Cofactor vs Coenzyme
Cofactors are non-protein molecules that help enzymes work, while coenzymes are a specific type of cofactor that undergoes chemical changes during enzyme reactions.
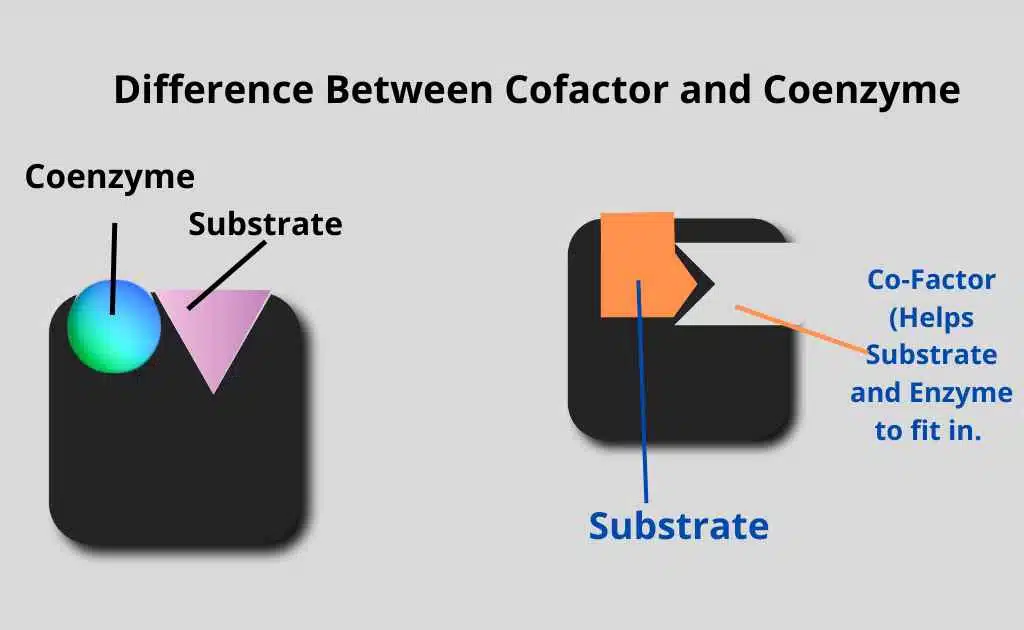
Difference Between Cofactor and Coenzyme Table
Minerals and vitamins play a vital role in metabolic activities. It plays a role in anabolic and catabolic pathways that lead to the synthesis of compounds like lipids, nucleic acids, proteins (Translation), and carbohydrates as coenzymes or cofactors.
| Coenzyme | Cofactor |
| It carries chemical groups between enzymes. | They bind to an enzyme |
| Also known as Co-substrates. | Also known as Helper molecules. |
| Coenzyme are loosely bound to enzymes. | Some cofactors covalently bound the enzyme. |
| Can be easily removed | It can be removed only by denaturation. |
| Form Chemical molecule | Form Chemical compound |
| Organic substances | Inorganic substances |
| They act as carriers. | Speed up the reaction |
| Example Coenzyme A | Example calcium ion – transglutaminase |
Detailed overview of Difference Between Cofactor and Coenzyme
- Definition
Cofactors are inorganic ions like metal ions that help in enzyme activity, while coenzymes are organic molecules, often vitamins and derivatives, that bind to the enzyme and aid catalysis. - Examples
Common cofactors include zinc, copper, iron, and magnesium ions, while common coenzymes include NAD+, FAD, Coenzyme A, and tetrahydrofolate. - Binding
Cofactors bind tightly to the enzyme and remain permanently attached, while coenzymes bind loosely and can dissociate after the reaction. - Reusability
Cofactors are reused in many reactions, while coenzymes are consumed and regenerated in each reaction cycle. - Specificity
Cofactors have a more general, nonspecific role, while coenzymes are specific to particular types of chemical reactions. - Source
Cofactors are obtained from the diet and environment, while coenzymes are synthesized internally or from dietary precursors. - Deficiency
Cofactor deficiency is rare, while coenzyme deficiency can lead to impaired enzymatic reactions. - Involvement in Reactions
Cofactors facilitate enzymatic reactions by stabilizing enzyme structure or aiding in electron transfer, while coenzymes play a more direct role in substrate binding and catalysis.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is another name for coenzyme?
Coenzyme is also known as Co-substrate.
What is another name for cofactor?
Co-factor is also known as Helper molecules.
What is the chemical nature of cofactor and coenzyme?
Coenzymes are organic molecules, whereas cofactors are inorganic in nature.
Is coenzyme a cofactor?
Coenzyme is a type of cofactor, but it differs in chemical nature.






Leave a Reply