Does The Speed Of Wind Affect How Fast Sound Waves Travel Through It?
Yes, the speed of wind can affect how fast sound waves travel through it. As the wind speed increases, the speed of sound waves through the air also increases, due to the reduced air resistance. This is known as the “wind-speed effect” and is a well-documented phenomenon in acoustics.
Does the Speed of Wind Affect How Fast Sound Waves Travel Through It?
Sound waves are vibrations that travel through a medium, such as air. The speed of sound waves depends on the properties of the medium, including its density and temperature. The wind can affect the speed of sound waves in a few ways.
- Wind can slow down or accelerate the speed of sound waves. The wind speed is added to or subtracted from the speed of sound, depending on the direction of the wind. For example, if the wind is blowing in the same direction as the sound waves, the sound waves will travel faster. If the wind is blowing in the opposite direction as the sound waves, the sound waves will travel slower.
- Wind can refract sound waves. Refraction is the bending of waves as they travel through a medium. When wind blows over a surface, it creates a temperature gradient, which causes the air to have different densities at different heights. This temperature gradient can cause sound waves to bend, or refract.
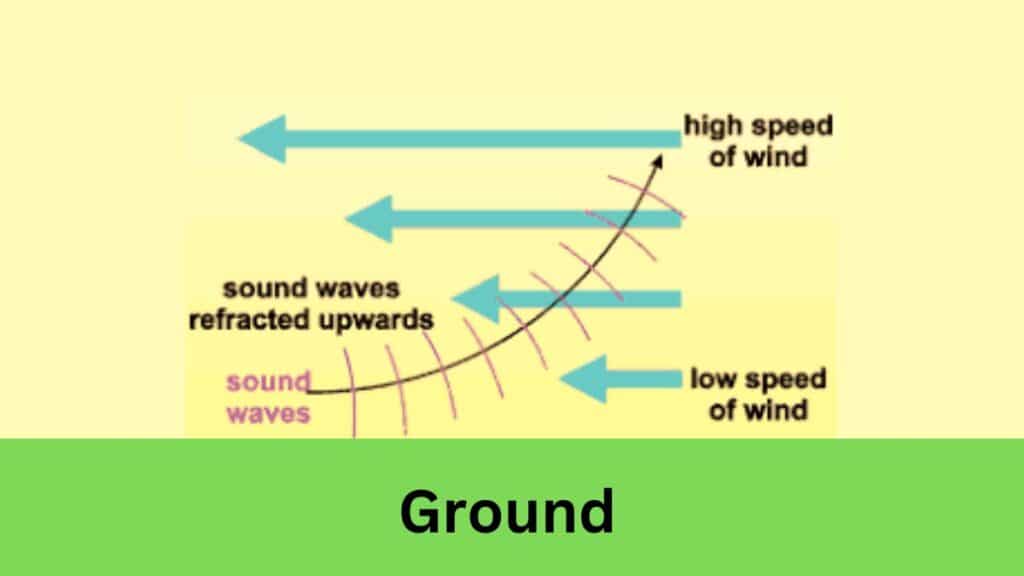
- Wind can attenuate sound waves. Attenuation is the loss of energy in a wave as it travels through a medium. The wind can attenuate sound waves by causing them to collide with air molecules. This collision causes the sound waves to lose energy and become weaker.
The effect of wind on the speed of sound waves is generally small for moderate wind speeds. However, for strong wind speeds, the effect can be significant. For example, a wind speed of 10 m/s can increase the speed of sound waves by about 1%.
The effect of wind on the speed of sound waves can be important in a number of applications. For example, it can be used to improve the accuracy of sound ranging, which is a technique used to determine the distance to a sound source. It can also be used to improve the design of acoustic systems, such as loudspeakers and microphones.
Factors affect the speed of sound waves
In addition to wind, the speed of sound waves can also be affected by other factors, such as temperature, humidity, and the composition of the air.
- Temperature: Sound waves travel faster in warm air than in cold air. This is because the molecules in warm air are moving faster than the molecules in cold air.
- Humidity: Sound waves travel slower in humid air than in dry air. This is because the water vapor in humid air absorbs some of the sound energy.
- Composition of the air: Sound waves travel faster in air that is free of impurities than in air that contains impurities. This is because impurities can scatter the sound waves, making them travel slower.



Leave a Reply