Difference Between Cell Wall And Cell Membrane
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of life. Robert Hooke, an English scientist, came up with the idea of the term cell in 1665. The shape and size of the cells are determined by their functions and compositions. There are different types of cells that can be differentiated by the presence or absence of some cell organelles.
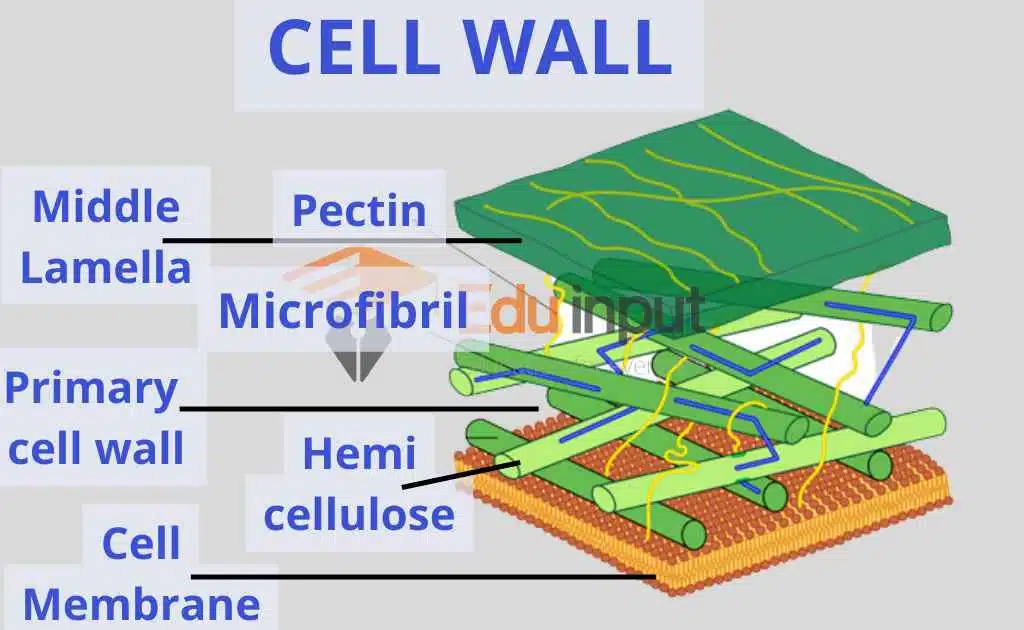
Cell Wall
The cell wall is present only in plants, fungi, and bacteria. The image above represents a plant cell wall.
The cell wall is the most important part of the plant cell. It is tough, flexible, and sometimes rigid in its texture, and it is present outside the cell. It is made up of long fibers of carbohydrates including hemicellulose and pectin. Storage of Carbohydrates for use in plant growth, especially in seeds, is a function of this storage unit.
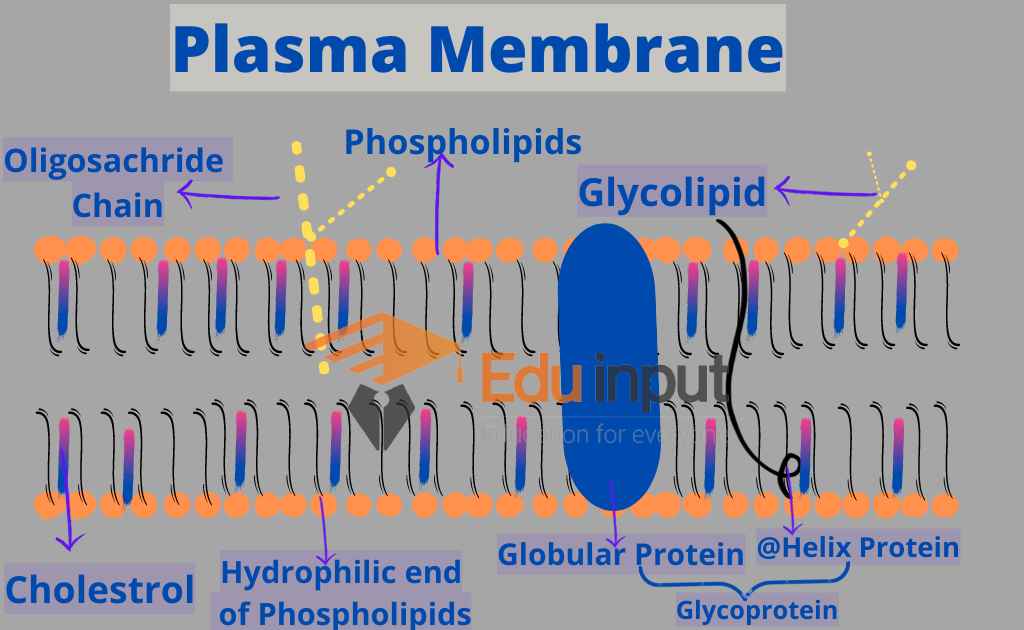
Cell Membrane
Cell Membrane is present in all organisms including plants. The cell membrane is also known as the plasma membrane. It is the outermost covering of animal cells. It is a semipermeable membrane composed of lipids and proteins.
The cell membrane, also known as the plasma membrane, is composed of a phospholipid bilayer that separates the cytosol from the outer environment. It selectively allows the passage of certain substances into the cell and excludes others.
Difference Between Cell Wall And Cell Membrane
One of the fundamental differences between the plasma membrane and the cell wall is in the type of organisms that they are found. The cell wall is present only in plants and the cell membrane is present in every living organism including plants.
| Cell Wall | Cell Membrane |
| Present only in plants and in some fungi, bacteria, and algae. | Present in all living cells, (in humans, animals, plants, bacteria, etc.) |
| It is made up of pectin, chitin, lignin, glycoproteins, glycolipids, sugar, and cellulose. | It is a lipid bilayer. And is composed of lipoproteins and carbohydrates. |
| The cell wall is 0.1 μm to several μm in thickness | The cell membrane is 7.5–10 nm in thickness |
| It is the outermost part of the plant cell | It is the outermost covering of the animal cells |
| It is a thick and rigid structure with a fixed shape. | It is a thin and delicate structure. It is flexible to change the shape as needed. |
| The cell wall is fully permeable to smaller molecules. | The membrane is selectively permeable and controls the movement of the substance. |
| It protects the cell from external hazards and cushions it against shocks. | It protects and maintains the internal environment of the cell. |
| The cell wall is non-living, and metabolically inactive | The cell membrane is alive and metabolically active. |





Leave a Reply