Difference Between Hapten and Adjuvant
Key Difference: Haptens and adjuvants are substances used in immunology but serve very different purposes in the immune response. Haptens are small molecules that, by themselves, are not capable of inducing an immune response. However, when they bind to a larger protein molecule, they can become immunogenic, meaning they can then elicit an immune response.
In contrast, adjuvants are substances that are added to vaccines to enhance the body’s immune response to the vaccine. Adjuvants do not directly provoke an immune response; instead, they stimulate the immune system to respond more vigorously to the antigen present in the vaccine.
Comparative Analysis:
- Role in Immune Response:
- Hapten: Becomes immunogenic only when attached to a larger protein.
- Adjuvant: Enhances the immune response to an antigen.
- Mechanism:
- Hapten: Small molecule that needs to bind to a larger carrier molecule to elicit an immune response.
- Adjuvant: Works by stimulating the immune system, enhancing the response to the antigen in a vaccine.
- Use in Vaccines:
- Hapten: Not typically used in vaccines.
- Adjuvant: Commonly used to boost the effectiveness of vaccines.
- Examples:
- Hapten: Penicillin, poison ivy oils.
- Adjuvant: Aluminum salts, squalene.
- Immunological Effect:
- Hapten: Can induce sensitivity when coupled with a carrier protein.
- Adjuvant: Increases the body’s immune response to the antigen.
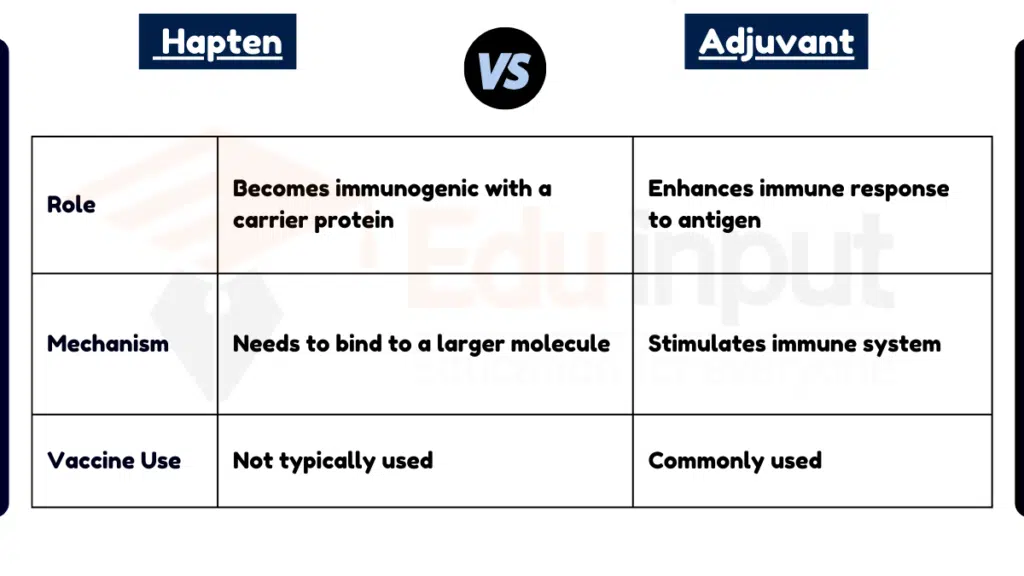
Table Summary of Hapten vs Adjuvant
| Feature | Hapten | Adjuvant |
|---|---|---|
| Role | Becomes immunogenic with a carrier protein | Enhances immune response to antigen |
| Mechanism | Needs to bind to a larger molecule | Stimulates immune system |
| Vaccine Use | Not typically used | Commonly used |
| Examples | Penicillin, poison ivy oils | Aluminum salts, squalene |
| Effect | Induces sensitivity with a carrier | Boosts immune response to antigen |




Leave a Reply