What is Vegetative Propagation?-Definition, Types, And Examples
Vegetative propagation is a way of asexual reproduction in plants. It happens in vegetative parts of plants such as leaves, roots, and stems. It can occur by using the fragmentation and regeneration method. It may develop new organisms by regeneration and fragmentation of the vegetative parts of the plant body.
Regeneration occurs through mitosis. On the other hand, flowering plants reproduce sexually, and meiosis occurs in megaspore mother cells to produce new offspring.
Types and Examples of Vegetative Propagation
There are two types of vegetative propagation based on human interference.
- Natural vegetative propagation
- Artificial vegetative propagation
Natural Vegetative Propagation
Natural vegetative propagation occurs when plants grow and naturally develop new plants without any human intervention. It can be implemented by the growth of adventitious roots. Thus, new plants may come out from the roots, stems, and leaves of the parent plant body.
The vegetative plant structures that arise from the stem are known as rhizomes, tubers, runners, bulbs, etc. The plants propagate vegetatively through the following vegetative parts.
Vegetative Propagation through Stem
Runners grow horizontally above the ground. The buds are formed at the nodes of the runners.

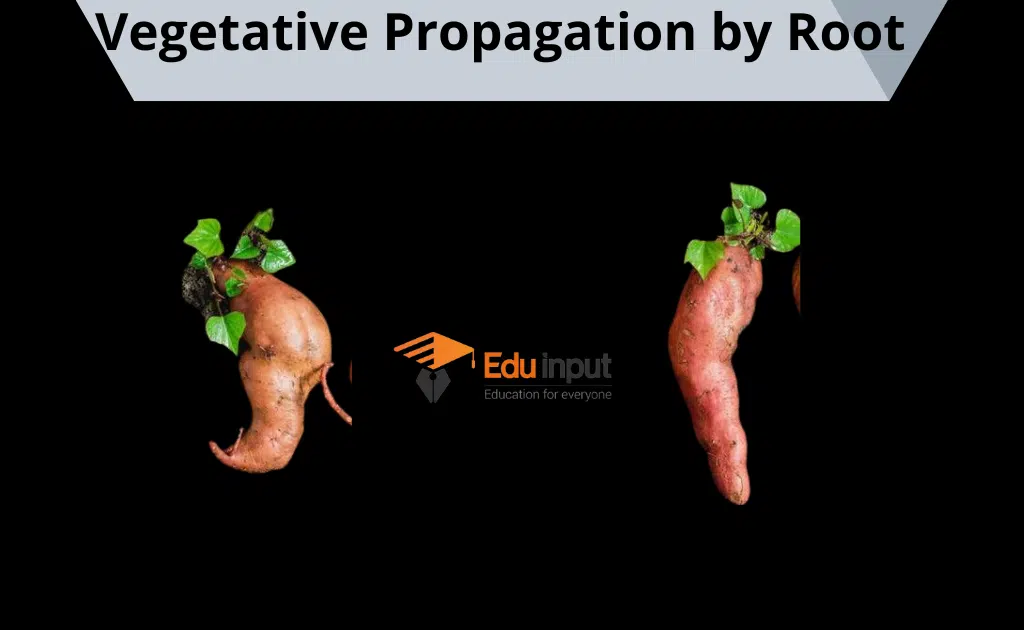
Vegetative Propagation through Roots
New plants grow out of swollen roots which are known as tubers. Buds are formed at the base of the stem. These tubers grow into a new plant.
Vegetative Propagation through Leaves
Leaves of a few plants get separated from the parent plant and develop into new plants.

Vegetative Propagation through Bulbs
An underground stem is present in bulbs, leaves are attached to that stem. These leaves can store food. An apical bud is present in the center of the bulb, that produces leaves and flowers. The lateral bud grows into a shoot.

Artificial Vegetative Propagation
A type of vegetative reproduction which is carried out by humans. Here are some most common types of Artificial Vegetative Propagation.
Artificial Vegetative Propagation through Cutting
A stem or leaf of a plant is cut and grown in soil. Sometimes cuttings are treated with hormones to increase root growth. The new plant is formed from the adventitious roots.

