Cartilaginous Fish- Classification, Characteristics and Diagram
The word fish is a general term that refers to different types of water animals such as hagfish, lampreys, fish with hard bones, and fish with cartilage (soft bones). Scientists used to include all fish under one category called Pisces, but now, fish is divided into three main groups:
- Placodermi – This group included fish with spiny bones, but they are extinct now.
- Chondrichthyes – Fish with cartilaginous skeleton, like sharks, are included in this group.
- Osteichthyes – This group includes fish with hard, bony skeletons.
What is a cartilaginous fish?
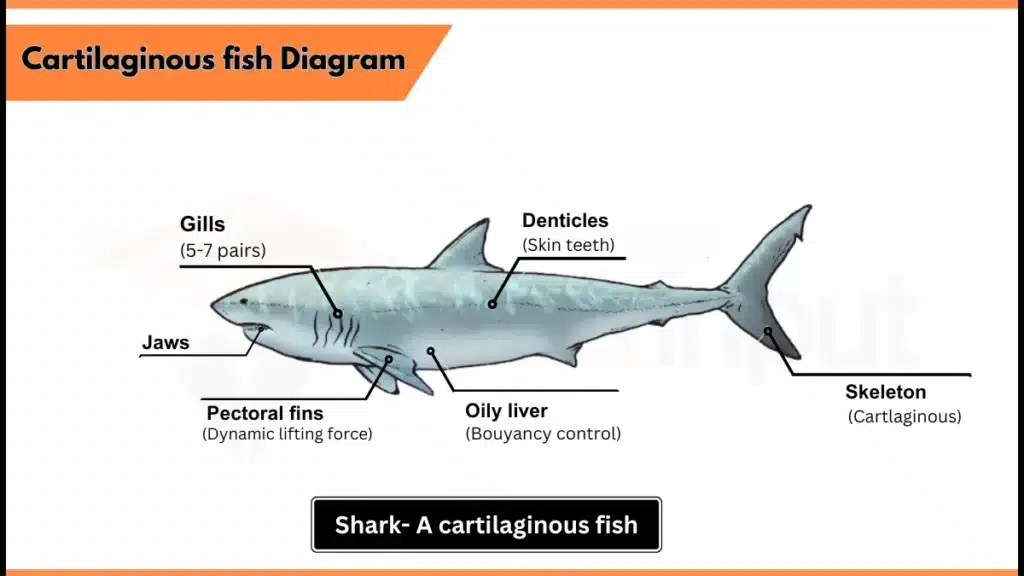
Cartilaginous fish is from Chondrichthyes group, and their skeleton is composed of flexible cartilage rather than bone. Their skin is embedded with tooth-like scales, called denticles. They are cold-blooded organisms, which means their body temperature changes with water. Some are intense hunters such as sharks, while others feed on small animals like shellfish.
Examples include sharks, rays, skates, and chimaeras.
A detailed diagram of cartilaginous fish
Classification of cartilaginous fish
| Kingdom | Animalia |
| Phylum | Chordata |
| Subphylum | Vertebrata |
| Infraphylum | Gnathostomata |
| Class | Chondrichthyes |
Characteristics of cartilaginous fish
Here are the key characteristics of cartilaginous fish including their structure, function and sub-classes.
- Cartilaginous fish are ocean animals with jaws and backbones (vertebrates).
- They have a skeleton made of flexible cartilage, not hard bone.
- All cartilaginous fishes have tough skin, except for electric rays, which have soft skin.
- Mostly, they have tooth-like tiny scales that are embedded in their skin, called denticles.
- The jaw in these fish is attached to the skull in an amphistylic (partially connected) way, giving them strength for biting.
- The number of gills for respiration is 5-7 pairs.
- They do not have air bladders (swim bladders) for floating.
- Their sense organs, called the lateral line system, help them detect water pressure changes and nearby movements.
- They have unevenly-shaped tail, meaning the upper part is longer than the lower part (heterocercal tail).
- Male cartilaginous fish contain reproductive organs called claspers.
- Fertilization occurs inside the female’s body and it depends on the type of species:
- Viviparous – give birth to live young
- Ovoviviparous – lay eggs that hatch inside the body
- Oviparous – lay eggs outside the body
- There are two subclasses of cartilaginous fish:
- Elasmobranchii – includes sharks, rays, and skates.
- Holocephali – includes chimaeras (fish with long, slender tails).




Leave a Reply