Difference Between Liquefaction and Saccharification
Key Difference
Liquefaction and saccharification are two processes commonly used in the conversion of starches into sugars, particularly in the production of biofuels and brewing. Liquefaction is the process of breaking down complex starch molecules into simpler, more manageable molecules like dextrins. This is typically achieved through the application of heat and enzymes like alpha-amylase.
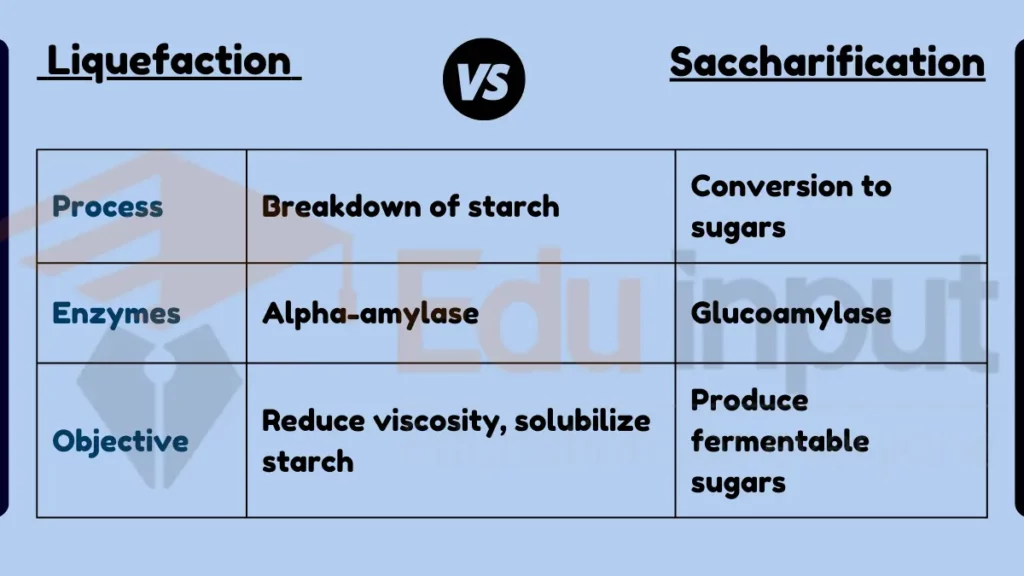
Saccharification follows liquefaction and involves further breaking down these simpler molecules into fermentable sugars, primarily glucose. This is done using enzymes like glucoamylase. While liquefaction focuses on making starches more soluble and reducing their viscosity, saccharification is about converting these starches into sugars suitable for fermentation.
Comparative Analysis
- Process in Starch Conversion:
- Liquefaction: Initial breakdown of complex starch molecules into simpler forms.
- Saccharification: Further conversion of these simpler forms into fermentable sugars.
- Enzymes Used:
- Liquefaction: Primarily uses alpha-amylase.
- Saccharification: Uses enzymes like glucoamylase.
- Objective:
- Liquefaction: To reduce starch viscosity and solubilize it.
- Saccharification: To produce fermentable sugars.
- Application:
- Both: Essential in biofuel production, brewing, and the production of syrups.
- End Products:
- Liquefaction: Produces dextrins and oligosaccharides.
- Saccharification: Produces simple sugars like glucose.
Table Summary
| Feature | Liquefaction | Saccharification |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Breakdown of starch | Conversion to sugars |
| Enzymes | Alpha-amylase | Glucoamylase |
| Objective | Reduce viscosity, solubilize starch | Produce fermentable sugars |
| Application | Biofuels, brewing | Same as liquefaction |
| End Products | Dextrins, oligosaccharides | Simple sugars (glucose) |
Also Read:



Leave a Reply