Data Encryption in the Cloud – Types, Examples, and Software
Data encryption has become a critical component of cloud security in today’s digital landscape. As businesses and individuals increasingly rely on cloud services to store and process sensitive information, protecting data from unauthorized access and breaches is paramount.
This article explores the concept of data encryption in the cloud, various encryption methods used, examples of data encryption in the cloud, the role of encryption in Google Cloud Storage, how cloud encryption works, popular cloud encryption software, and industry standards and recommendations for cloud encryption.
Data Encryption in the Cloud
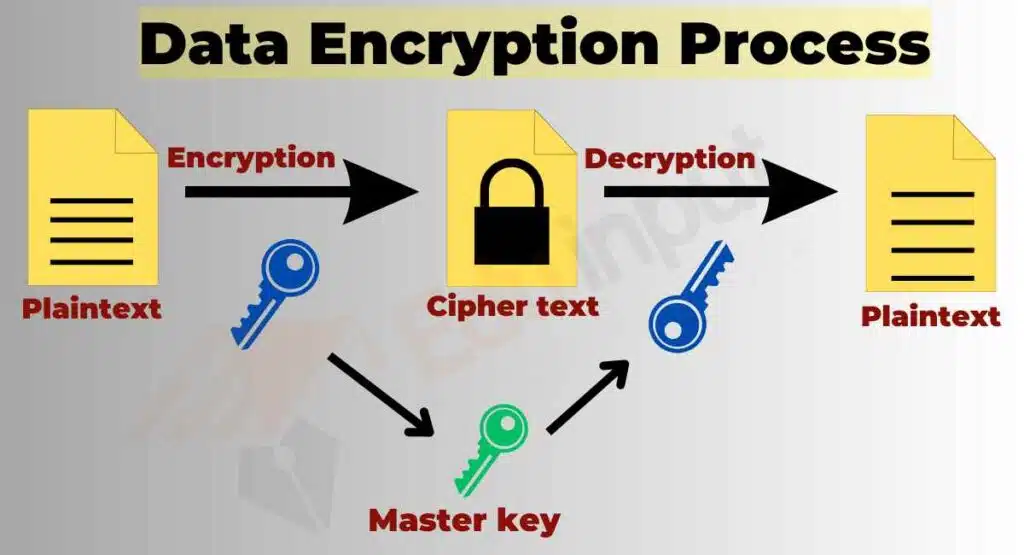
Data encryption is the process of converting plaintext data into cipher text, making it unreadable without the proper encryption key. In the cloud, data encryption is essential to ensure the confidentiality and integrity of sensitive information.

Data encryption in the cloud protects sensitive information from unauthorized access and breaches. Organizations can ensure the confidentiality and integrity of their data by utilizing various encryption methods, such as symmetric and asymmetric encryption, and employing secure key management practices.
It adds an extra layer of security, making it extremely difficult for unauthorized parties to access and decipher encrypted data.
Types of Data Encryption in the Cloud
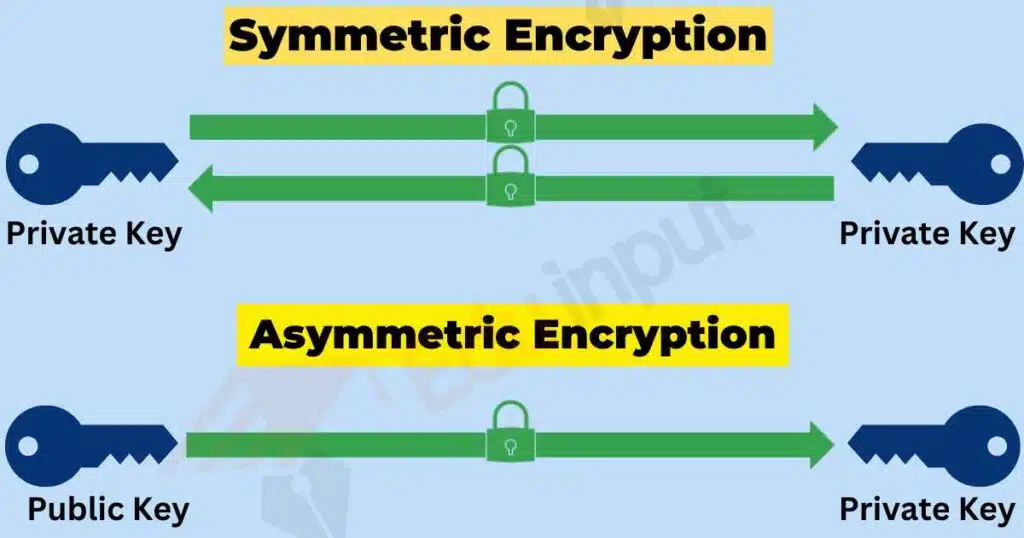
Cloud encryption solutions utilize two approaches to encrypt and decrypt data, symmetric and asymmetric.
