Calcium-Discovery, Properties, And Applications
Calcium is a chemical element with the symbol ‘Ca’ and atomic number 20. It is a silvery-white metal that is essential for human health and is one of the most abundant elements in the Earth’s crust. Calcium is known for its importance in the formation of strong bones and teeth, but it also plays a role in many other bodily functions.
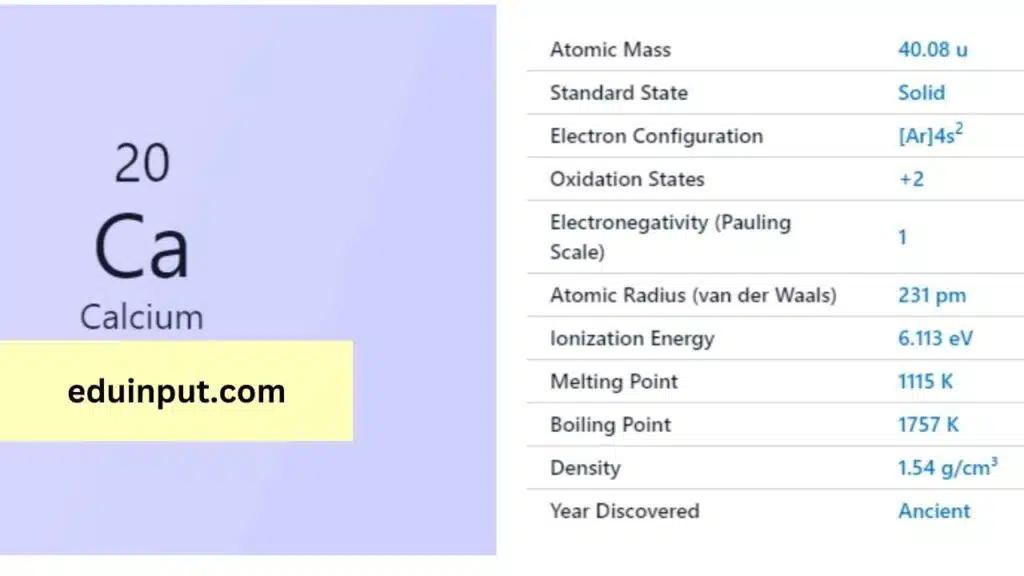
| Property | Value |
| Name | Calcium |
| Symbol | Ca |
| Atomic number | 20 |
| Relative atomic mass (Ar) | Group in the periodic table |
| Standard state | Solid at 298 K |
| Appearance | Silvery white |
| Classification | Metallic |
| Period in the periodic table | 2 |
| Group name | Alkaline earth metal |
| Block in the periodic table | 4 |
| Block in periodic table | s |
| Shell structure | 2.8.8.2 |
| CAS Registry | 7440-70-2 |
Discovery
Calcium has been known since ancient times, but it was first isolated in 1808 by Sir Humphry Davy. He used electrolysis to isolate calcium from a mixture of lime and mercuric oxide.
Physical Properties
Calcium is a silvery-white metal with a density of 1.55 g/cm3. It has a melting point of 842°C and a boiling point of 1,484°C. Calcium is a relatively soft metal that can be cut with a knife.
Chemical Properties
Calcium is a highly reactive element and reacts with a variety of other elements and compounds. It reacts with water to produce calcium hydroxide and hydrogen gas. It also reacts with acids to produce calcium salts.
