Difference Between BUN and Creatinine
December 24, 2023
Table of Contents
Key Difference
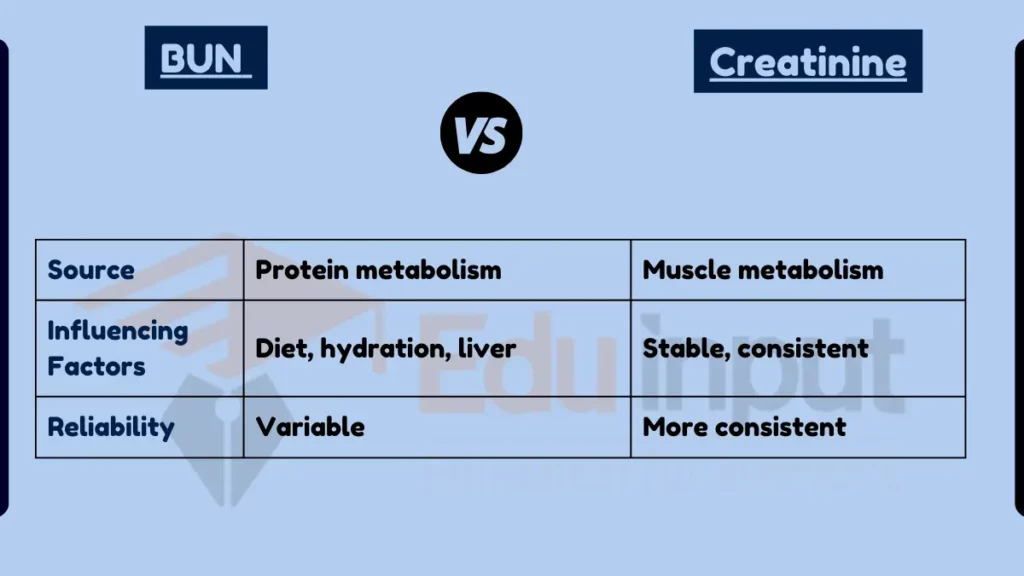
Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN) and Creatinine are both waste products measured to evaluate kidney function, but they differ in their source and reliability. BUN is the waste product of protein metabolism and can be influenced by factors like diet and liver function. Creatinine, a waste product of muscle metabolism, is a more stable indicator as it is less influenced by external factors and provides a more consistent measure of kidney function.
Comparative Analysis
- Source of Production:
- BUN: Result of protein metabolism.
- Creatinine: Byproduct of muscle metabolism.
- Factors Influencing Levels:
- BUN: Affected by diet, hydration, liver function.
- Creatinine: Relatively stable, less affected by external factors.
- Diagnostic Reliability:
- BUN: Can vary, less reliable for kidney function alone.
- Creatinine: More reliable indicator of kidney function.
- Combined Assessment:
- BUN-to-Creatinine Ratio: Used to differentiate between different types of kidney problems.
- Clinical Significance:
- Both are crucial in diagnosing and monitoring kidney disease, but creatinine is more specific to kidney function.
Table Summary
| Feature | BUN (Blood Urea Nitrogen) | Creatinine |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Protein metabolism | Muscle metabolism |
| Influencing Factors | Diet, hydration, liver | Stable, consistent |
| Reliability | Variable | More consistent |
| Combined Use | BUN-to-Creatinine Ratio | Kidney function indicator |
| Clinical Significance | Less kidney-specific | Kidney function specific |
Also Read:
File Under:



Leave a Reply