Difference Between Case Study and Research
Key Difference
Case studies and research are both valuable tools in academic and professional fields but serve different purposes and methodologies. A case study is a detailed examination of a specific instance, situation, or individual, often used to explore complex issues in real-world settings. It provides in-depth insights into a particular subject.
Research, on the other hand, is a broader term that encompasses the systematic investigation and study of materials and sources to establish facts and reach new conclusions. It often involves hypothesis testing, data collection, and analysis across a wider scope.
Comparative Analysis
- Scope and Focus:
- Case Study: Concentrates on a specific instance or example.
- Research: Broader inquiry, exploring a general or specific topic.
- Methodology:
- Case Study: Qualitative, narrative analysis, in-depth investigation.
- Research: Can be qualitative or quantitative, involves systematic data collection and analysis.
- Purpose:
- Case Study: To provide a detailed understanding, and explore the nuances of a single case.
- Research: To discover, interpret, or revise facts, theories, and applications.
- Generalizability:
- Case Study: Findings are often not generalizable.
- Research: Aims for findings that can be generalized or applied broadly.
- Applications:
- Case Study: Used in business, psychology, social sciences for practical insights.
- Research: Applied across all scientific and scholarly disciplines.
Table Summary of Case Study vs Research
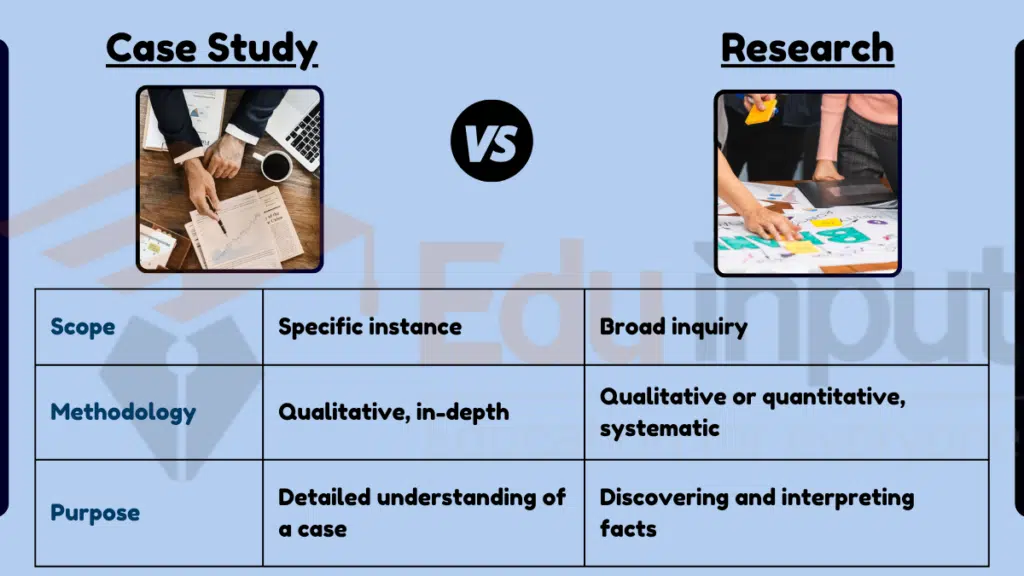
| Feature | Case Study | Research |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | Specific instance | Broad inquiry |
| Methodology | Qualitative, in-depth | Qualitative or quantitative, systematic |
| Purpose | Detailed understanding of a case | Discovering and interpreting facts |
| Generalizability | Limited | Broader applicability |
| Applications | Business, psychology, social sciences | All academic disciplines |



Leave a Reply