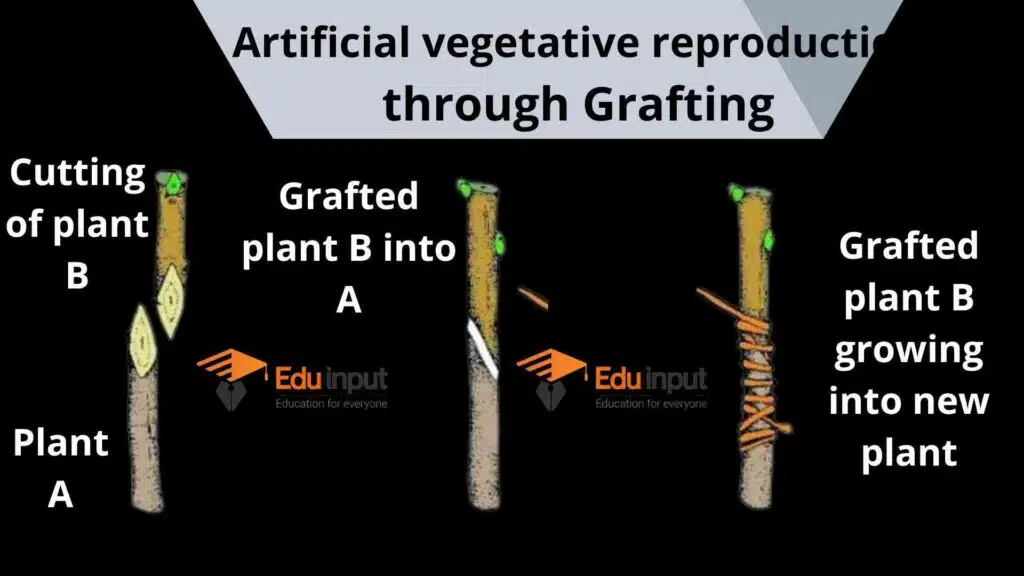
Artificial Vegetative Propagation through Grafting
A cutting from a particular plant is cut and attached to the stem of another plant that is grown in the ground. The tissues of the graft incorporate with the tissues of the rooted plant and develop as a single plant over time.
Artificial Vegetative Propagation through Layering
In this, the stem of the plant is bent to the ground and covered with soil. Adventitious roots arise from the plant parts covered with the soil. This attached stem with developing roots is known as a layer.
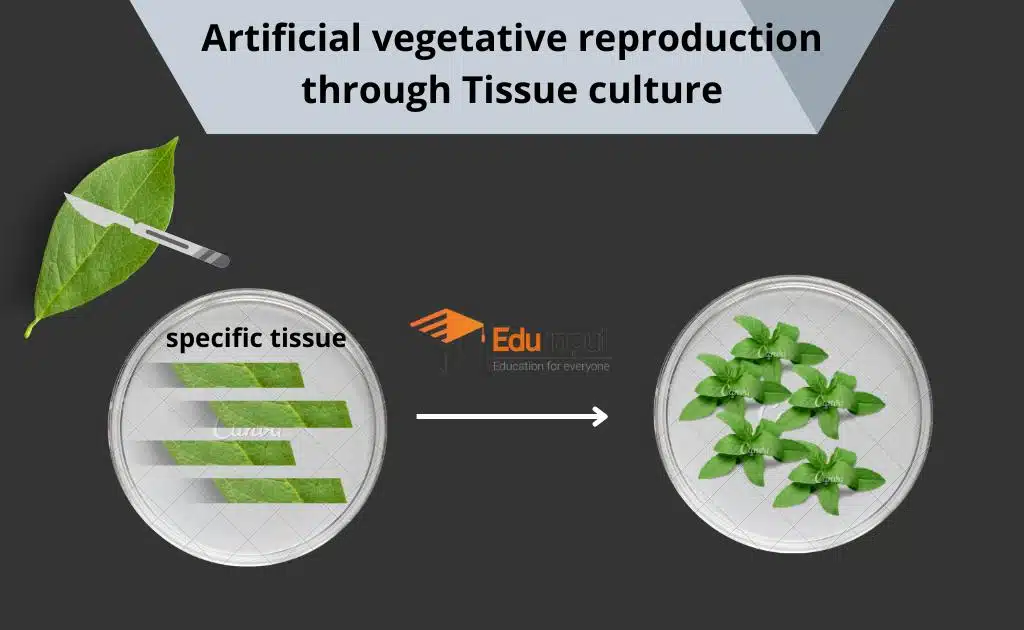
Artificial Vegetative Propagation through Tissue Culture
In this plant cells or tissues from different parts of plants are cultured artificially in laboratories. This strategy is used in increasing the number of rare and endangered plant species that are unable to grow under natural circumstances.
Related FAQs
What is vegetative propagation?
Vegetative propagation is a way of asexual reproduction in plants that occurs through vegetative parts of plants such as leaves, roots, and stems.
What are the types of vegetative propagation?
There are two types of vegetative propagation based on human interference.
Natural vegetative propagation
Artificial vegetative propagation
What is Artificial Vegetative Propagation and its types?
A type of vegetative reproduction which is carried out by humans is called artificial vegetative propagation. It has the following types:
Artificial Vegetative Propagation through Cutting
Artificial Vegetative Propagation through Grafting
Artificial Vegetative Propagation through Layering
Artificial Vegetative Propagation through Tissue Culture
What are the examples of vegetative propagation?
Here are some examples of vegetative propagation;
Vegetative Propagation through Stem (runners)
Vegetative Propagation through Roots (Tubers)
Vegetative Propagation through Leaves (Bryophyllum)
Vegetative Propagation through Bulbs







Leave a Reply