How To Analyze Data In Scientific Method?
In the scientific method, data analysis involves applying statistical techniques and logical reasoning to draw conclusions and make meaningful interpretations from collected data.
Here are the steps to analyze data in the scientific method:
- Define a Question to Investigate.
- Make Predictions based on observations and research.
- Gather Data through experiments, observations, or surveys.
- Analyze the Data using statistical methods or other techniques.
- Draw Conclusions based on the analyzed data.
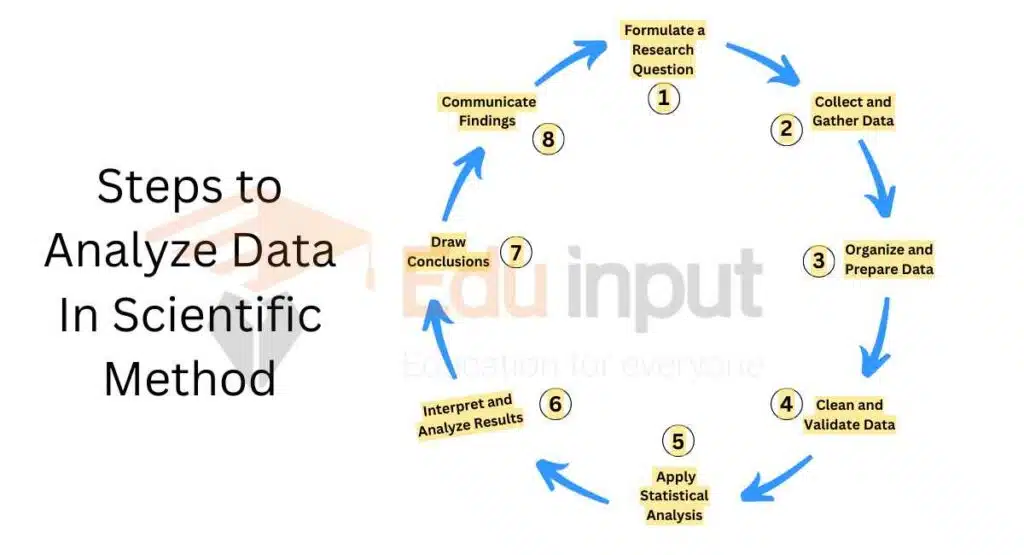
8 Steps for Analyzing Data in the Scientific Method
Data can be analyzed by following these steps:
1. Formulate a Research Question:
To analyze data in the scientific method, you should start by identifying a research question that is clear, measurable, and relevant to your topic of study.
2. Collect and Gather Data:
Design and conduct experiments, surveys, observations, or use other data collection methods to gather relevant information related to your research question. It is important to ensure that the data collected is reliable, accurate, and representative of that phenomenon you are studying.
3. Organize and Prepare Data:
To analyze data, sort and organize it systematically. Use tools like spreadsheets or databases. Label and structure the data for easy analysis.
4. Clean and Validate Data:
Review and clean the data to remove errors, outliers, and inconsistencies. Validate the data for integrity and reliability. Add missing data and other issues that affect accuracy.
5. Apply Statistical Analysis:
Choose appropriate statistical methods based on the data and research question. Use descriptive statistics (mean, median, standard deviation) to summarize and describe the data. Apply inferential statistics (t-tests, ANOVA, regression analysis) to draw conclusions and make inferences from the data.
6. Interpret and Analyze Results:
Analyze statistical analysis results in relation to your research question. Identify patterns, trends, relationships, or significant findings in the data. Consider analysis limitations and potential sources of error or bias.
7. Draw Conclusions:
Analyze and interpret the data to draw conclusions that address the research question. Determine if the results support or refute the hypothesis or research objective. Discuss the implications of the findings and their significance in the broader scientific context.
8. Communicate Findings:
Present findings clearly and concisely using visualizations like graphs, tables, or charts. Write a scientific report or prepare a presentation to communicate methods, results, and conclusions effectively. Share findings with the scientific community through publications, conferences, or other channels.



Leave a Reply