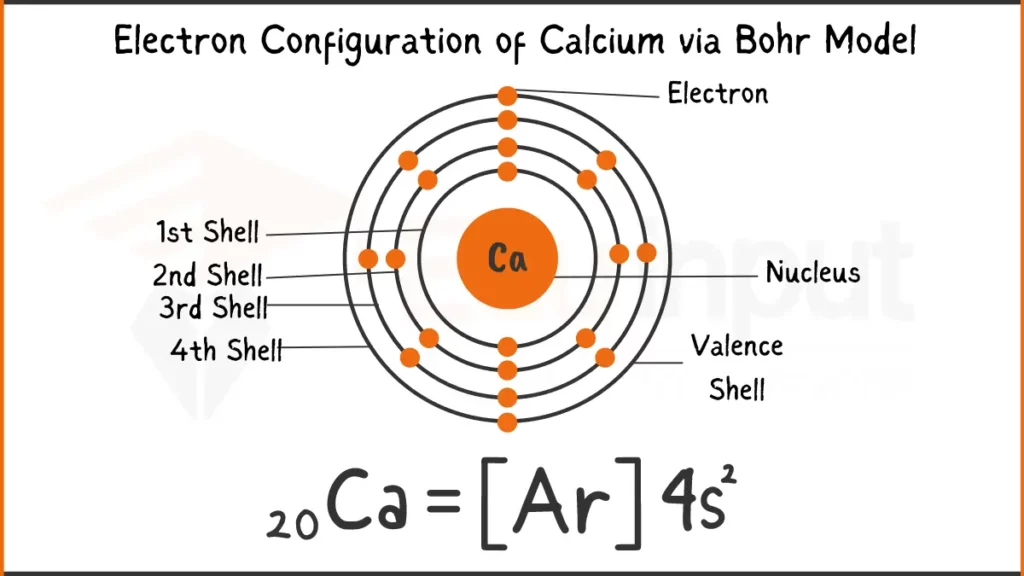
Electron Configuration of Calcium
Calcium (Ca) has 20 electrons. Its configuration is either 1s²2s²2p⁶3s²3p⁶4s² or [Ar]4s². Both depict the filling of subshells with electrons.
Electron Configuration of Calcium Via Bohr Model
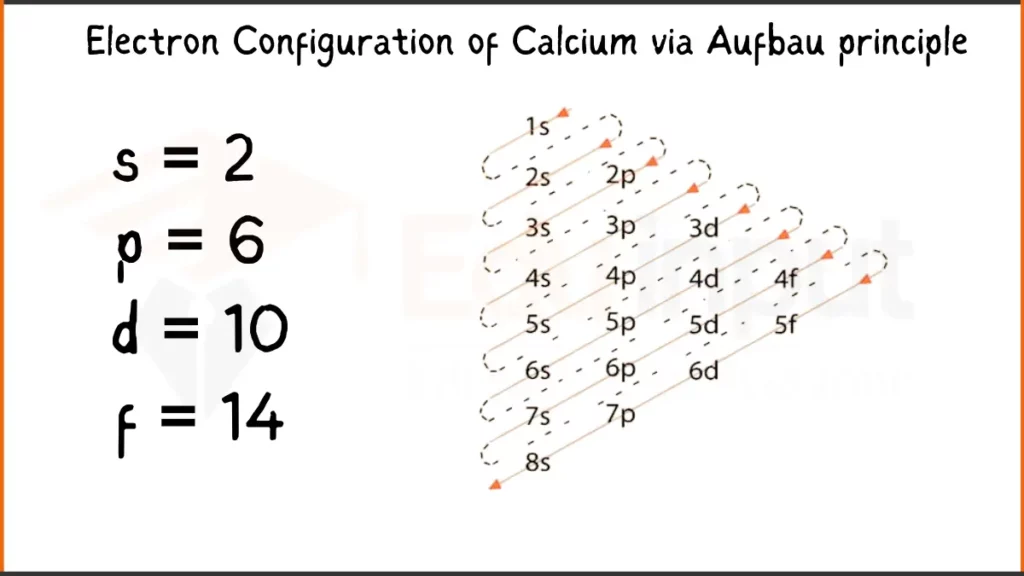
Electron Configuration of Calcium Via Aufbau Principle
Facts
- Calcium is the fifth most abundant element in the Earth’s crust and is found in various minerals, such as limestone, gypsum, and fluorite.
- Calcium is essential for strong bones and teeth, but it also plays a role in nerve function, muscle contraction, blood clotting, and enzyme activity.
- Calcium deficiency can lead to a range of health problems, including osteoporosis, muscle cramps, and irregular heartbeat.
- Calcium is used in the production of cement, cheese, and other foods.
Applications
Calcium has a range of applications in various industries. Some of the major applications of calcium include:
- Construction industry: Calcium is used in the production of cement, which is used to make concrete for buildings and roads.
- Food industry: Calcium is used as a nutrient in many foods, such as dairy products, and is added to other foods as a fortifying agent.
- Agriculture: Calcium is used as a soil conditioner to improve the quality of soil and promote plant growth.
- Pharmaceuticals: Calcium is used in the production of antacids and other medications.
Calcium is an essential mineral for strong bones and teeth, but it also plays a role in many other bodily functions. Its importance in human health has led to the widespread use of calcium supplements and the fortification of foods with calcium. Calcium’s unique physical and chemical properties make it a valuable element for various applications, including the construction, food, agriculture, and pharmaceutical industries.






Leave a Reply