (A) and Guanine (G).
Difference Between DNA and RNA
Here are the basic differences between DNA and RNA.
| DNA | RNA |
| Double-stranded Molecule | Single-stranded Molecule |
| Contains Thymine | Contains Uracil |
| Responsible for hereditary characteristics | Responsible for protein synthesis |
| Present in nucleus, mitochondria and chloroplast | Present in nucleolus, ribosome and cytosol |
| Contains deoxy ribose sugar | Contains slightly different sugar which lacks an oxygen atom |
| Larger-sized (millions of nucleotides) | Small-sized ( hundreds of nucleotides) |
| DNA is a more stable molecule | Rna is stable only in alkaline solution. |
Related FAQs
What is Nucleic Acid?
Nucleic acids are macromolecules that are present in all living organisms. They are also known as biopolymers. They are composed of nucleotides. Nucleic acids are polymers of a unit called a nucleotide.
What are the types of Nucleic Acid?
There are two types of nucleic acids;
DNA or Deoxyribonucleic Acid
RNA or Ribonucleic Acid
What is a nucleic acid made of?
Nucleic acids are made up of nucleotides, consisting of nitrogenous bases, a phosphate group, and a sugar derivative.




Leave a Reply