Advantages and Disadvantages of Star Topology
The main advantage of star topology is easy troubleshooting, as one device failure doesn’t affect others. However, a key disadvantage is the single point of failure. If the central hub fails, the entire network goes down.
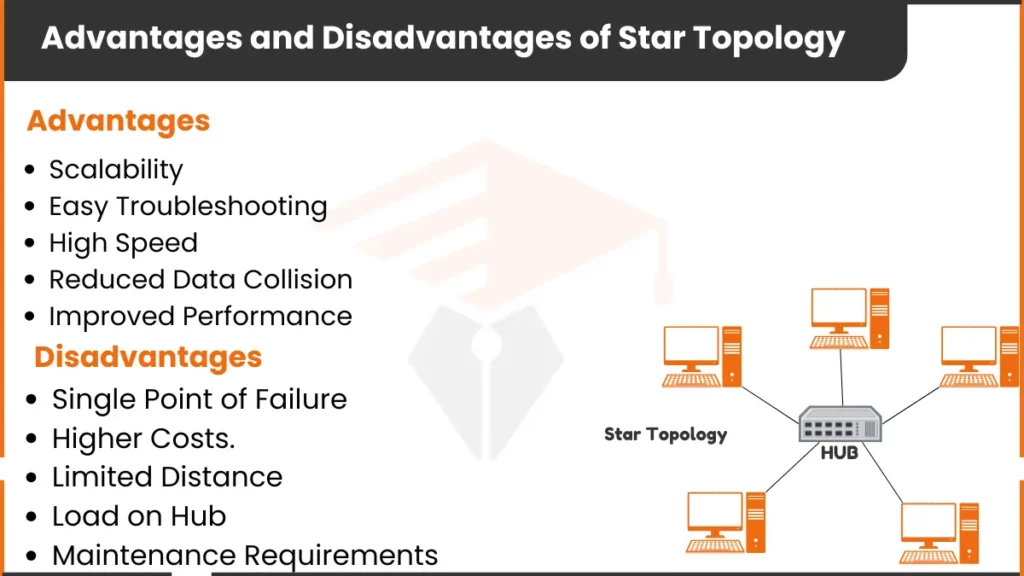
Advantages of Star Topology
Star topology has many benefits. These benefits make it popular in smaller networks.
Here are the advantages of the star topology
1. Scalability
Adding devices in a star topology is easy. Each device connects to the hub with its cable, so adding or removing a device does not disturb others. For example, in an office, you can easily connect a new computer, making it simple to expand the network.
2. Easy Troubleshooting
Star topology makes it easy to find and fix issues. Each device connects directly to the hub. If one device has a problem, it does not impact others. For example, if a printer stops working, other devices stay connected. This saves time in fixing issues.
3. High Speed
In star topology, each device has its connection to the hub. This allows data to move faster than in other setups. There is no waiting for data to reach other devices. This is useful in busy places like offices where data speed is important.
4. Reduced Data Collision
Star topology reduces data collision. Data collisions happen when devices send data at the same time. Since each device has a separate link to the hub, collisions are rare. This keeps the data flow smooth and steady.
5. Improved Performance
The hub manages all data flow. This control keeps the network organized and efficient. For example, in a school computer lab, the hub makes sure each computer sends and receives data smoothly. This makes the network work better.
6. High Security
Star topology offers good security. The hub controls which devices connect to the network. This helps keep data safe. For example, in an office, only authorized devices can connect to the hub. This adds a layer of protection.
Disadvantages of Star Topology
Star topology also has some downsides. Knowing these helps decide if it’s the right choice.
1. Single Point of Failure!
The hub is essential in a star topology. If the hub fails, the whole network stops working. This is a big risk. For example, in a school lab, if the hub breaks, all computers lose connection until fixed.
2. Higher Costs
Star topology is costly to set up. Each device needs its own cable to the hub. Quality hubs also cost more. For a small business or home, this setup may be expensive compared to simpler networks.
3. Limited Distance
Star topology is limited by cable length. Devices far from the hub may lose signal. This can make it hard to use star topology in large spaces. For example, in a large building, you may need extra equipment to keep the connection strong.
4. Load on Hub
The hub manages all data, so too many devices can overload it. This can slow down the network or cause interruptions. For example, in a busy office, an overloaded hub may delay data transfer and reduce network performance.
5. Maintenance Requirements
The hub requires regular maintenance to keep the network stable. Any issues with the hub can affect all devices. Regular checks and repairs may be necessary. This can add to the cost and effort required to keep the network running.
FAQs
What are the main drawbacks and advantages of the Star Model?
Advantages of Star Topology: Easy setup, Good performance, Simple troubleshooting
Drawbacks of Star Topology: Hub failure affects the network, Needs more cables Expensive hub or switch
what are the advantages and disadvantages of star topology over bus topology?
Advantages of Star over Bus Topology: Easier troubleshooting, Easier to scale, More Reliable
Disadvantages of Star over Bus Topology: Higher cost and hub failure affect the network, Need more hardware
What are the disadvantages of a star-star connection in a transformer?
Neutral points can float, causing instability, and allowing harmonic currents, Grounding issues may lead to shocks, Less effective for unbalanced loads.



Leave a Reply