Fourth Chapter Solved Exercise MCQs Of FSc First Year Physics
Fourth Chapter Solved Exercise MCQs of FSc First Year Physics are available now to help students prepare for their exams. Each question comes with a short explanation to make it easier to understand the correct answers. Use this resource to enhance your understanding and feel more confident as you prepare.
Fourth chapter solved MCQs with explanation
1. Which of the following types of forces cannot do the work on the particle?
(a) Frictional force
(b) Gravitational force
(c) Elastic force
(d) Centripetal force
Explanation: Option (d) is correct: Centripetal force is always perpendicular to the direction of motion, so it does no work.
2. Relation between horse power and watt is:
(a) 1 hp = 766 watt
(b) 1 hp = 746 watt
(c) 1 hp = 736 watt
(d) 1 hp = 796 watt
Explanation: Option (b) is correct: 1 horsepower is equal to 746 watts.
3. Proton, Neutron, electron and a particle have same momentum, which particle have greater mass?
(a) α-particle
(b) Proton
(c) Neutron
(d) Electron
Explanation: Option (a) is correct: when a proton, neutron, electron, and α-particle have the same momentum, the particle with the greater mass is the α-particle. Since momentum (p) is given by p=mvp = mvp=mv (where m is mass and v is velocity), for equal momentum, a higher mass must correspond with a lower velocity. Therefore, the α-particle, being the heaviest, has the greater mass.
4. Slope of work-time graph is
(a) Work
(b) Displacement
(c) Power
(d) None
Explanation: Option (c) is correct: The slope of a work-time graph represents power.
5. When two protons are brought together, then
(a) Their K.E. increases
(b) P.E. decreases
(c) P.E. increases
(d) P.E. remains same
Explanation: Option (c) is correct: As protons are brought closer, their potential energy increases due to the electrostatic repulsion between them.
6. A person holds a bucket of weight 60N. He walks 7m along the horizontal and then climbs up 5m. The work done by man is:
(a) 720 J
(b) 420 J
(c) 300 J
(d) None
Explanation: Option (c) is correct: Work done against gravity is calculated as force times vertical displacement.
7. The SI unit of power (watt) is equivalent to
(a) kgm/s²
(b) kgms⁻¹
(c) kgms
(d) None
Explanation: Option (d) is correct: the SI unit of power (watt) is equivalent to joules per second. This means that power measures the rate at which work is done or energy is transferred. Since 1 watt = 1 joule/second, it does not correspond to kgm/s² or any of the other options given.
8. Two masses of 1gm and 4gm are moving with the same K.E. The ratio of their linear momentum is:
(a) 1:16
(b) 1:2
(c) 2:1
(d) 4:1
Explanation: Option (b) is correct: Kinetic energy is proportional to the square of momentum. For the same kinetic energy, the momentum ratio is the square root of the inverse mass ratio.
9. Pick out the conventional source of energy:
(a) Wind energy
(b) Coal energy
(c) Tidal energy
(d) Biomass energy
Explanation: Option (d) is correct. The conventional source of energy is Coal energy. Conventional sources refer to those that have been used for a long time and are widely accepted, like fossil fuels (coal, oil, and natural gas). While biomass can also be considered traditional in some contexts, it is typically classified as a renewable energy source. Thus, coal energy is the most accurate choice for a conventional energy source.
10. Escape velocity of a body depends upon the
(a) Mass of the planet
(b) Mass of the body
(c) Velocity of the planet
(d) None
Explanation: Option (a) is correct: Escape velocity depends on the mass and radius of the planet, not the mass of the body.
11. KWh is the unit of
(a) Mass
(b) Work
(c) Power
(d) Time
Explanation: Option (b) is correct: KWh is a unit of energy, which is equivalent to work.
12. Which one is non-renewable energy source?
(a) Wind
(b) Tides
(c) Uranium
(d) All of these
Explanation: Option (c) is correct: Uranium is a non-renewable energy source as it is a finite resource.
13. Absolute P.E of a body at infinity is
(a) Zero
(b) Negative
(c) Infinity
(d) Both a & b
Explanation: Option (c) is correct. The potential energy of a body at infinity is considered to be zero as a reference point.
14. Which one of the following does not effect the orbital velocity of a satellite?
(a) mass of planet
(b) mass of satellite
(c) pull of earth
(d) None
Explanation: Option (b) is correct: The orbital velocity of a satellite depends on the mass of the planet and its distance from the planet, but not on the mass of the satellite itself.
15. When speed of a body is double then.
(a) K.E is doubled
(b) Its acceleration is doubled
(c) P.E is doubled
(d) Its momentum is doubled
Explanation: Option (d) is correct: Kinetic energy is proportional to the square of velocity, so doubling the velocity quadruples the kinetic energy. Momentum is mass times velocity, so doubling the velocity doubles the momentum.
16. Consumption of energy by a 60-watt bulb in 2 second is:
(a) 120 J
(b) 60 J
(c) 30 J
(d) 0.02 J
Explanation: Option (a) is correct: Power is energy per unit time. So, energy = power * time. 60 watts * 2 seconds = 120 joules.
17. Dot product of force and velocity is:
(a) Pressure
(b) Work
(c) Momentum
(d) Power
Explanation: Option (b) is correct: The dot product of force and velocity is the work done.
18. A force of 10N displaces a body by 6m in 3 seconds the power of agency applying the force is:
(a) 180 W
(b) 5 W
(c) 20 W
(d) None
Explanation: Option (c) is correct: Power is work done per unit time. Work done = force * distance = 10N * 6m = 60 J. Power = 60 J / 3 s = 20 W.
19. If we go above the surface of earth, the gravitational constant
(a) Remains constant
(b) Becomes zero
(c) Varies inversely to the square of the distance
(d) Varies directly to the square of the distance
Explanation: Option (c) is correct: Because gravitational force decreases as you move away from a mass. According to Newton’s law of universal gravitation, the force of gravity \( F \) between two masses varies with the formula:
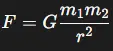
Here, \( G \) is the gravitational constant, \( m_1 \) and \( m_2 \) are the masses, and \( r \) is the distance between their centers. As you increase the distance \( r \) (moving above the Earth’s surface), the gravitational force decreases as the square of that distance increases, demonstrating the inverse square relationship.
20. The typical source of wave energy is
(a) sun
(b) moon
(c) earth
(d) mars
Explanation: Option (a) is correct: The sun is the primary source of energy for most waves, particularly ocean waves, as it drives atmospheric processes that create wind, which in turn generates waves on the water’s surface.







Leave a Reply