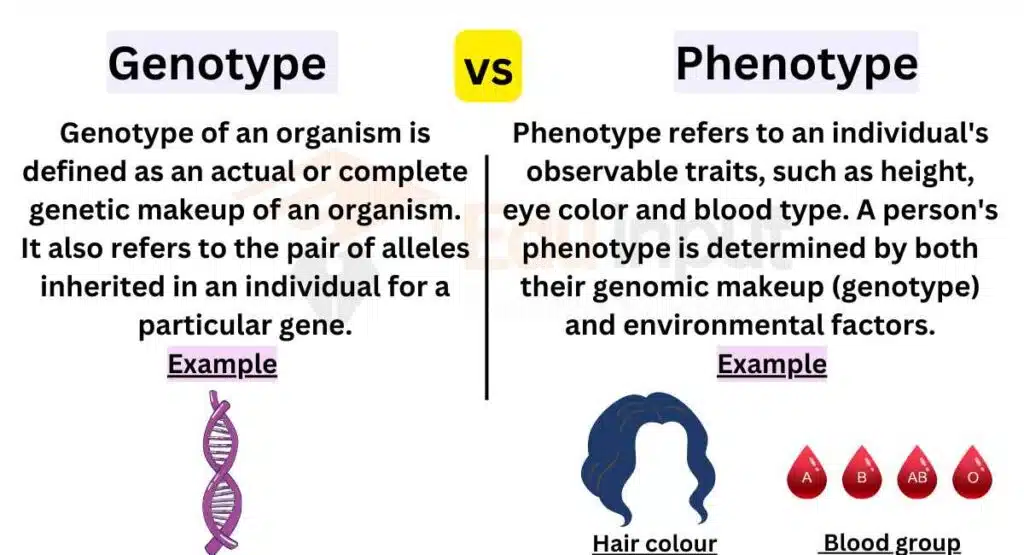
Genotype vs Phenotype- What’s the Difference?
Genotype is the inherited (from parents) genetic instructions, while phenotype is the observable result expressed from those instructions. The main difference between genotype and phenotype is the difference of instruction vs. expression.
The genotype represents the underlying genetic instructions. In comparison, the phenotype is the observable expression of these instructions, expressed as the organism’s physical and functional characteristics.
Key Differences
- Focus: Genotype focuses on the internal, coded instructions, while phenotype focuses on the external, observable expression.
- Deterministic vs. Probabilistic: Genotype sets the potential, but phenotype is shaped by gene-environment interactions, making it less predictable.
- Inheritance vs. Influence: Genotype is directly inherited, while both genes and environment influence phenotype.
Genotype vs Phenotype
Here are the main differences between Genotype and Phenotype:
| Factors | Genotype | Phenotype |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Genetic makeup of an organism | Observable physical traits or characteristics of an organism |
| Composition | Combination of alleles inherited from parents | Expression of genes and interaction with the environment |
| Representation | Represented by letters or symbols | Represented by physical appearance or traits |
| Influence | Determines the potential traits an organism can have | Determines the actual traits expressed by an organism |
| Inheritance | Passed down from parents to offspring | May be influenced by both genetic and environmental factors |
| Variability | Can vary within a population | Can vary among individuals within a population |
| Examples | AA, Aa, bb, CC | Brown hair, blue eyes, tall stature |
Difference Between Genotype And Phenotype Example
Example: Hair color
Genotype: This refers to the specific combination of alleles you inherit for the hair color gene, represented by letters like AA (both brown hair alleles), Aa (one brown and one blonde allele), or aa (both blonde hair alleles).
Phenotype: This is your actual hair color, which results from the expression of your genotype. While someone with an AA genotype will most likely have brown hair, the environment (e.g., nutrition) and other genes can influence the exact shade or even cause exceptions.
Conversely, someone with Aa genotype could have brown or blonde hair depending on the expression of their alleles.




Leave a Reply