Symmetric Encryption
Symmetric encryption uses a single key for both encryption and decryption. This method is efficient and fast, making it suitable for large amounts of data. However, the key must be securely shared between the parties involved.
Asymmetric Encryption
Asymmetric encryption, also known as public-key encryption, utilizes two separate keys: a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption. This method eliminates the need for securely sharing a single key but is computationally more intensive.
Examples of Data Encryption in the Cloud
Several cloud service providers offer data encryption solutions to protect sensitive information. Here are a few examples:
- Amazon Web Services (AWS) provides various encryption options, including server-side encryption for storage services like Amazon S3 and Amazon EBS.
- AWS Key Management Service (KMS) allows you to manage and control encryption keys.
- Microsoft Azure offers Azure Storage Service Encryption for Blob, File, and Queue storage, encrypting data at rest.
- Azure Key Vault enables secure key management and encryption key storage.
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP) provides Google Cloud Storage encryption by default, ensuring that all data stored in GCP is encrypted at rest.
- Google Cloud Key Management Service (KMS) allows you to manage encryption keys.
How Does Cloud Encryption Work?
Cloud encryption involves several key components and processes. Here’s an overview of how cloud encryption works:
Key Generation
Encryption keys, either symmetric or asymmetric, are generated using cryptographic solid algorithms.
Data Encryption
The data is encrypted using the encryption keys, transforming it into unreadable ciphertext.
Key Management
Encryption keys are securely managed and stored using industry-standard key management practices. This includes key rotation, access controls, and protection against unauthorized access.
Data Transmission
Encrypted data is securely transmitted over the network to the cloud service provider.
Data Storage
Encrypted data is stored in the cloud provider’s infrastructure, protecting it from unauthorized access.
Data Decryption
When authorized users or applications need to access the data, decryption is performed using the appropriate encryption keys, transforming the cipher text back into plaintext.
Cloud Encryption Software
Several cloud encryption software solutions offer enhanced security for data stored in the cloud. Here are a few notable examples:
Boxcryptor
Boxcryptor provides end-to-end encryption for popular cloud storage services, including Dropbox, Google Drive, and Microsoft One Drive. It ensures that data remains encrypted and protected, even when stored in third-party cloud environments.
Vera Crypt
VeraCrypt is open-source disk encryption software that allows you to create encrypted virtual drives and encrypt individual files and folders. It provides strong encryption algorithms and can secure data both locally and in the cloud.
Cipher Cloud
Cipher Cloud offers cloud-native encryption solutions to secure data at rest, in transit, and in use. It provides granular encryption controls and integrates with various cloud applications, ensuring comprehensive data protection.
Tresorit
Tresorit is a cloud storage and file synchronization service that utilizes end-to-end encryption. It encrypts data on the client side, meaning that files are encrypted before they leave your device, ensuring that only you have access to the decryption keys.
Cloud Encryption Standards and Recommendations
Industry standards and recommendations have been established to ensure effective and secure cloud encryption. These provide guidelines and best practices for implementing encryption in cloud environments. Some prominent standards and recommendations include:
National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST)
NIST provides cryptographic standards and guidelines, including the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), which is widely adopted for securing sensitive information.
Cloud Security Alliance (CSA)
CSA offers the Cloud Control Matrix (CCM), which includes control objectives and guidance for secure cloud computing. It covers various aspects, including encryption, to ensure robust cloud security.
European Union Agency for Cybersecurity (ENISA)
ENISA publishes guidelines and recommendations for cloud security, including encryption. Its guidelines aim to help organizations understand and implement encryption technologies effectively.
International Organization for Standardization (ISO)
ISO has developed standards such as ISO/IEC 27001 and ISO/IEC 27017, which provide guidance on information security management and cloud security controls, respectively.
Implementing these standards and following industry recommendations helps organizations establish a strong foundation for secure cloud encryption practices.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between symmetric and asymmetric encryption in the cloud?
Symmetric encryption uses a single key for encryption and decryption, while asymmetric encryption utilizes a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption.
Is cloud encryption necessary if the cloud provider already offers encryption?
While cloud providers may offer encryption, implementing an additional layer of encryption adds an extra level of security, ensuring that even if the provider’s security is compromised, your data remains protected.
Can encrypted data in the cloud be decrypted without the encryption key?
No, encrypted data in the cloud cannot be decrypted without the proper encryption key. Encryption ensures that only authorized individuals or applications with the correct key can access and decrypt the data.
Is cloud encryption only relevant for businesses, or should individuals also implement it?
Cloud encryption is relevant for both businesses and individuals. It helps protect sensitive personal information and prevents unauthorized access to personal data stored in the cloud.





Leave a Reply