Cytokinesis and Karyokinesis-An Overview
Cytokinesis and Karyokinesis are two important processes that happen during cell division. Cytokinesis is the last stage of cell division. During cytokinesis, cells divide into two daughter cells. The cytoplasm divides between them, forming a cleavage furrow. Then, the plasma membrane forms around the dividing cytoplasm, creating two new membranes. This allows each daughter cell to receive its copy of the nucleus and organelles.
Cytokinesis is a complicated process that involves many proteins and structures. Scientists don’t fully understand why some cells divide asymmetrically, whereas others divide symmetrically.
Process Of Cytokinesis
During cytokinesis, the cytoplasm is divided between the two daughter cells, while the nuclei remain connected. The cleavage furrow formation is initiated by the assembly of actin filaments around the equatorial region of the dividing nucleus. Actin polymerization is mediated by Rho-like GTPases (ROP) and their effector proteins.

Cytokinesis In Plants
In plants, cytokinesis occurs after the formation of the phragmoplast. The phragmoplast is a structure composed of microtubules that form at the center of the cell plate during late telophase.
The phragmoplast is responsible for the separation of the cytoplasm between the two daughter cells. The phragmoplatins are then degraded and the cell plate is closed.
Karyokinesis
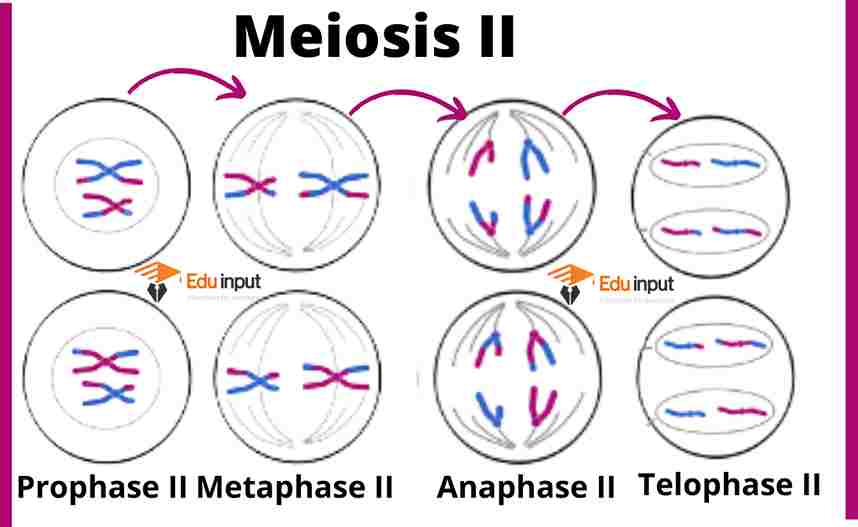
Karyokinesis is the term given to describe the movement of chromosomes during cell division. The word comes from the Greek words karyo (meaning nucleus) and kinesis (meaning motion).
It is important to understand the basics of chromosome structure before delving into the details of karyokinesis. Chromosomes are long chains of DNA that contain genes. During cell division, the chromosomes move around inside the cell. This movement is called karyokinesis or mitosis.
Chromosome movement occurs during cell division. The movement of chromosomes is called Karyokinesis.
Types of Karyokinesis
There are two types of Karyokinesis:
- Mitotic Karyokinesis
- Meiotic Karyokinesis
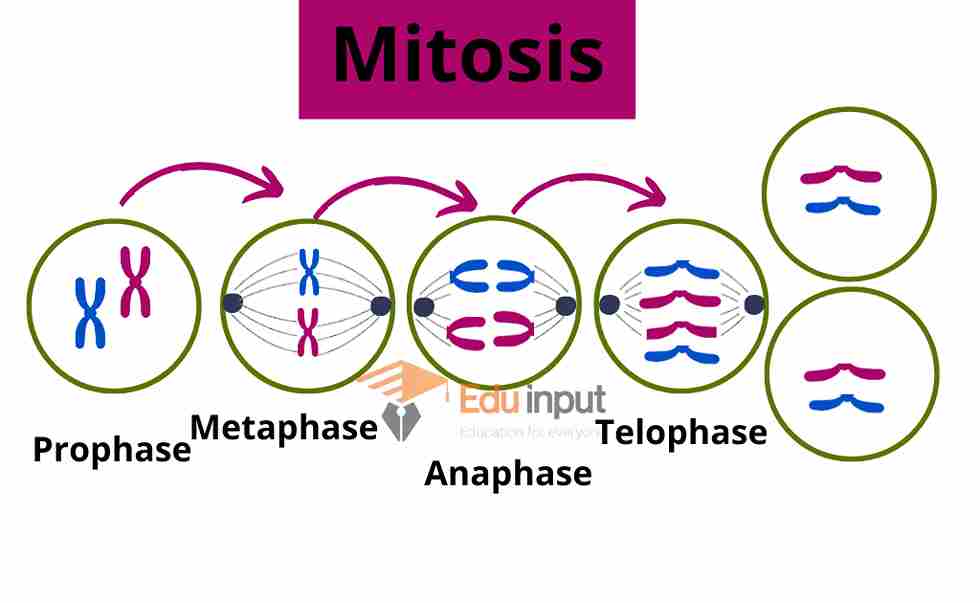
In mitosis, the chromosomes separate and divide into daughter cells. In meiosis, the chromosomes break down and recombine to form new combinations of genes.
Karyokinesis is the division of cells into daughter cells during mitosis. In humans, karyokinesis occurs at the end of prophase I of meiosis II. Karyokinesis is a phase of nuclear division in eukaryotic organisms, including animals and fungi, in which chromosomes separate into two groups.
Karyokinesis In Different Feilds
The term was first introduced by German biologist Karl Ernst von Baer in 1828.
• In botany, it refers to the separation of the chromosomes into two sets before cytokinesis.
• In zoology, it refers to the division of cells into two daughter cells after the formation of the primary body axis.
• In human embryology, it refers to a stage of the second meiotic division where the chromatids separate into two groups. In humans, this occurs at the beginning of metaphase II.
• In cytogenetics, it refers to the segregation of chromosomes into two groups during the first meiotic division.
• In molecular biology, it refers to the splitting of DNA strands into two groups during replication.
• In biochemistry, it refers to the breaking down of nucleotides into their constituent parts.




Leave a Reply