Plutonium-Discovery, Properties, And Apllications
Plutonium is a radioactive metallic element with the symbol Pu and atomic number 94. It is one of the heaviest elements known and is primarily produced in nuclear reactors as a by-product of the fission of uranium-238.
Plutonium is a silvery-gray metal that tarnishes in air and reacts with water and acids. It has several isotopes, with plutonium-239 being the most important for both nuclear power and nuclear weapons.

| Property | Value |
| Name | Plutonium |
| Symbol | Pu |
| Atomic number | 94 |
| Relative atomic mass (Ar) | Group in the periodic table |
| Standard state | Solid at 298 K |
| Appearance | Silvery white |
| Classification | Metallic |
| Period in the periodic table | |
| Group name | Actinoid |
| Period in periodic table | 7 (actinoid) |
| Block in periodic table | f |
| Shell structure | 2.8.18.32.24.8.2 |
| CAS Registry | 7440-07-5 |
Discovery
Plutonium was first discovered in 1940 by a team of scientists led by Glenn T. Seaborg at the University of California, Berkeley. It was the second synthetic element to be produced, after neptunium, and was created by bombarding uranium-238 with deuterium nuclei in a cyclotron.
Physical Properties
Plutonium is a dense, silvery-gray metal that tarnishes in the air. It has a melting point of 641°C and a boiling point of 3,228°C. It is malleable and ductile and can be easily formed into various shapes. Plutonium is a radioactive element and emits alpha particles.
Chemical Properties
Plutonium is highly reactive and reacts readily with oxygen, water, and acids. It forms a wide variety of compounds, including oxides, halides, and sulfides. Plutonium is a potent fuel for nuclear reactors and is used in nuclear weapons.
Electronic Configuration of Plutonium
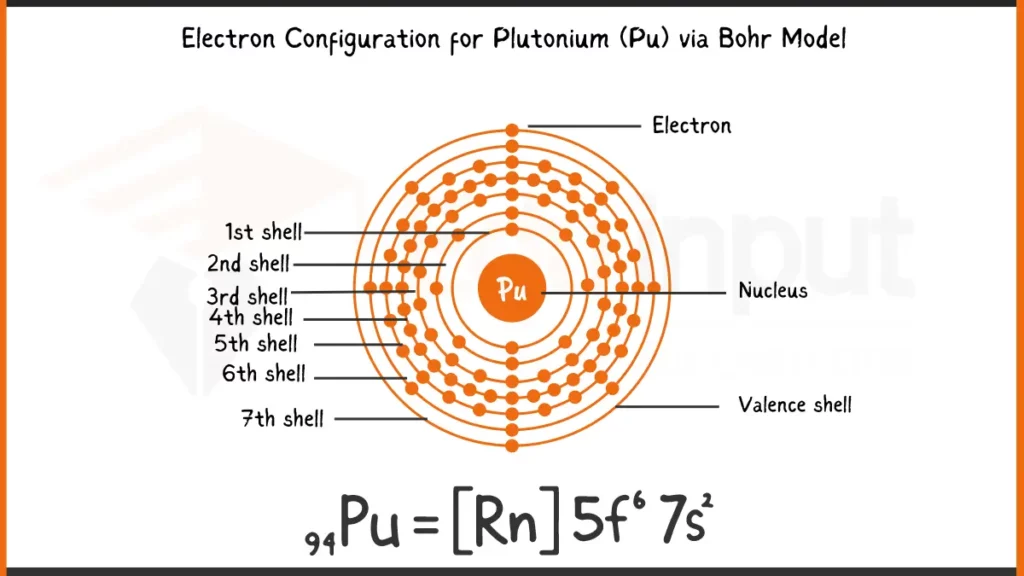
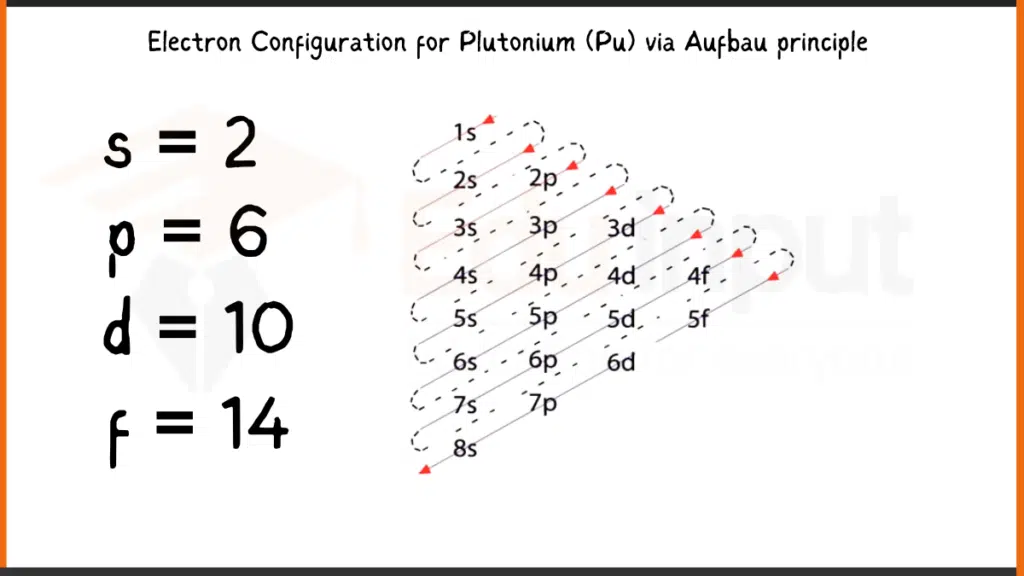
Plutonium (Pu), boasting 94 electrons, arranges its electrons following the Aufbau principle. Its complete configuration is 1s²2s²2p⁶3s²3p⁶4s²3d¹⁰4p⁶5s²4d¹⁰5p⁶5f⁶6s²7s², showing the unique filling of the 5f subshell with six electrons (5f⁶) before the 6d subshell.
Electronic Configuration of Plutonium via Bohr Model
Electronic Configuration of Plutonium via Aufbau Principle
Facts
- Plutonium has 15 known isotopes, with plutonium-239 being the most important for both nuclear power and nuclear weapons.
- Plutonium was named after the planet Pluto.
- The half-life of plutonium-239 is about 24,100 years.
- Plutonium is used in nuclear batteries, which are used to power spacecraft and remote scientific instruments.
- Plutonium is also used as a heat source in thermoelectric generators.
Applications
Plutonium is primarily used as a fuel for nuclear reactors and nuclear weapons. It can also be used in nuclear batteries, thermoelectric generators, and as a radiation source for medical and scientific purposes.
Plutonium is a radioactive metallic element that was discovered in 1940 by a team of scientists led by Glenn T. Seaborg. It has several isotopes, with plutonium-239 being the most important for both nuclear power and nuclear weapons. Plutonium is highly reactive and is used primarily as a fuel for nuclear reactors and nuclear weapons. It also has other applications, such as in nuclear batteries and thermoelectric generators. Plutonium is a potent source of energy but also poses significant risks due to its radioactive properties.






Leave a Reply