Barium-Discovery, Properties, And Applications
Barium is a chemical element with the symbol ‘Ba’ and atomic number 56. It is a soft, silvery-white metal that is found in the Earth’s crust. Barium is known for its ability to react with other elements and compounds and has many industrial uses.
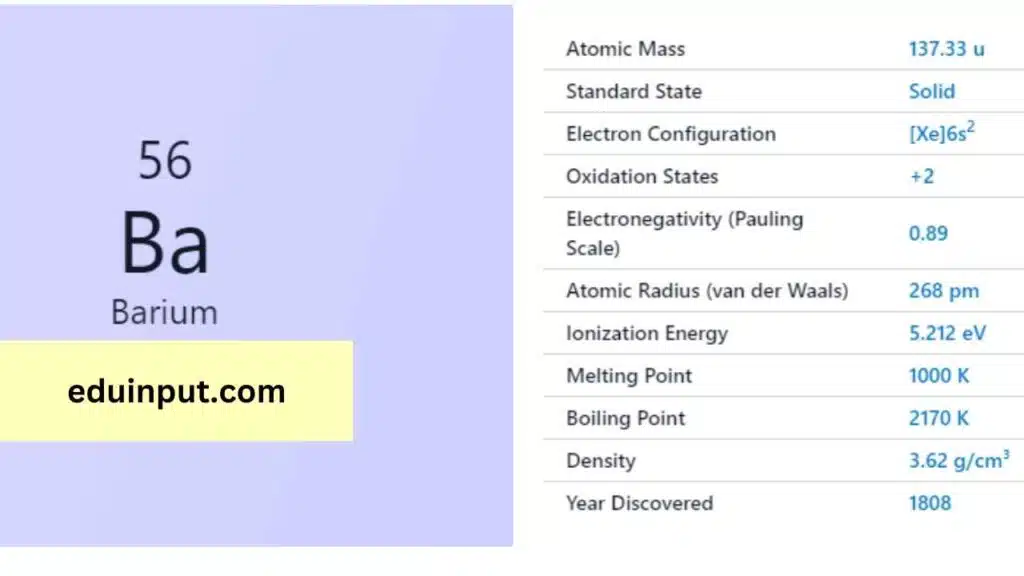
| Property | Value |
| Name | Barium |
| Symbol | Ba |
| Atomic number | 56 |
| Relative atomic mass (Ar) | Block in the periodic table |
| Period in the periodic table | Solid at 298 K |
| Appearance | Silvery white |
| Classification | Metallic |
| Group in periodic table | 2 |
| Group name | Alkaline earth metal |
| Period in periodic table | 6 |
| Block in periodic table | s |
| Shell structure | 2.8.18.18.8.2 |
| CAS Registry | 7440-39-3 |
Discovery
Barium was first discovered in 1774 by Carl Wilhelm Scheele in Sweden. However, it was Sir Humphry Davy who first isolated the element in 1808 using electrolysis.
Physical Properties
Barium is a soft, silvery-white metal with a density of 3.51 g/cm3. It has a melting point of 727°C and a boiling point of 1,872°C. Barium is a highly reactive element and reacts with water and oxygen when exposed to air.
Chemical Properties
Barium is a highly reactive element and reacts with a variety of other elements and compounds. It reacts with water to produce barium hydroxide and hydrogen gas. Barium also reacts with acids to produce barium salts.
Facts
- Barium has two stable isotopes and a number of radioactive isotopes.
- Barium is used in the production of drilling muds for oil and gas wells.
- Barium is also used in the production of glass and ceramics.
- Barium sulfate is used as a contrast agent in medical imaging tests such as X-rays and CT scans.
Applications
Barium has a range of applications in various industries. Some of the major applications of barium include:
- Drilling muds: Barium is used in the production of drilling muds for oil and gas wells. The barium sulfate in the drilling mud helps to control the pressure in the well and prevent blowouts.
- Glass and ceramics: Barium is used in the production of glass and ceramics to increase their refractive index and improve their durability.
- Medical imaging: Barium sulfate is used as a contrast agent in medical imaging tests such as X-rays and CT scans. The barium sulfate helps to make the images clearer and more detailed.
- Electronics: Barium titanate is used in the production of capacitors and other electronic components due to its ability to store electrical charge.
Barium is a versatile metal with many industrial uses. Its ability to react with other elements and compounds has made it a valuable element in the production of drilling muds, glass and ceramics, and electronic components. Barium sulfate’s use as a contrast agent in medical imaging tests has revolutionized the field of medicine, while its properties as a heavy element have made it a valuable tool for studying the behavior of other elements and compounds.






Leave a Reply