10 Examples of Glycoproteins
Glycoproteins are proteins that have carbohydrates (sugar molecules) covalently attached to them. They are involved in cell signaling, structural support, and immune response regulation. Hemoglobin, Immunoglobulins, collagen, and hormones are a few examples of glycoproteins.
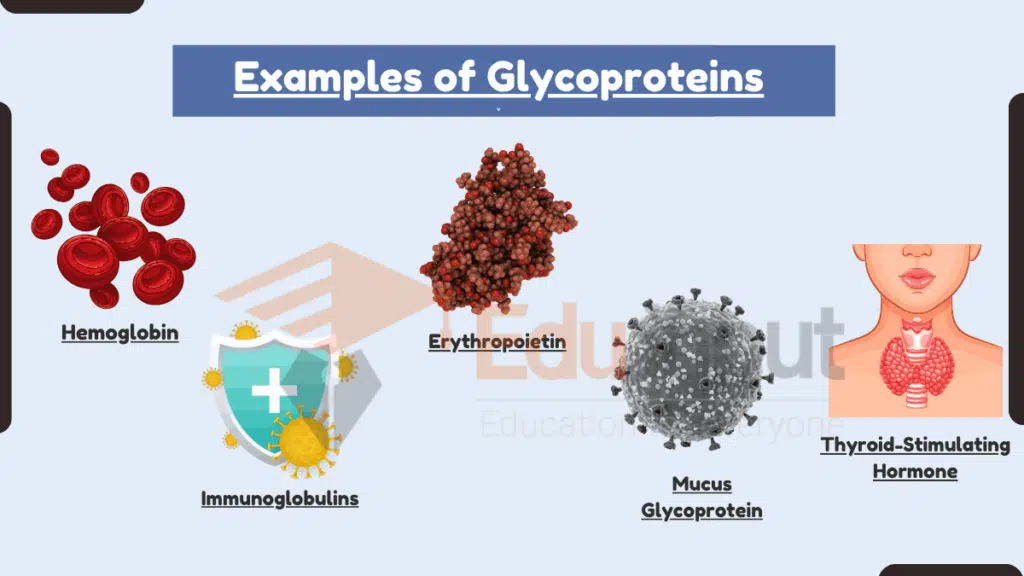
Examples of Glycoproteins
In this article, we will explore 10 examples of glycoproteins found in different organisms and biological processes:
1: Hemoglobin
Hemoglobin is a well-known glycoprotein found in red blood cells. It transports oxygen from the lungs to tissues and carries carbon dioxide back to the lungs for exhalation. The glycosylation of hemoglobin helps maintain its structure and stability.
2: Immunoglobulins (Antibodies)
Immunoglobulins, also known as antibodies, are glycoproteins produced by white blood cells (B cells) as part of the immune response. The carbohydrate portions of antibodies are essential for their binding to pathogens and immune system signaling.
3: Erythropoietin
Erythropoietin is a glycoprotein hormone produced by the kidneys in response to low oxygen levels in the blood. It stimulates the production of red blood cells in the bone marrow, helping to maintain adequate oxygen supply to tissues.
4: Mucus Glycoproteins
Mucus glycoproteins are found in the mucus lining of various tissues, including the respiratory and digestive tracts. They play a crucial role in protecting and lubricating these surfaces and are responsible for the slimy consistency of mucus.
5: Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH)
Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) is an example of glycoprotein that is produced by the anterior pituitary gland and regulates thyroid gland activity. It contains glycosylation sites that affect its stability and binding to thyroid receptors.
6: Mucins
Mucins are a family of glycoproteins that make up the gel-like mucus in various bodily tissues. They are essential for maintaining the integrity of mucosal barriers and trapping pathogens.
7: Integrins
Integrins are glycoproteins found on the surface of cells, where they play a crucial role in cell adhesion to other cells and the extracellular matrix. They are involved in various cellular processes, including cell migration and signaling.
8: Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH)
Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) is a glycoprotein hormone produced by the anterior pituitary gland. It plays a key role in regulating the development of ovarian follicles in females and sperm production in males.
9: E-Cadherin
E-Cadherin is a glycoprotein that functions as a cell adhesion molecule in epithelial tissues. It helps cells bind together to form tight junctions, contributing to tissue integrity and barrier function.
10: Glycoprotein IIb/IIIa
Glycoprotein IIb/IIIa is a glycoprotein complex found on the surface of platelets. It plays a crucial role in blood clotting by facilitating platelet aggregation at the site of vascular injury.




Leave a Reply