Physical Layer of OSI Model – Function of Physical Layer
The physical layer is the bottom layer of the OSI model. It transfers a stream of bits and defines how the data is transmitted over the network and what control signals are used.
Its main function is to control how a stream of bits is sent and received over the physical medium. It deals with the transmission of data on the physical medium. In other words, the physical layer provides a means of transferring data over the physical media.
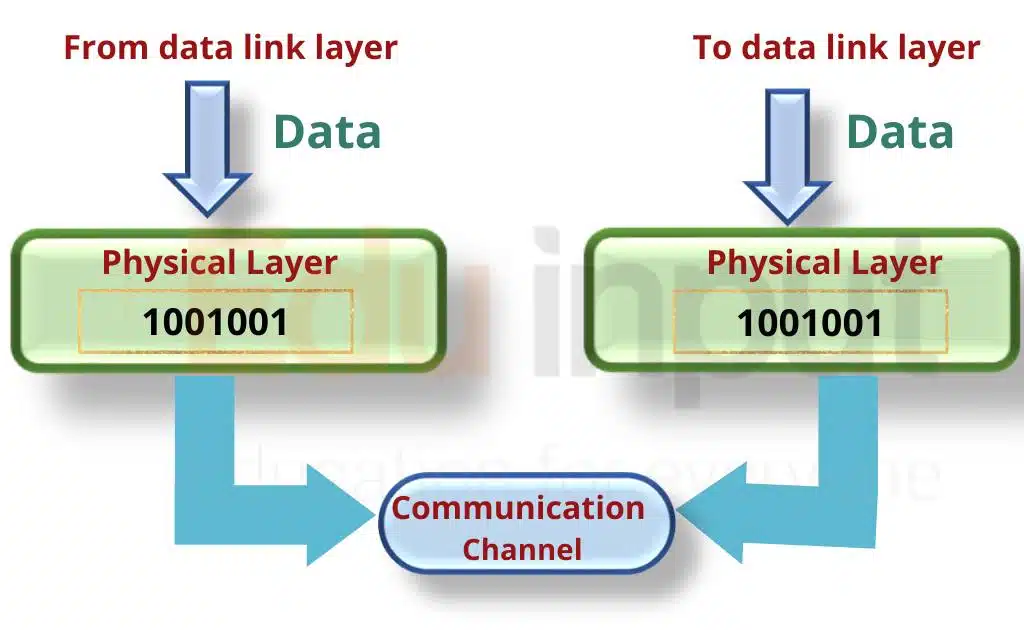
Role of Physical Layer in the network
It is the first layer in the network.
It is the medium used to transfer the data.
The data which is transferred in this layer is the low-level data.
Functions of the Physical Layer
The physical layer performs the different functions
Characteristics of Media
The physical layer defines the characteristics and type of communication channel.
The media over which the information between two computer systems is sent is called transmission media or communication channel. Transmission media comes in two forms.
Guided Media
In guided media, communication devices are directly connected with each other by using some physical media like wires. Some examples of bounded media are wire pair, coaxial and fiber optics.
Unguided Media
In unguided media, communication devices communicate with each other through air or space using broadcast radio signals, microwave signals and infrared signals. Unguided media are used where it is impossible to install cables.
Data can be transferred all over the world. Some examples of unguided media for communication are as follow:
Microwave, Satellite communication, Broadcast Radio, etc.
Representation of Bits
The bits are encoded into electrical signals for transmission. The physical layer defines the type of coding.
Data rate
The physical layer defines the number of bits that will be sent on each second.
Synchronization
The clock of sender and receiver are also synchronized.
Line configuration
The physical layer defines the attachment of communication devices with the medium.
Transmission Modes.
The physical layer defines the direction of transmission between two devices: simplex, half-duplex or full-duplex.
The common protocols used at this level are IEEE 802, IEEE 802.2, FDDI…
Examples of protocols that use physical layers include:
- Digital Subscriber Line.
- Integrated Services Digital Network.
- Infrared Data Association.
- Universal Serial Bus (USB.)
- Bluetooth.
- Controller Area Network.
- Ethernet.




Leave a Reply